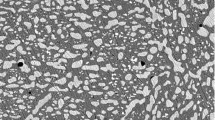
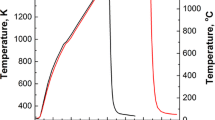
Abstract
Austenitic Fe–Cr–Mn stainless steels interstitially alloyed with nitrogen have received considerable interest lately, due to their many property improvements over conventional Fe–Cr–Ni alloys. The addition of nitrogen to Fe–Cr–Mn stabilizes the fcc structure and increases the carbon solubility. The benefits of increased interstitial nitrogen and carbon content include: enhanced strength, hardness, and wear resistance. This study examines the effect of carbon, silicon, molybdenum, and nickel additions on the phase stability and tensile behavior of nitrogen-containing Fe–Cr–Mn alloys. Nitrogen and carbon concentrations exceeding 2.0 wt.% were added to the base Fe–18Cr–18Mn composition without the formation of nitride or carbide precipitates. Minor additions of molybdenum, silicon, and nickel did not affect nitrogen interstitial solubility, but did reduce carbon solubility resulting in the formation of M23C6 (M=Cr, Fe, Mo) carbides. Increasing the interstitial content increases the lattice distortion strain, which is directly correlated with an increase in yield stress.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gavriljuk V, Berns H (1999) High nitrogen steels. Springer-Verlag, ISBN 3-540-66411-4
Berns H, Gavriljuk V (2007) Key Eng Mater 345–346:421
Foct F (2003) High nitrogen steels and interstitial alloying. HNS 2003, Schaffenhausen, Switzerland, 26–28 March 2003
Rawers J (2004) Proc Instn Mech Eng vol 218, Part L, J Mater Des Appl, pp 239
Rawers J, Tylczak J (2003) Characterizing alloy additions to high-nitrogen steels. THERMEC 2003, Leganes, Madrid, Spain, 7–11 July 2003
Menzel J, Stein G (1988) Dahlmann P Massive nitrogen-alloyed austenitic bolt materials. HNS 1988, Lille, France, 18–20 May 1988
Uggowitzer P, Harzenmoser M (1988) Strengthening of austenitic stainless steels by nitrogen, HNS 1988, Lille, France, 18–20 May 1988
Speidel M (1990) Properties of high nitrogen steels. HNS 1990, Aachen Germany, 10–12 Oct 1990
Rawers J (2003) Preliminary study into the stability of interstitial nitrogen and carbon in steels. HNS 2003, Schaffenhausen, Switzerland, 26–28 March 2003
Berns H (2003) Alloy development and processing. HNS 2003, Schaffenhausen, Switzerland, 26–28 March 2003
Speidel M (2003) From high-nitrogen steels to high interstitial alloys. HNS 2003, Schaffenhausen, Switzerland, 26–28 March 2003
Bernauer J, Gabriele S, Speidel M (2004) Combined influence of carbon and nitrogen on the mechanical and corrosion properties of Cr–Mn steel grade, HNS 2004, Ostend, Belgium, 19–22 Sept. 2004
Schmalt F, Berns B, Gavriljuk V (2004) Mechanical Properties of a stainless austenitic CrMnCN steel, HNS 2004, Ostend, Belgium, 19–22 Sept. 2004
Gavriljuk V, Rawers J, Shanina B, Berns H (2003) Mater Sci Forum 426–432:943
Dong H, Lin Q, Rong F, Su J, Xin C, Lang Y, Kang X (2003) Development and applications of nitrogen alloyed stainless steels in China. HNS 2003, Schaffenhausen, Switzerland, 26–28 March 2003
Gavriljuk V, Shanina B, Berns H, Mater Sci Eng A (in press)
Shanina B, Gavriljuk V, Berns H (2007) Mater Sci Forum 539–543:4993
Rawers J, Uggowitzer P (1998) Characterization of Fe–C/N steel. HNS 1998, Espoo, Finland, 24–29 May 1998
Rawers J (2003) WEAR 258:32
METALS Desk Handbook (1985) chpt. 15, ASM, pp 30, ISBN: 0-87170-188-X
Gersten J, Smith F (2001) The physics and chemistry of materials. J. Wiley and Sons, p 63, ISBN 0-471-05794-0
Liang J, Yang Z, Li W, Yi B (2006) Study of the properties of high-nitrogen stainless steel in 1Cr18Mn18N. HNS conference, Jiuzhaigong, Siuhaun, China, 29–30 Aug 2006
Kikuchi K, Kajihari M, Frisk K (1988) Solubility of nitrogen in austenitic stainless steel. pp 63, HNS 1988, Lille, France, 18–20 May 1988
Kim S, Lee T (1998) Precipitation sequence in austenitic steels. pp 109, HNS1998, Lille, France, 18–20 May 1988
Wahlberg G, Rolander G, Andren H (1998) Interaction between nitrogen and substitutional elements in austenitic stainless steels. pp 163, HNS 1998
Anthanahen B, Uggowitzer P, Cui M, Speidel M, Stein G (1998) New high nitrogen ferritic steels. pp 58, HNS 1998
Foct J, Magnii T, Perrot P, Vogt J (1991) Duplex stainless steel ’91. Bougogne, France, pp 49, 28–30 Oct 1991
Guttmann M (1991) In: Gunn RN (ed) Duple stainless steels. William Andrew Plb, p 79, ISBN 9781884207617
Bavay J (1993) In: Lacombe P, Baroux B, Beranger B (eds) Stainless steels. Les Editions de Physique, Les Ulis, Cedex A, France, p 551, ISBN 2-86883-189-3
Cheng L, Bottger A, deKeijser T, Mittemeijer E (1990) Scripta Metall Mater 24:509
Rawers J, Duttlinger N, Mater Sci Technol (accepted for publication)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rawers, J.C. Alloying effects on the microstructure and phase stability of Fe–Cr–Mn steels. J Mater Sci 43, 3618–3624 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-2576-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-2576-3