Abstract
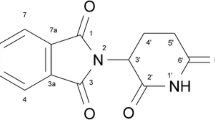
Two covalently bonded β-Cyclodextrin (β-CD) based CSPs were prepared by immobilizing the native β-CD and mono-6-deoxy-6-(3-benzylimidazolium tosylate)-β-CD (β-CD-BIMOTs) onto modified silica gel. β-CD-BIMOTs is a β-CD based CSP with ionic liquid (3-benzylimidazolium tosylate) substituent. The enantioseparation capability of the synthesized CSPs was examined using 4 racemic mixtures of β-blockers (propranolol, metoprolol, pindolol and atenolol). The results indicated that β-CD-BIMOTs based CSP afforded more favorable enantioseparations than native β-CD based CSP. In order to study the mechanism of enantioseparation, inclusion complexes β-CD-BIMOTs and β-blockers were prepared and these inclusion complexes were characterized by using 1H NMR and NOESY. In addition, the separation conditions such as pH and composition of mobile phase were varied to study the role of β-CD and ionic liquid in enantioseparation. In general, it can be concluded that the complete enantioseparation of propranolol and metoprolol is achieved through the formation of inclusion complex with β-CD-BIMOTs and the formation π-π interaction with the ionic liquid moiety of β-CD-BIMOTs. The result also showed the poor enantioseparation of pindolol and atenolol on the β-CD-BIMOTs based CSP due to the strong interaction at the exterior torus of β-CD-BIMOTs.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mehvar, R., Brocks, D.R.: Stereospecific pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of beta-adrenergic blockers in humans. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 4, 185–200 (2001)
Wilson, A.G., Brooke, O.G., Lloyd, H.J., Robinson, B.F.: Mechanism of action of β-adrenergic receptor blocking agents in angina pectoris: comparison of action of propranolol with dexpropranolol and practolol. Br. Med. J. 4, 399–401 (1969)
Borchard, U.: Pharmacological properties of beta-adrenoceptor blocking drugs. J. Clin. Bas. Cardiol. 1, 5–9 (1998)
Hoffman, B.B.: Catecholamines, sympathomimetic drugs, and adrenergic receptor antagonists, The pharmacological basis of therapeutics (1996)
Armstrong, D.W.: Direct enantiomeric separations in liquid chromatography and gas chromatography. In: Issaq, H.J. (ed.) A Century of Separation Science, pp. 555–578. Marcel Dekker, New York (2002)
Stoschitzky, K., Lindner, W., Zernig, G.: Racemic beta-blockers-fixed combinations of different drugs. J. Clin. Bas. Cardiol. 1, 15–19 (1998)
Hedeland, M., Isaksson, R., Pettersson, C.: Cellobiohydrolase I as a chiral additive in capillary electrophoresis and liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 807, 297–305 (1998)
Aboul-Enein, H.Y., Abou-Basha, L.I.: HPLC separation of nadolol and enantiomers on chiralcel OD column. J. Liq. Chrom. Rel. Techno. 19, 383–392 (1996)
Armstrong, D.W., DeMond, W.: Cyclodextrin bonded phases for the liquid chromatographic separation of optical, geometrical, and structural isomers. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 22, 411–415 (1984)
Armstrong, D.W., Ward, T.J., Armstrong, R.D., Beesley, T.E.: Separation of drug stereoisomers by the formation of beta-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes. Science 232, 1132–1135 (1986)
Stalcup, A.M., Chang, S.C., Armstrong, D.W., Pitha, J.: (S)-2-Hydroxyprophyl-β-cyclodextrin, a new chiral stationary phase for reversed-phase liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 513, 181–194 (1990)
Armstrong, D.W., Stalcup, A.M., Hilton, M.L., Duncan, J.D., Faulkner Jr., J.R., Chang, S.C.: Separation of metallocene enantiomers by liquid chromatography: chiral recognition via cyclodextrin bonded phases. Anal. Chem. 57, 481–484 (1985)
Scriba, G.K., Altria, K.: Using cyclodextrins to achieve chiral and non-chiral separations in capillary electrophoresis. LC GC EUROPE. 22, 420 (2009)
Hinze, W.L., Riehl, T.E., Armstrong, D.W., Demond, W., Alak, A., Ward, T.: Liquid chromatography separation of enantiomers using a chiral β-cyclodextrin bonded stationary phase and conventional aqueous-organic mobile phase. Anal. Chem. 57, 237–242 (1985)
Daffe, V., Fastrez, J.: Cyclodextrin-catalysed hydrolysis of oxazol-5(4H)-ones. Enantioselectivity of the acid-base and ring-opening reactions. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, 789–796 (1983)
Juvancz, Z., Szejtli, J.: The role of cyclodextrins in chiral selective chromatography. Trends Anal. Chem. 21, 379–388 (2002)
Szejtli, J.: Medicinal applications of cyclodextrins. Med. Res. Rev. 14, 353–386 (1994)
Wang, Y., Young, D.J., Tan, T.T.Y., Ng, S.C.: “Click” immobilized perphenylcarbamated and permethylated cyclodextrin stationary phases for chiral high-performance liquid chromatography application. J. Chromatogr. A 1217, 5103–5108 (2010)
Poon, Y.F., Muderawan, I.W., Ng, S.C.: Synthesis and application of mono-2 A-azido-2 A-deoxyperphenylcarbamoylated β-cyclodextrin and mono-2 A-azido-2 A-deoxyperacetylated β-cyclodextrin as chiral stationary phases for high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1101, 185–197 (2006)
Ahuja, S.: Chiral Separations by Chromatography. American Chemical Society, Oxford University Press, Oxford (2000)
Zhou, Z., Li, X., Chen, X.: Synthesis of ionic liquids functionalized β-cyclodextrin-bonded chiral stationary phases and their applications in high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 678, 208–214 (2010)
