Abstract
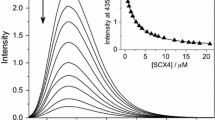
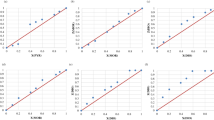
Pillar[n]arenes are a relatively new class of macrocyclic host molecules which have not been extensively studied for their ability to form inclusion complexes. The properties and host–guest inclusion complexes of dimethoxypillar[5]arene (DMPill[5]) hosts with the polarity-sensitive fluorescent probes 8-anilinonaphthalene-1-sulfonic acid (1,8-ANS) and 2-anilinonaphthalene-6-sulfonic acid (2,6-ANS) as guests were investigated in nonaqueous solvents via fluorescence spectroscopy. The binding properties of DMPill[5] were found to depend significantly on the shape of the guest molecule, as well as on the properties of the solvent. Formation of host–guest inclusion complexes of DMPill[5] with these two fluorescent ANS guests occurred in the polar aprotic solvents acetonitrile, acetone, and tetrahydrofuran. Fluorescence titration experiments were performed to determine the nature and strength of the complexation. In the case of 1,8-ANS, 1:1 host–guest complexation was observed in all three solvents, with average binding constant K values of 408, 1000 and 5500 M−1 in acetone, acetonitrile, and tetrahydrofuran, respectively. This large dependence of the binding constant on solvent provides insight into the nature of the binding in these complexes. In the case of 2,6-ANS, 2:1 host–guest complexation was observed; this difference with 1,8-ANS was explained in terms of the shape and size of these two isomeric guests. These results show that DMPill[5] is an excellent host for these neutral aromatic guests, and shows strong binding abilities even in these nonaqueous solvents. The strength (or lack) of binding in different solvents was found to be dependent on a range of factors beyond solvent polarity, including guest and solvent shape and size, and most importantly, specific solvent–solute interactions.
Graphic abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ogoshi, T., Ed. Pillararenes, Royal Society of Chemistry Monographs in Supramolecular Chemistry, London, UK, (2015)
Ogoshi, T., Yamagishi, T.-A., Nakamoto, Y.: Pillar-shaped macrocyclic hosts pillar[n]arenes: New key players for supramolecular chemistry. Chem. Rev. 116, 7937–8002 (2016)
Ogoshi, T., Kanai, S., Fujinami, S., Yamagishi, T., Nakamoto, Y.: Para-bridged symmetrical pillar[5]arenes: Their Lewis acid catalyzed synthesis and host–guest property. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 5022–5023 (2008)
Li., C.: Pillararene-based supramolecular polymers: From molecular recognition to polymeric aggregates. Chem. Commun. 50, 12420–12433 (2014 )
Murray, J., Kim, K., Ogoshi, T., Yao, W., Gibb, B.C.: The aqueous supramolecular chemistry of cucurbit[n]urils, pillar[n]arenes and deep-cavity cavitands. Chem. Soc. Rev. 46, 2479–2496 (2017)
Zhang, H., Zhao, Y.: Pillararene-based assemblies: Design principle, preparation and applications. Chem. Eur. J. 19, 16862–16879 (2013)
Yao, Y., Xue, M., Chen, J., Zhang, M., Huang, F.: An amphiphilic pillar[5]arene: Synthesis, controllable self-assembly in water, and application in calcein release and TNT absorption. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 15712–15715 (2012)
Zhang, Z., Luo, Y., Chen, J., Dong, S., Yu, Y., Ma, Z., Huang, F.: Formation of linear supramolecular polymers that is driven by C–H…π interactions in solution and in the solid state. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 50, 1397–1401 (2011)
Jie, K., Zhou, Y., Li, E., Zhao, R., Huang, F.: Separation of aromatics/cyclic aliphatic hydrocarbons by nonporous adaptive pillarene crystals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 57, 12845–12849 (2018)
