Abstract
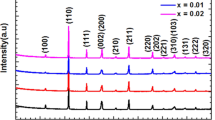
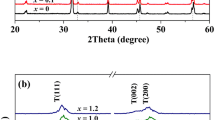
Ferroelectric (K0.455Li0.045Na0.5)(Nb0.9Ta0.1)O3 + x mol% BaCO3 ceramic compositions with Ba2+ as an A-site dopant in the range of x = 0–1.2 mol% were synthesized by conventional ceramic processing route. Effect of Ba2+ content on the microstructure, ferroelectric, dielectric, and piezoelectric properties of the ceramics was investigated. The results of X-ray diffraction reveal that Ba2+ diffuse into the (K0.455Li0.045Na0.5)(Nb0.9Ta0.1)O3 lattices to form a solid solution with a perovskite structure having typical orthorhombic symmetry. As Ba2+ content increases, cell volume and tetragonality increase in the crystal structure of the ceramics. Increasing doping level of Ba2+ inhibits grain growth in the ceramics and reduces both the Curie temperature (T c) and tetragonal–orthorhombic phase transition temperature (T o-t). The bulk density, remnant polarization P r, room-temperature dielectric constant (ε′RT), planar electromechanical coupling factor k p , and piezoelectric charge coefficient d 33 are found to increase as Ba2+ concentration increases from 0 to 0.8 mol% and then decrease as Ba2+ content increases further from 0.8 to 1.2 mol%. High piezoelectric properties of d 33 = 187 pC/N and k p = 48 % are found in 0.8 mol% Ba2+ composition. Optimum amount of Ba2+ dopant takes the polymorphic phase boundary region consisting of orthorhombic and tetragonal crystal structures of the ceramic system near the room temperature and enhances its piezoelectric properties.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jaffe B, Cook WR, Jaffe H (1971) Piezoelectric ceramics. Academic, New York, p 115
Tressler JF, Alkoy S, Newnham RE (1998) J Electroceram 2:257
Gomah-Pettry J-R, Said S, Marchet P, Mercurio J-P (2004) J Eur Ceram Soc 4:1165
Liu W, Ren X (2009) Phys Rev Lett 103:257602
Hollenstein E, Davis M, Damjanovic D, Setter N (2005) Appl Phys Lett 87:182905
Ichiki M, Zhang L, Tanaka M, Maeda R (2004) J Eur Ceram Soc 24:1693
Saito Y, Takao H, Tani T, Nonoyama T, Takatori K, Homma T, Nagaya T, Nakamura M (2004) Nature 432:84
Matsubara M, Yamaguchi T, Sakamoto W, Kikuta K, Yogo T, Hirano S (2005) J Am Ceram Soc 88:1190
Matsubara M, Kikuta K, Hirano S (2005) J Appl Phys 97:114105
Li JF, Wang K, Zhang BP, Zhang LM (2006) J Am Ceram Soc 89:706
Jaeger RE, Egerton L (1962) J Am Ceram Soc 45:209
Guo Y, Kakimoto K, Ohsato H (2004) Appl Phys Lett 85:4121
Saito Y, Takao H (2006) Ferroelectrics 338:17
Zhang SJ, Xia R, Shrout TR, Zang GZ, Wang JF (2006) J Appl Phys 100:104108
Yang ZP, Chang YF, Wei LL (2007) Appl Phys Lett 90:042911
Lin D, Kwok KW, Chan HLW (2007) J Appl Phys 102:034102
Chandramani Singh K, Chongtham Jiten, Radhapiyari Laishram, Thakur OP, Bhattacharya DK (2010) J Alloy Compd 496:717
Tennery VJ, Hang KW (1968) J Appl Phys 39:4749
Koduri R, Hermosilla LS (2006) Physica Status Solidi (A) Appl Res 203:2119
Ahn ZS, Schulze WA (1987) J Am Ceram Soc 70:C18
Tashiro S, Ishii K (2006) J Ceram Soc Jpn 114:386
Malic B, Bernard J, Holc J, Jenko D, Kosec M (2005) J Eur Ceram Soc 25:2707
Ruban AV, Skriver HL, Norskov JK (1998) Phys Rev Lett 80:1240
Stokes AR, Wilson AJC (1944) Proc Phys Soc 56:174
Lin D, Kwok KW, Chan HLW (2007) J Phys D Appl Phys 40:6778
Arlt G, Hennings D, de With G (1985) J Appl Phys 58:1619
Cho JH, Lee YH, Kim BI (2010) J Ceram Proc Res 11:237
Takahashi H, Numamoto Y, Tani J, Matsuta K, Qiu J, Tsurekawa S (2006) Jpn J Appl Phys 45:L30
Randall CA, Kim N, Kucera J-P, Cao W, Shrout TR (1988) J Am Ceram Soc 81:677
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the Department of Science and Technology, India, under the Research Project No. SR/S2/CMP-0017/2011.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gaur, R., Singh, K.C. & Laishram, R. Structural and piezoelectric properties of barium-modified lead-free (K0.455Li0.045Na0.5)(Nb0.9Ta0.1)O3 ceramics. J Mater Sci 48, 5607–5613 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-013-7355-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-013-7355-0