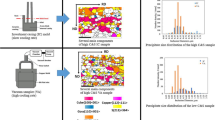
Abstract
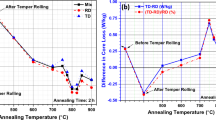
With the addition of Co, Mo and Ni to high-alloyed non-oriented electrical steels with 3Si–0.1Sn–0.08Sb, Ni increased grain size more than Co and Mo. A very low level of core loss (W 15/50 = 2.2 W/kg) and high magnetic induction (B 50 = 1.7 T) were obtained in the Ni added steel. However, Co and Mo deteriorated the magnetic properties substantially. With respect to the texture effect on magnetic properties, core loss decreased and magnetic induction increased proportionally to texture factor (ratio of the sum of cube and Goss texture to γ fiber), while correlations of anisotropies of core loss and magnetic induction to the texture factor appeared parabolic.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang SK, Huang WY (2005) ISIJ Int 45:918
Texture measurement software, Res-Mat Co, McGill University
Liu WC, Morris JG (2004) Met Mat Trans A 35A:265
Shimanaka H, Ito Y, Matsumura K, Fukuda B (1982) J Magn Magn Mater 26:57
Birsan M, Szpunar JA (1996) J Appl Phys 80:6915
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, S.K. Effects of Co, Mo, and Ni on magnetic properties in 3Si–0.1Sn–0.08Sb alloyed non-oriented electrical steels. J Mater Sci 41, 7380–7386 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-0805-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-0805-1