Abstract
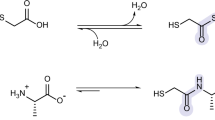
Hydrothermal reactions of formaldehyde (CH2O), which is mainly formed by CO2, are considered to be of most importance in the abiotic synthesis of complex organic molecules in chemical evolution on the primitive Earth. We show the hydrothermal formation of amino acids and oligopeptides in neutral or weak acidic solutions from CH2O in the presence of metals and metal oxides. In these hydrothermal processes, metal or metal oxides selectively catalyzed a series of hydrothermal reactions from CH2O to amino acids, whereas the further reactions for the formation of oligopeptides proceeded without any catalyst. Our experimental observation may provide a possible clue to understanding the initial chemical evolution in Earth’s primitive atmosphere of the origin of life.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miller SL (1953) Science 117:528
Plankensteiner K, Hannes R, Benjamin S, Bernd MR (2004) Angew Chem Int Ed 43:1886
Wächterhäuser G (1990) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:200
Huber C, Wächterhäuser G (1997) Science 276:245
Huber C, Wächterhäuser G (1998) Science 281:670
Wächterhäuser G (2000) Science 289:1307
Dörr M, Käbbohrer J, Grunert R, Kreisel G, Brand WA, Werner RA, Geilmann H, Apfel C, Robl C, Weigand W (2003) Angew Chem Int Ed 42:1540
Huber C, Eisenreich W, Hecht S, Wächterhäuser G (2003) Science 301:938
Corliss JB, Dymond J, Dordon LI, Edmond JM, Herzen RP, Ballard RPV, Green RD, Williams K, Bainbridge A, Crane K, Van Adel TH (1979) Science 203:1073
Severin K (2000) Angew Chem Int Ed 39:589
Kasting JF (1993) Science 259:920
Wofsy SC, Mcconnell JC, Mcelroy MBJ (1972) Geophys Res 77:4477
Pinto JP, Gladstone GR, Yung YL (1980) Science 210:183
Mojzsis SJ, Arrhenius G, Mckeegan KD, Harrison TM, Nutman AP, Friends CRL (1996) Nature 384:55
Largiuni O, Becagli S, Innocenti M, Stortini AM, Traversi R, Udisti R (2005) J Environ Monitor 7:1299
Morooka S, Wakai C, Matubayasi N, Nakahara M (2005) J Phys Chem A 109:6610
Tian G, Yuan HM, Mu Y, He C, Feng SH (2007) Org Lett 9:2019
Butlerow A (1861) Annalen 120:295
Schwartz AW, De Graaf RM (1993) J Mol Evol 36:101
Orgel LE (2000) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:12503
Reid C, Orgel LE (1967) Nature 216:455
Larralde R, Robertson MP, Miller SL (1995) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:8158
Feng SH, Xu RR (2001) Acc Chem Res 34:239
Imai E, Honda H, Hatori K, Brack A, Matsuno K (1999) Science 283:831
Alargov DK, Deguchi S, Tsujii K, Horikoshi K (2002) Origin Life Evol B 32:1
Miller SL, Lazcano A (1996) Cell 85:793
Lazcano A, Miller SL (1999) J Mol Evol 49:424
Keefe AD, Miller SL, Mcdonald G, Bada J (1995) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:11904
Miller SL, Bada JL (1988) Nature 334:609
Nisbet EG, Sleep NH (2001) Nature 409:1083
Acknowledgements
We thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China for support through the Research Fund for Creative Research Team.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, S., Tian, G., He, C. et al. Hydrothermal biochemistry: from formaldehyde to oligopeptides. J Mater Sci 43, 2418–2425 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-007-2009-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-007-2009-8