Wang, R.Q., Ong, T.T., Ng, S.C.: Chemically bonded cationic β-cyclodextrin derivatives as chiral stationary phases for enantioseparation applications. Tetrahedron Lett. 53, 2312–2315 (2012)
Wang, R.Q., Ong, T.T., Tang, W., Ng, S.C.: Cationic cyclodextrins chemically-bonded chiral stationary phases for high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 718, 121–129 (2012)
Zhang, J., Shen, X., Chen, Q.: Separation processes in the presence of cyclodextrins using molecular imprinting technology and ionic liquid cooperating approach. Curr. Org. Chem. 15, 74–85 (2011)
Zhou, Z., Li, X., Chen, X., Hao, X.: Synthesis of ionic liquids functionalized β-cyclodextrin-bonded chiral stationary phases and their applications in high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 678, 208–214 (2010)
Wasserscheid, P., Keim, W.: Ionic liquids-new “solutions” for transition metal catalysis. Angew. Chem. 39, 3772–3789 (2000)
Pandey, S.: Analytical applications of room-temperature ionic liquids: a review of recent efforts. Anal. Chim. Acta 556, 38–45 (2006)
Canongia Lopes, J.N., Pádua, A.A.: Nanostructural organization in ionic liquids. J. Phy. Chem. B 110, 3330–3335 (2006)
Anderson, J.L., Armstrong, D.W.: High-stability ionic liquids. A new class of stationary phases for gas chromatography. Anal. Chem. 75, 4851–4858 (2003)
Li, X., Zhou, Z.: Enantioseparation performance of novel benzimido-β-cyclodextrins derivatized by ionic liquids as chiral stationary phases. Anal. Chim. Acta 819, 122–129 (2014)
Li, X., Zhou, Z., Dai, W.L., Li, Z.: Preparation of a novel cyclodextrin derivative of benzimido-β-cyclodextrin and its enantioseparation performance in HPLC. Analyst 136, 5017–5024 (2011)
Zhong, N., Byun, H.S., Bittman, R.: An improved synthesis of 6-O-monotosyl-6-deoxy-β-cyclodextrin. Tetrahedron Lett. 39, 2919–2920 (1998)
Ong, T.T., Tang, W., Muderawan, W., Ng, S.C., Chan, H.S.O.: Synthesis and application of single-isomer 6-mono (alkylimidazolium)-β-cyclodextrins as chiral selectors in chiral capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 26, 3839–3848 (2005)
Yatabe, J., Kageyama, T.: Preparation of hydrophobic silica with isocyanate. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 102, 595–598 (1994)
Cwiertnia, B., Hladon, T., Stobiecki, M.: Stability of diclofenac sodium in the inclusion complex with β-cyclodextrin in the solid state. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 51, 1213–1218 (1999)
Daruházi, Á.E., Szente, L., Balogh, B., Mátyus, P., Béni, S., Takács, M., Lemberkovics, E.: Utility of cyclodextrins in the formulation of genistein: Part 1. Preparation and physicochemical properties of genistein complexes with native cyclodextrins. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 48, 636–640 (2008)
Arnold, R.G., Nelson, J.A., Verbanc, J.J.: Recent advances in isocyanate chemistry. Chem. Rev. 57, 47–76 (1957)
Simons, D.M., Arnold, R.G.: Relative reactivity of the isocyanate groups in toluene 2,4-diisocyanate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 78, 1658–1659 (1956)
Lumley, B., Khong, T.M., Perrett, D.: The characterization of chemically bonded chromatographic stationary phases by thermogravimetry. Chromatographia 60, 59–62 (2004)
Pino, V., Afonso, A.M.: Surface-bonded ionic liquid stationary phases in high-performance liquid chromatography-a review. Anal. Chim. Acta 714, 20–37 (2012)
Li, S., Purdy, W.C.: Direct separation of enantiomers using multiple-interaction chiral stationary phases based on the modified β-cyclodextrin-bonded stationary phase. J. Chromatogr. A 625, 109–120 (1992)
Zhang, D.D., Zhao, P.Y., Huang, N.J., Wu, Y.L., Zhai, Y.M.: Study of α-cyclodextrin or dimethylcyclodextrin/toluene in CF COOD/DO. In: The 5th International Symposium on Cyclodextrins. Editions de Sante´, pp. 146–149 (1990)
Guo, Z., Jin, Y., Liang, T., Liu, Y., Xu, Q., Liang, X., Lei, A.: Synthesis, chromatographic evaluation and hydrophilic interaction/reversed-phase mixed-mode behavior of a “Click β-cyclodextrin” stationary phase. J. Chromatogr. A 1216, 257–263 (2009)
Buszewski, B., Noga, S.: Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC)-a powerful separation technique. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 402, 231–247 (2012)
Raoov, M., Mohamad, S., Abas, M.R.: Removal of 2, 4-dichlorophenol using cyclodextrin-ionic liquid polymer as a macroporous material: characterization, adsorption isotherm, kinetic study, thermodynamics. J. Hazard. Mater. 263, 501–516 (2013)
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to seize this opportunity to express their gratitude to the University Malaya for the IPPP grant PG027/2013A and UMRG grant (RP006A-13SUS and RP011B-14SUS). The authors also acknowledge Ministry of Higher Education (MOHE) for providing fellowship to one of the authors-cum-researchers, Ms. NurulYani Rahim.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict if interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahim, N.Y., Tay, K.S. & Mohamad, S. β-Cyclodextrin functionalized ionic liquid as chiral stationary phase of high performance liquid chromatography for enantioseparation of β-blockers. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 85, 303–315 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-016-0629-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-016-0629-9