Abstract
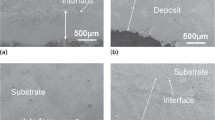
Cu–38Ni alloy was deposited on C71500 (Cu–30Ni) substrates by a laser-aided direct metal deposition technique using CO2 and diode lasers. Structure–property relationships of deposited specimens were investigated by optical microscopy, electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction techniques, and microhardness and tensile measurements. Laser-deposited specimens’ microstructures were primarily dendritic, forming columnar grains growing epitaxially from the substrate and subsequent layers along the preferred crystallographic growth. The grain growth pattern and grain size distribution was significantly different in both specimens. The lattice parameter of the solid solution phase was relatively larger in diode laser-formed specimen; CO2 laser-formed specimens showed relatively higher but non-uniform hardness distribution whereas a very uniform hardness distribution was observed in diode laser formed specimens. Diode laser formed specimens showed higher tensile properties compared to CO2 laser formed specimens which were comparable to C71500 substrates. Microstructure and mechanical behavior were explained based on laser processing parameters.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mao X, Fang F, Yang F, Jiang J, Tan R (2009) Effect of annealing on microstructure and properties of Cu–30Ni alloy tube. J Mater Process Technol 209:2145–2151
Jie Z, Qing W, Yingmin W, Lishi W, Chuang D (2010) Effect of heat treatment on the highly corrosion-resistant Cu70Ni27.7Fe2.3 alloy. J Alloy Compd 505:505–509
Drolenga LJP, Ijsseling FP, Kolster BH (1983) The influence of alloy composition and microstructure on the corrosion behaviour of Cu–Ni alloys in seawater. Mater Corros 34:167–178
Kang S, Domalavage PK, Grant NJ (1986) Mechanical properties of rapidly solidified modified cupro–nickel alloys. Mater Sci Eng 78:33–44
Caron RN, Barth RG, Tyler DE (2004) ASM handbook online, vol 9. ASM International, Novelty, pp 775–788
Chakrabarti DJ, Laughlin DE, Chen SW, Chang YA (1992) ASM handbook online, vol 3. ASM International, Novelty, pp 2.167–2.182
Dündar S (2004) Dendritic solidification in a copper nickel alloy. Turk J Eng Environ Sci 28:129–134
Doherty RD, Feest EA, Holm K (1973) Dendritic solidification of Cu–Ni alloys: part I. Initial growth of dendrite structure. Metall Mater Trans B 4:115–124
Lo SH, Gibbon WM, Holliongshead RS (1987) Corrosion resistance enhancement of marine alloys by rapid solidification. J Mater Sci 22:3293–3296. doi:10.1007/BF01161194
Bhattacharya S, Dinda GP, Dasgupta AK, Mazumder J (2011) Microstructural evolution of AISI 4340 steel during direct metal deposition process. Mater Sci Eng A 528:2309–2318
Baril D, Angers R, Baril J (1992) Fabrication and tensile properties of rapidly solidified Cu–10 wt% Ni alloy. Mater Sci Eng A 158:7–10
Adak B, Nash P, Chen D, Swiglo A (2005) Microstructural characterization of laser cladding of Cu–30Ni. J Mater Sci 40:2051–2054. doi:10.1007/s10853-005-1231-5
Mazumder J, Choi J, Nagarathnam K, Koch J, Hetzner D (1997) The direct metal deposition of H13 tool steel for 3D components. JOM 49:55–60
Mazumder J, Schifferer A, Choi J (1999) Direct materials deposition: designed macro and microstructure. Mater Res Innov 3:118–131
Koch JL, Mazumder J (2000) U.S. Patent Number 6,122,564, 19 Sept 2000
Mazumder J, Dutta D, Kikuchi N, Ghosh A (2000) Closed loop direct metal deposition: art to part. Opt Lasers Eng 34:397–414
Dinda GP, Dasgupta AK, Mazumder J (2009) Laser aided direct metal deposition of Inconel 625 superalloy: microstructural evolution and thermal stability. Mater Sci Eng A 509:98–104
