Abstract
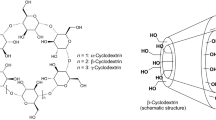
Possibility of encapsulation of riboflavin and alloxazine by α- and β-cyclodextrins in aqueous solution was studied by 1H NMR and solubility methods. Thermodynamic parameters of 1:1 inclusion complex formation (K, ΔcG0, ΔcH0 and ΔcS0) were obtained and analyzed in terms of influence of reagent’s structure on complexation process. It was shown that α-cyclodextrin displays low binding affinity to riboflavin and alloxazine. On the contrary, β-cyclodextrin forms with riboflavin and alloxazine more stable inclusion complexes. Binding is accompanied by the negative enthalpy and entropy changes that are determined by predominance of van der Waals interactions and possible H-bonding. The presence of ribityl substituent in riboflavin molecule prevents the deep penetration of this compound into macrocyclic cavity. Proposed on the basis of 1H NMR data the partial insertion of the hydrophobic part of riboflavin and alloxazine molecules into the β-cyclodextrin cavity causes the enhancement of aqueous solubility of the encapsulated substances. In comparison with α-cyclodextrin, the solubilizing effect of β-cyclodextrin is more pronounced due to its higher binding affinity to alloxazine and riboflavin.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Vos, P., Bučko, M., Gemeiner, P., et al.: Multiscale requirements for bioencapsulation in medicine and biotechnology. Biomaterials 30, 2559–2570 (2009)
Champagne, C.P., Fustier, P.: Microencapsulation for the improved delivery of bioactive compounds into foods. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 18, 184–190 (2007)
Branco, M.C., Schneider, J.P.: Self-assembling materials for therapeutic delivery. Acta Biomater. 5, 817–831 (2009)
Sagar, G.H., Arunagirinathan, M.A., Bellare, J.R.: Self-assembled surfactant nano-structures important in drug delivery: a review. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 45, 133–159 (2007)
Goldberg, M., Langer, R., Jia, X.Q.: Nanostructured materials for applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 18, 241–268 (2007)
Szente, L., Szejtli, J.: Cyclodextrins as food ingredients. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 15, 137–142 (2004)
Szeitli, J., Szente, L.: Elimination of bitter, disgusting tastes of drugs and foods by cyclodextrins. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 61, 115–125 (2005)
Loftsson, T., Duchêne, D.: Cyclodextrins and their pharmaceutical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 329, 1–11 (2007)
Vyas, A., Saraf, S., Saraf, S.: Cyclodextrins based novel drug delivery systems. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 62, 23–42 (2008)
Del Valle, E.M.M.: Cyclodextrins and their uses: a review. Process Biochem. 39, 1033–1046 (2004)
Szejtli, J.: In: Davies, J.E.D., MacNicol, D.D., Vögtle, F., Attwood, J.L. (eds.) Comprehensive Supramolecular Chemistry: Cyclodextrins, vol. 3. Oxford, Elsevier (1996)
Massey, V.: The chemical and biological versatility of riboflavin. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 28, 283–296 (2000)
Heelis, P.F.: The photophysical and photochemical properties of flavins (isoalloxazines). Chem. Soc. Rev. 11, 15–39 (1982)
Saleh, A.M.: Stability of riboflavin in solubilized systems. Pharmazie. 29, 474–478 (1974)
Smith, E.C., Metzler, D.E.: The photochemical degradation of riboflavin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 85, 3285–3288 (1963)
Chastain, J., McCormick, D.B.: In: Muller, F. (ed.) Chemistry and Biochemistry of Flavoenzymes, pp. 196–200. CRC Press, Boston (1991)
Sikorska, E., Khmelinskii, I.V., Williams, S.L., et al.: Spectroscopy and photophysics of 6,7-dimethyl-alloxazine: experimental and theoretical study. J. Mol. Struct. 697, 199–205 (2004)
Szymusiak, H., Konarski, J., Koziol, J.: An INDO/S MO study of alloxazine and its monomethyl derivatives. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, 229–236 (1990)
Komasa, J., Rychlewski, J., Koziol, J.: Electronic structure of alloxazine and its methyl derivatives. J. Mol. Struct. (Theochem). 170, 205–212 (1988)
Habib, H.J., Asker, A.F.: Photostabilization of riboflavin by incorporation into liposomes. J. Parent Sci. Technol. 45, 124–127 (1991)
Loukas, Y.L., Jayasekera, P., Gregoriadis, G.: Characterization and photoprotection studies of a model γ-cyclodextrin-included photolabile drug entrapped in liposomes incorporating light absorbers. J. Phys. Chem. 99, 11035–11040 (1995)
Loukas, Y.L.: A Plackett–Burman screening design directs the efficient formulation of multicomponent DRV liposomes. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 26, 255–263 (2001)
Wang, X.-M., Chen, H.-Y.: A spectroelectrochemical study of the interaction of riboflavin with β-cyclodextrin. Spectrochim. Acta A 51, 599–605 (1996)
Wang, X.-M., Yan, M.-D., Zhu, J., Chen, H.-Y.: The surface-enhanced Raman spectroelectrochemical study on the interaction between β-cyclodextrin and the electrochemically generated radical intermediate of flavin. J. Electroanal. Chem. 451, 187–192 (1998)
Roy, D.K., Deb, N., Ghosh, B.C., Mukherjee, A.K.: Inclusion of riboflavin in β-cyclodextrin: a fluorimetric and absorption spectrometric study. Spectrochim. Acta A 73, 201–204 (2009)
Loukas, Y.L., Vraka, V., Gregoriadis, G.: Use of nonlinear least-squares model for the kinetic determination of the stability constant of cyclodextrin inclusion complexes. Int. J. Pharm. 144, 225–231 (1996)
Loukas, Y.L.: Multiple complex formation of unstable compounds with cyclodextrins: efficient determination and evaluation of the binding constant with improved kinetic studies. Analyst 122, 377–381 (1997)
Loukas, Y.L.: Multiple complex formation of fluorescent compounds with cyclodextrins: efficient determination and evaluation of the binding constant with improved fluorometric studies. J. Phys. Chem. B 101, 4863–4866 (1997)
Job, P.: Ann. Chim. 9, 113–203 (1928)
Higuchi, T., Connors, K.A.: Phase-solubility techniques. Adv. Anal. Chem. Instrum. 4, 117–212 (1965)
Saenger, W., Jacob, J., Gessler, K., et al.: Structures of the common cyclodextrins and their larger analogues—beyond the doughnut. Chem. Rev. 98, 1787–1802 (1998)
Blyshak, L.A., Warner, I.M., Patonay, G.: Evidence for non-inclusional association between α-cyclodextrin and polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons. Anal. Chim. Acta 232, 239–243 (1990)
Terekhova, I.V., Kumeev, R.S., Alper, G.A.: Inclusion complex formation of α- and β-cyclodextrins with aminobenzoic acids in aqueous solution studied by 1H NMR. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 59, 301–306 (2007)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (grant №09-03-97563). We are grateful to E. Gorbachev for help with calculations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Terekhova, I.V., Tikhova, M.N., Volkova, T.V. et al. Inclusion complex formation of α- and β-cyclodextrins with riboflavin and alloxazine in aqueous solution: thermodynamic study. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 69, 167–172 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-010-9827-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-010-9827-z