Abstract
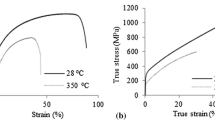
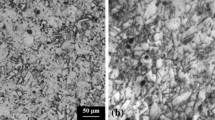
In situ measurements of the strain-induced martensitic transformation (SMTs) of SUS304 stainless steel that takes place during tensile loading at room temperature were performed around the notch of a dumbbell-shaped specimen where high stress concentration occurs. Even in the low plastic strain regime, with loading to 0.2 % proof stress (σ 0.2), some SMTs occurred. However, the area fraction of the Fe-α′-martensite phase did not increase significantly even when the sample was loaded to the ultimate tensile strength (σ UTS). After the σ UTS point, the total fraction of the Fe-α′ phase increased dramatically to the fracture point (σ f). The phase textures of Fe-α′ and Fe-γ were almost equal at (σ UTS − σ f)/2, and the Fe-α′ phase was observed over almost the entire measurement area around the notch at the σ f point. However, the area fraction of the Fe-α′ phase at the σ f point decreased far away from the fracture surface, to an extent that the total fraction of the Fe-α′ phase was almost the same as that of the Fe-γ phase in an area about 1.7 mm from the fracture face. Different martensite characteristics were detected in the stainless steel, depending on the applied load level. This was attributed to the severity of deformation. In particular, deformation twinning, created around σ UTS, and severe plastic deformation before fracture make a strong Fe-α′ phase. Details of this phenomenon are interpreted using various approaches, including electron backscatter diffraction analysis and finite element analysis.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nakajima M, Akita M, Uematsu Y, Tokaji K (2010) Proc Eng 2:323
Jia N, Peng RL, Chai GC, Johansson S, Wang YD (2008) Mater Sci Eng A 491:425
Chen X, Wang Y, Gong M, Xia Y (2004) J Mater Sci 39:4869. doi:10.1023/B:JMSC.0000035327.55210.99
Okayasu M, Sato K, Takasu S (2010) J Mater Sci 45:1220. doi:10.1007/s10853-009-4068-5
Dan WJ, Zhang WG, Li SH, Lin ZQ (2007) Comput Mater Sci 40:101
Tamura I (1982) Met Sci 16:245
Zong-yu X, Sheng Z, Xi-Cheng W (2010) J Iron Steel Res Int 17:51
Beese AM, Mohr D (2011) Acta Mater 59:2589
Zhang HW, Hei ZK, Liu G, Lu J, Lu K (2003) Acta Mater 51:1871
Varma SK, Kalyanam J, Murr LE, Srinivas V (1994) J Mater Sci Lett 13:107
Murr LE, Staudhammer KP, Hecker SS (1982) Metall Trans A 13A:627
Hertzberg RW (1996) Deformation and fracture mechanics of engineering materials, 4th edn. Wiley, New York, p 18
Dieter GE (1986) Mechanical metallurgy, 3rd edn. McGraw-Hill, Inc, New York, p 314
Ogata T, Yuri T, Ono Y, Cryo J (2007) Soc Jpn 42:10 in Japanese
Shen YF, Li XX, Sun X, Wang YD, Zuo L (2012) Mater Sci Eng A 552:514
Mirzadeh H, Najafizadeh A (2010) Mater Sci Eng A 527:1856
Das A, Sivaprasad S, Ghosh M, Chakraborti PC, Tarafder S (2008) Mater Sci Eng A 486:283
Talonen J, Nenonen P, Pape G, Hänninen H (2005) Metall Mater Trans A 36A:421
Nebel Th, Elfler D (2003) Sādhanā 28:187
Lee W-S, Lin C-F (2000) Scr Mater 43:777
Huang GL, Matlock DK, Krauss G (1989) Metall Trans A 20A:1239
Muller-Bollenhagen C, Zimmermann M, Christ H-J (2010) Int J Fatigue 32:936
Spencer K, Embury JD, Conlon KT, Véron M, Bréchet Y (2004) Mater Sci Eng A 387–389:873
Hecker SS, Stout MG, Staudhammer KP, Smith JL (1982) Metall Trans A 13A:619
Benzerga AA, Leblond J-B (2010) Adv Appl Mech 44:169
Kinoshita Y, Yardley VA, Tsurekawa S (2011) J Mater Sci 46:4261. doi:10.1007/s10853-010-5241-6
Choi J-Y, Jin W (1997) Scr Mater 36:99
Nakajima M, Uematsu Y, Kakiuchi T, Akita M, Tokaji K (2011) Proc Eng 10:299
Acknowledgement
This study was technically supported by Mr. Yuki Sato at Akita Prefectural University in Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okayasu, M., Fukui, H., Ohfuji, H. et al. Strain-induced martensite formation in austenitic stainless steel. J Mater Sci 48, 6157–6166 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-013-7412-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-013-7412-8