Abstract
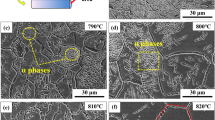
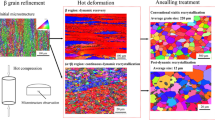
In the present study, two powders near-β Ti alloys having a nominal composition of Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-XCr-1Fe (X = 1–2, wt%) were studied. The alloys were produced via the blended elemental powder metallurgy technique using hydrogenated Ti powder. Microstructure evolution and the distribution of the alloying elements between the phases were investigated after each step of thermo-mechanical processing (TMP). Microstructures were refined through the TMP in both alloys. Porosity was reduced with deformation at 1173 K (900 °C) in the β phase field. The β → α phase transformation occurred during soaking at 1023 K (750 °C) in the α + β phase field. Fragmentation of the continuous grain boundary α occurred because of the 40 % deformation at 1023 K (750 °C). Variation in the concentration of the alloying elements in each phase took place through the diffusion during soaking in the α + β phase field, e.g. exit of β-stabilisers from the α-phase. However, the α phase remained supersaturated with β stabilisers. Deformation had no influence on the distribution of the alloying elements. An addition of 1 % Cr content slightly affects the amount of the α phase formed and β grain size, but it has no noticeable effect on the distribution of the alloying elements between the phases.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moiseev VN (1998) Met Sci Heat Treat 40:482
Moiseev VN (2000) Met Sci Heat Treat vol. 42:81
Froes FH, Eylon D (1990) Int Mater Rev 35:162
Moxson V, Senkov ON, Froes FH (1998) Int J Powder Metall 34:45
Carman A, Zhang LC, Ivasishin OM, Savvakin DG, Matviychuk MV, Pereloma EV (2011) Mater Sci Eng A 528:1686
Savvakin DG, Carman A, Ivasishin OM, Matviychuk MV, Gazder AA, Pereloma EV (2012) Metall Mater Trans A 43:716
Ivasishin OM, Savvakin DG, Moxson VS, Bondareva KA, Froes FH (2002) Mater Technol Adv Perform Mater 17:20
Sauer C, Luetjering G (2001) J Mater Process Tech 117:311
Chesnutt J, Froes FH (1977) Metall Mater Trans A 8:1013
Clement N, Lenain A, Jacques PJ (2007) JOM 59:50
Terlinde G, Duerig T, Williams J (1983) Metall Mater Trans A 14:2101
Weiss I, Semiatin SL (1998) Mater Sci Eng A 243:46
Nag S, Banrjee R, Hwang JY, Harper M, Fraser HL (2009) Philos Mag 89:535
Zhao YQ, Xin SW, Zeng WD (2009) J Alloys Compd 481:190
Polmear IJ (2006) Light alloys from traditional alloys to nanocrystals, 4th edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Banerjee S, Mukhopadhyay P (2007) Phase transformations: example from titanium and zirconium alloys. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Terlinde G, Rathien HJ, Schwalbe KH (1988) Metall Trans A 19A:1037
Jones NG, Dashwood RJ, Dye D, Jackson M (2008) Mater Sci Eng A 490:369
Zhang SZ, Liu ZQ, Wang GD, Chen LQ, Liu XH, Yang R (2009) J Cent South Univ Technol 16:354
Nakajima H, Ogasawara K, Yamaguchi S, Koiwa M (1990) Mater Trans JIM 31:249
Neumann G, Tuijn C (2008) Self-diffusion and impurity elements diffusion in pure metals: handbook of experimental data 14:149. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Gibbs GB, Graham D, Tomlin DH (1963) Philos Mag 8:1269
Lee SY, Iijima Y, Hirano KI (1991) Mater Trans JIM 32:451
Massalski TD, Okamoto H, Subramanian PR, Kasprzak L (eds) (1990) Binary alloys phase diagrams. ASM International, Materials Park
Lenain A, Clement N, Veron M, Jacques P (2007) Mater Sci Forum 3712:539–543
Li C, Wu X, Chen JH, Zwaag SV (2011) Mater Sci Eng A 528:5854
Yang YF, Luo SD, Schaffer GB, Qian M (2011) Mater Sci Eng A 528:6719
Ivasishin OM, Markovsky PE (1996) JOM 48:48
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Engineering Materials Institute strategic grant. The authors acknowledge the technical support during Gleeble tests by Mr. B. De Jong and Dr. L. Chen, UOW and use of UOW Electron Microscopy Centre, in particular JEOL 7001F, which was purchased with ARC support (LE0882613). Mr. Mansur Ahmed gratefully acknowledges the University of Wollongong Postgraduate Award (UPA) and the useful discussions with Mr. M. Reid, UOW.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmed, M., Gazder, A.A., Savvakin, D.G. et al. Microstructure evolution and alloying elements distribution between the phases in powder near-β titanium alloys during thermo-mechanical processing. J Mater Sci 47, 7013–7025 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-012-6652-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-012-6652-3