Xue, M., Yang, Y., Chi, X., Zhang, Z., Huang, F.: Pillararenes, a new class of macrocycles for supramolecular chemistry. Acc. Chem. Res. 45, 1294–1308 (2012)
Macias, A.T., MacKerell Jr., A.D.: CH/π interactions involving aromatic amino acids: Refinement of the CHARMM tryptophan force field. J. Comput. Chem. 26 , 1452–1463 (2005)
Nishio, M., Umezawa, Y., Honda, K., Tsuboyama, S., Suezawa, H.: CH/π hydrogen bonds in organic and organometallic chemistry. Cryst. Eng. Comm. 11, 1757–1788 (2009)
Tao, H., Cao, D., Liu, L., Kou, Y., Wang, L., Meier, H.: Synthesis and host-guest properties of pillar[6]arenes. Sci. Chin. 55, 223–228 (2012)
Ma, Y., Chi, X., Yan, X., Liu, J., Yao, Y., Chen, W., Huang, F., Hou, J.-L.: per-Hydroxylated pillar[6]arene: Synthesis, X-ray crystal structure, and host-guest complexation. Org. Lett. 14, 1532–1535 (2012)
Yu, G., Xue, M., Zhang, Z., Li, J., Han, C., Huang, F.: A water-soluble pillar[6]arene: Synthesis, host-guest chemistry, and its application in dispersion of multiwalled carbon nanotubes in water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134 13248–13251
Santra, S., Kopchuk, D.S., Kovalev, I.S., Zyryanov, G.V., Majee, A., Charushin, V.N., Chupakhin, O.N.: Solvent-free synthesis of pillar[6]arenes. Green Chem. 18, 423–426 (2016)
Yu, G., Zhou, J., Shen, J., Tang, G., Huang, F.: Cationic pillar[6]arene/ATP host-guest recognition: Selectivity, inhibition of ATP hydrolysis, and application in multidrug resistance treatment. Chem. Sci. 7, 4073–4078 (2016)
Liu, Y., Zhou, F., Yang, F., Ma, D.: Carboxylated pillar[n]arene (n = 5–7) host molecules: High affinity and selective binding in water. Org. Biomol. Chem. 17, 5106–5111 (2019)
Schönbeck, C., Li, H., Han, B.-H., Laursen, B.W.: Solvent effects and driving forces in pillarene inclusion complexes. J. Phys. Chem. B 119, 6711–6720 (2015)
Fernández-Rosas. J., Gómez-González, B., Pessȇgo, M., Rodríguez-Dafonte, P., Parajó, M., Garcia-Rio, L.: Comparison of pillar[5]arene and calix[4]arene anion receptor ability in aqueous media. Supramol. Chem. 28, 464–474 (2016)
D'Anna, F., Rizzo, C., Vitale, P., Marullo, S., Ferrante, F.: Supramolecular complexes formed by dimethoxypillar[5]arenes and imidazolium salts: a joint experimental and computational investigation. New J. Chem. 41, 12490–12505 (2017)
Zhang, H., Nguyen, K. T., Ma, X., Yan, H., Guo, J., Zhu, L., Zhao, Y.: Host–guest complexation driven dynamic supramolecular self-assembly. Org. Biomol. Chem. 11, 2070–2074 (2013)
Tan, L., Zhang, Y., Li, B., Wang, K., Zhang, S. X., Tao, Y., Yang, Y.: Selective recognition of “solvent” molecules in solution and the solid state by 1,4-dimethoxypillar[5]arene driven by attractive forces. New J. Chem. 38, 845–851 (2014)
Wang, L., Xia, D., Chao, J., Zhang, J., Wei, X., Wang, P.: A Dimethoxypillar[5]arene/azastilbene host–guest recognition motif and its applications in the fabrication of polypseudorotaxanes. Org. Biomol. Chem. 17, 6038–6042 (2019)
Robinson, G.W., Robbins, R.J., Fleming, G.R., Morris, J.M., Knight, A.E.W., Morrison, R.J.S.: Picosecond studies of the fluorescence probe molecule 8-anilino-1-naphthalenesulfonic acid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 100, 7145–7150 (1978)
Upadhyay, A., Bhatt, T., Tripathi, H.B., Pant, D.D.: Photophysics of 8-anilino-1-naphthalenesulfonate. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A. Chem. 89, 201–207 (1995)
