Abstract
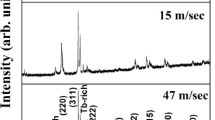
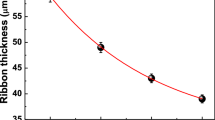
The structure and soft magnetic properties of Fe68.5Si18.5B9Nb3Cu1 (at.%) alloy ribbons produced through planar flow melt spinning at different wheel speeds viz. 34, 17 and 12 m/s have been investigated using X-ray diffraction, differential scanning calorimetry, transmission electron microscopy, vibrating sample magnetometer and positron lifetime spectroscopy. Amorphous ribbons formed with different wheel speeds manifested different enthalpy and activation energy of crystallization. The volume fraction of nanocrystalline phase, saturation magnetization and permeability are found to increase whereas coercivity is found to decrease with increasing wheel speed on annealing. A detailed analysis of positron lifetime spectra obtained from the as-spun ribbons has been used to rationalize the variation in microstructure and magnetic properties. The presence of larger number of defects at higher wheel speed increases the volume fraction of nanocrystalline phase on annealing which improves the soft magnetic properties.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yoshizawa Y, Yamauchi K (1989) Hitachi Metals Ltd, Tokyo EU Patent no. 0299498
Yoshizawa Y, Oguma S, Yamauchi K (1988) J Appl Phys 64:6044
Takayama S, Oi T (1979) J Appl Phys 50:1595
Arvindha Babu D, Majumdar B, Sarkar R, Akhtar D, Chandrasekaran V (2008) J Phys D 41:195002
Arvindha Babu D, Srivastava AP, Majumdar B, Srivastava D, Akhtar D (2010) Metall Mater Trans A 41:1313
Allia P, Tiberto P (1994) IEEE Trans Magn 30:461
Knobel M, Sinnecker JP, Saenger JF, Sato Turtelli R (1993) Philos Mag B 68:861
El Ghannami M, Kulik T, Hernando A, Fernandez Barquin L, Gomez Sal JC, Gorria P, Barandiaran JM (1994) J Magn Magn Mater 133:314
Panda AK, Roy S, Singh SR, Rao V, Pramanik S, Chattoraj I, Mitra A, Ramchandrarao P (2001) Mater Sci Eng A 304–306:457
Gopinathan KP, Sundar CS (1984) In: Anantharaman TR (ed) Metallic glasses: production, properties and applications. Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland
Narasimhan MC, Flanders NJ (1979) US Patent no. 4142571
Majumdar B, Akhtar D (2005) Bull Mater Sci 28:395
Tkatch VI, Limanovskii AI, Denisenko SN, Rassolov SG (2001) Mater Sci Eng A 323:91
Kissinger HE (1957) Anal Chem 29:1702
Majumdar B, Bysak S, Akhtar D (2007) J Magn Magn Mater 309:300
Srivastava AP, Srivastava D, Dey GK, Sudarsan K, Pujari PK (2009) Metall Mater Trans A 40:1757
Locvas A, Kiss LF, Balogh I (2000) J Magn Magn Mater 215–216:463
Fujii H, Yardley VA, Matsuzaki T, Tsurekawa S (2008) J Mater Sci 43:3837 10.1007/s10853-007-2220-7
Herzer G (1997) In: Buschow KHJ (ed) Handbook of magnetic materials, vol 10. Elsevier Science B.V., p 415
Herzer G (1991) Mater Sci Eng A 133:1
Alben R, Becker JJ (1978) J Appl Phys 47:1653
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by Defence Research and Development Organization (DRDO), Government of India. The authors thank Dr. P. K. Pujari, BARC for positron experiments, Dr. G. K. Dey, Head, Materials Science Division, BARC for fruitful discussions and Shri Trilochan Sahoo, PXE, Balasore for FESEM studies. Authors are grateful to Dr. G. Malakondiah, Director DMRL, for his continued support and permission to publish this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srinivas, M., Majumdar, B., Akhtar, D. et al. Influence of wheel speed during planar flow melt spinning on the microstructure and soft magnetic properties of Fe68.5Si18.5B9Nb3Cu1 ribbons. J Mater Sci 46, 616–622 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-010-4770-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-010-4770-3