Singh J, Mazumder J (1987) Effect of extended solid solution of Hf on the microstructure of the laser clad Ni–Fe–Cr–Al–Hf alloys. Acta Metall 35:1995–2003
Kadolkar PB, Watkins TR, De Hosson JThM, Kooi BJ, Dahotre NB (2007) State of residual stress in laser-deposited ceramic composite coatings on aluminum alloys. Acta Mater 55:1203–1214
Pilloz M, Pelletier JM, Vannes AB (1992) Residual stresses induced by laser coatings: phenomenological analysis and predictions. J Mater Sci 27:1240–1244. doi:10.1007/BF01142030
Bhattacharya S, Dinda GP, Dasgupta AK, Natu H, Dutta B, Mazumder J (2011) Microstructural evolution and mechanical, and corrosion property evaluation of Cu–30Ni alloy formed by direct metal deposition process. J Alloy Compd 509:6364–6373
http://www.itl.nist.gov/div898/handbook/pri/section5/pri56.htm. Accessed 19 Dec 2013
Chichkov BN, Momma C, Nolte S, von Alvensleben F, Tünnermann A (1996) Femtosecond, picosecond and nanosecond laser ablation of solids. Appl Phy A 63:109–115
Pelletier JM, Sahour MC, Pilloz M, Vannes AB (1993) Influence of processing conditions on geometrical features of laser claddings obtained by powder injection. J Mater Sci 28:5184–5188. doi:10.1007/BF00570061
Tolochko NK, Laoui T, Khlopkov YV, Mozzharov SE, Titov VI, Ignatiev MB (2000) Absorptance of powder materials suitable for laser sintering. Rapid Prototyping J 6:155–160
Gäumann M, Henry S, Cléton F, Wagnière J-D, Kurz W (1999) Epitaxial laser metal forming: analysis of microstructure formation. Mater Sci Eng, A 271:232–241
Gäumann M, Bezençon C, Canalis P, Kurz W (2001) Single-crystal laser deposition of superalloys: processing–microstructure maps. Acta Mater 49:1051–1062
Dinda GP, Dasgupta AK, Mazumder J (2012) Texture control during laser deposition of nickel-based superalloy. Scripta Mater 67:503–506
Mokadem S, Bezençon C, Drezet J-M, Jacot A, Wagnière J-D, Kurz W (2004) Microstructure control during single crystal laser welding and deposition of Ni-base superalloys. In: Rappaz M, Beckermann C, Trivedi R (eds.), Solidification processes and microstructures: a symposium in Honor of Prof. W. Kurz, The Minerals, Metals, and Materials Society, Pennsylvania, pp 67–75
van den Burg M, De Hosson J, Th M (1993) Martensitic transformations in laser processed coatings. Acta Metall Mater 41:2557–2564
Tenney DR, Carpenter JA, Houska CR (1970) X-ray diffraction technique for the investigation of small diffusion zones. J Appl Phys 41:4485–4492
James MR, Gnanamuthu DS, Moores RJ (1984) Mechanical state of laser melted surfaces. Scripta Metall Mater 18:357–361
Riabkina-Fishman M, Zevin LS, Zahavi J (1988) X-ray diffraction study of phase composition and residual stresses in laser-treated 1045 steel. J Mater Sci Lett 7:741–744
Lubarda VA (2003) On the effective lattice parameter of binary alloys. Mech Mater 35:53–68
Danilchenko VE, Sidorin YM (1996) Influence of laser treatment on martensitic transformation characteristics in Fe–Ni alloys. Mater Sci Forum 228–231:563–566
Sun GF, Bhattacharya S, Dinda GP, Dasgupta A, Mazumder J (2011) Influence of processing parameters on lattice parameters in laser deposited tool alloy steel. Mater Sci Eng A 528:5141–5145
Acknowledgements
The current investigation was financially supported by the Office of Naval Research. Authors would like to thank the colleagues at the Electron Microscope Analysis Laboratory (EMAL) in University of Michigan and Focus: HOPE for their help in this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhattacharya, S., Dinda, G.P., Dasgupta, A.K. et al. A comparative study of microstructure and mechanical behavior of CO2 and diode laser deposited Cu–38Ni alloy. J Mater Sci 49, 2415–2429 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-013-7883-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-013-7883-7