Wagner, B.D., Arnold, A.E., Gallant, S.T., Grinton, C.R., Locke, J.K., Mills, N.D., Snow, C.A., Uhlig,T.B., Vessey, C.N.: The polarity sensitivity factor (PSF) of some fluorescent probe molecules used for studying supramolecular systems and other heterogeneous environments. Can. J. Chem. 96, 629–635 (2018)
Wagner, B.D.: Fluorescence studies of supramolecular host-guest inclusion complexes. In: H.S., Nalwa (ed.), Handbook of photochemistry and photobiology, pp. 1-58. American Scientific Publishers, Los Angeles (2003)
Wagner, B.D., MacDonald, P.J.: The fluorescence enhancement of 1-anilinonaphthalene-8-sulfonate (ANS) by modified beta-cyclodextrins. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A. 114, 151–157 (1998)
Wagner, B.D., Fitzpatrick, S.J.: A comparison of the host-guest inclusion complexes of 1,8-ANS and 2,6-ANS in parent and modified cyclodextrins. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 38, 467–478 (2000)
Favrelle, A., Gouhier, G., Guillen, F., Martin, C., Mofaddel, N., Petit, S., Mundy, K.M., Pitre, S.P., Wagner, B.D.: Structure-binding effects: Comparative binding of 2-anilino-6-naphthalenesulfonate by a series of alkyl- and hydroxyalkyl-substituted β-cyclodextrins. J. Phys. Chem. B 119, 12921–12930 (2015)
Wagner, B.D., Fitzpatrick, S.J., Gill, M.A., MacRae, A.I., Stojanovic, N.: A fluorescent host-guest complex of cucurbituril in solution: A molecular Jack O’Lantern. Can. J. Chem. 79, 1101–1104 (2001)
Wagner, B.D., Stojanovic, N., Day, A.I., Blanch, R.J.: Host properties of cucurbit[7]uril: Fluorescence enhancement of anilinonaphthalene sulfonates. J. Phys. Chem. B 107, 10741–10746 (2003)
Stojanovic, N., Murphy, L. D, Wagner, B. D.: Fluorescence-based comparative binding studies of the supramolecular host properties of PAMAM dendrimers using anilinonaphthalene sulfonates: Unusual host-dependent fluorescence titration behaviour. Sensors 10, 4053–4070 (2010)
Ogoshi, T.: Synthesis of novel pillar-shaped cavitands “Pillar[5]arenes” and their application for supramolecular materials. J. Inclusion Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 72, 247–262 (2012)
Muňoz de la Peňa, A., Salinas, F., Gómez, M.J., Acedo, M.I., Sánchez Peňa, M.: Absorptiometric and spectrofluorimetric study of the inclusion complexes of 2-naphthyloxyacetic acid and 1-naphthylacetic acid with β-cyclodextrin in aqueous solution. J. Inclus. Phenom. Mol. Recog. Chem. 15, 131–143 (1993)
Nigam, S., Durocher, G.: Spectral and photophysical studies of inclusion complexes of some neutral 3H-indoles and their cations and anions with β-cyclodextrin. J. Phys. Chem. 100, 7135–7142 (1996)
Ogoshi, T., Yamagishi, T.: Pillar[5]- and pillar[6]arene-based supramolecular assemblies built by using their cavity-size-dependent host–guest interactions. Chem. Commun. 50, 4776–4787 (2014)
Szejtli, J.: Introduction and general overview of cyclodextrin chemistry. Chem. Rev. 98, 1743–1753 (1998)
Funding
This work was funded by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada and by the University of Prince Edward Island.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
T.A.M.: Experimental work, writing first draft, editing; B.D.W.: Project conception, supervision, editing, final draft, submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Misener, T.A., Wagner, B.D. Fluorescence-based investigations of the host–guest inclusion of anilinonaphthalene sulfonic acids (1,8- and 2,6-ANS) by dimethoxypillar[5]arene in nonaqueous solvents. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 100, 131–141 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-021-01063-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-021-01063-9