Abstract
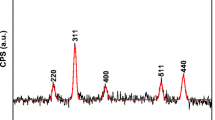
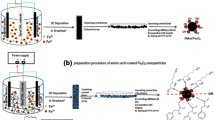
Adsorption of 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTS) on magnetite nanoparticles during its formation has been investigated to optimise the preparation of stable aqueous dispersion of amine derivatised magnetite nanoparticles. APTS adsorbs chemically on the surface of magnetite particle modifying its surface which is evident from thermal and C, H, N analysis. The variation of particle size has been observed with change of APTS concentration. X-ray diffractogram shows the formation of pure inverse spinel phase magnetite with average crystallite size 7 nm when equimolar (Fe3O4: APTS = 1:1) quantity of APTS was used during its synthesis. The presence of free surface –NH2 groups and Fe–O–Si bonds was observed by FTIR. Raman spectrum further confirms the presence of surface –NH2 groups. Transmission electron microscopy shows formation of particles of average size between 7 nm and 12 nm. The effective hydrodynamic diameter of the APTS coated particle agglomerates is 45.8 nm in stable aqueous colloidal dispersion, which is evident from photon correlation spectroscopy. VSM measurements at room temperature of both silanised and unsilanised magnetite shows their superparamagnetic nature with saturation magnetisation 41 e.m.u/g and 56 e.m.u/g, respectively. Avidin has been immobilised on the surface through glutaraldehyde, which demonstrates the possibility of the synthesised material to be used in protein immobilisation to form bioactive magnetic particles.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chaterjee J, Haik Y, Chen CJ (2001) J Magn Magn Mater 225:21
Bilková Z, Slováková M, Horák D, Lenfeld J (2002) J Chromatogr B 770:177
Pourfarzaneh M, Camel RS, London J, Dawes CC (1982) Method Biochem Anal 28:267
Homes E, Korsnes L (1990) Genet Anal Technol Appl 7:145
Sonti SV, Bose A (1991) J Colloid Inter Sci 170:575
Cupta PK, Hung CT (1989) Life Sci 44:175
Coradin T, Lopez PJ (2003) Chembiochem 4:251
Whitehead RA, Chagnon MS, Groman EU, Josephson L (1985) USP 4554,088
Ma M, Zhang Y, Yu W (2003) Colloids Surfaces A: Physicochem Eng Aspects 212(2–3):219
Yamaura M, Sampaio LC, Macêdo MA, Nakamura M, Toma HE (2004) J Magn Magn Mater 279(2–3):210
Shen X-C, Fang X-Z, Zhou Y-H, Liang H (2004) Chem Lett 33(11):1468–1469
Kobayashi H, Matsunaga T (1991) J Colloid Interface Sci 141:505
Massart R, Cabuil V (1987) J Chem Phys 84(7–8):967
Bee A, Massart R (1990) J Magn Magn Mater 122:1
Cornell RM, Schwertmann U (1996) The iron oxides: structure, properties, reactions, occurrence and uses. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, p 207
Brinker CJ, Schere GW (1990) Sol–gel science: the physics and chemistry of sol-gel processing. Academic Press, Inc
Cornell RM, Schwertmann U (1996) The iron oxides: structure, properties, reactions, occurrence and uses. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, p 135
De Faria LA, Venâncio Silva S, De Oliveria MT (1997) J Raman Spectroscopy 28:873
Hartridge A, Bhattacharya AK, Sengupta M, Majumdar CK, Das D, Chintalapudi SN (1997) J Magn Magn Mater 176:L89
Rao ZM, Wu TH, Peng SY (1995) Acta Phys Chim Sin 11:395
Mckittrick MW, Jones CW (2003) Chem Mater 15:1132
Bruce IJ, Sen T (2005) Langmuir 21:7029
Ambastha RD, Wattal PK, Singh S, Bahadur D (2003) J Magn Magn Mater 267:335
Bruke NAD, Stöver HDH, Dawson FP (2002) Chem Mater 14:4752
Cullity BD (1972) Introduction to magnetic materials. Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, p 190
Acknowledgements
Authors are thankful to CSIR New Delhi for providing financial support for this work. Dr D. Das, IUC-DAE Consortium for Scientific Research, Kolkata, Dr M. K. Panigrahi, IIT Kharagpur and Dr D. Bahadur, IIT Bombay, Powai are gratefully acknowledged for Mössbauer, Raman and VSM studies, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohapatra, S., Pramanik, N., Mukherjee, S. et al. A simple synthesis of amine-derivatised superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for bioapplications. J Mater Sci 42, 7566–7574 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-007-1597-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-007-1597-7