Abstract
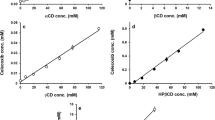
The purpose of this study was to investigate the physicochemical properties of drug-saturated aqueous cyclodextrin (CD) solutions. Phase solubility profiles of different drugs were determined in aqueous solutions containing γ-cyclodextrin (γCD) and/or hydroxypropyl-γ-cyclodextrin (HPγCD) in absence or presence of water-soluble polymers. 1H-NMR and turbidity analysis were performed as well as permeation studies. Phase solubility diagrams showed that the observed γCD content (1–20% w/v) was only slightly different from the theoretical values for aqueous solutions that had been saturated with indomethacin, diclofenac sodium or amphotericin B, all displayed A-type profiles, while it was less than the theoretical value in solutions that had been saturated with corticosteroids (hydrocortisone and dexamethasone) that displayed BS-type profiles. In the latter case self-assemble of drug/CD complexes decreased the overall CD solubility. Water-soluble polymers enhanced aqueous solubility of the drugs tested by stabilizing the drug/CD complexes, i.e. enhancing their stability constants, without affecting the observed aqueous γCD solubility. When the drug solubility leveled off (the BS-type profiles) the amount of dissolved γCD increased and approached the theoretical values. Hydrocortisone formed partial inclusion complex with γCD and HPγCD and no non-inclusion or aggregates could be detected in diluted solutions by 1H-NMR. Both permeation and turbidity studies showed that formation of dexamethasone/γCD complex promoted CD aggregation. All these observations indicate that CD aggregate formations play a role in CD solubilization of lipophilic and poorly water-soluble drugs and that the water-soluble polymers enhance the complexation efficiency of γCD and HPγCD by stabilizing the self-assembled drug/CD nanoparticles and promote non-inclusion complex formation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Loftsson, T., Brewster, M.E.: Pharmaceutical applications of cyclodextrins 1. Drug solubilization and stabilization. J. Pharm. Sci. 85(10), 1017–1025 (1996)
Rajewski, R.A., Stella, V.J.: Pharmaceutical applications of cyclodextrins 2. In vivo drug delivery. J. Pharm. Sci. 85(11), 1142–1169 (1996)
Bonini, M., Rossi, S., Karlsson, G., Almgren, M., Lo Nostro, P., Baglioni, P.: Self-assembly of β-cyclodextrin in water. Part 1: Cryo-TEM and dynamic and static light scattering. Langmuir 22(4), 1478–1484 (2006)
Messner, M., Kurkov, S.V., Jansook, P., Loftsson, T.: Self-assembled cyclodextrin aggregates and nanoparticles. Int J Pharm 387, 199–208 (2010)
Szente, L., Szejtli, J., Kis, G.L.: Spontaneous opalescence of aqueous γ-cyclodextrin solutions: complex formation or self-aggregation? J. Pharm. Sci. 87(6), 778–781 (1998)
He, Y.F., Fu, P., Shen, X.H., Gao, H.C.: Cyclodextrin-based aggregates and characterization by microscopy. Micron 39(5), 495–516 (2008)
Gonzalez-Gaitano, G., Rodriguez, P., Isasi, J.R., Fuentes, M., Tardajos, G., Sanchez, M.: The aggregation of cyclodextrins as studied by photon correlation spectroscopy. J Inc Phenom Macrocycl Chem 44(1–4), 101–105 (2002)
Bikadi, Z., Kurdi, R., Balogh, S., Szeman, J., Hazai, E.: Aggregation of cyclodextrins as an important factor to determine their complexation behavior. Chem Biodivers 3(11), 1266–1278 (2006)
Pistolis, G., Malliaris, A.: Nanotube formation between cyclodextrins and 1,6-diphenyl-1,3,5-hexatriene. J. Phys. Chem. 100(38), 15562–15568 (1996)
Witte, F., Hoffmann, H.: Aggregation behavior of hydrophobically modified β-cyclodextrins in aqueous solution. J Incl Phenom Mol Recognit Chem 25(1–3), 25–28 (1996)
Pistolis, G., Malliaris, A.: Size effect of alpha, omega-diphenylpolyenes on the formation of nanotubes with γ-cyclodextrin. J Phys Chem B 102(7), 1095–1101 (1998)
Zhao, Y.L., Yu, L.: Self-assembly behavior of phenyl modified β-cyclodextrins. Sci China Ser B 49(3), 230–237 (2006)
Zhao, Y.L., Liu, Y.: Self-assembly behavior of inclusion complex formed by β-cyclodextrin with α-aminopyridine. Sci China Ser B 47(3), 200–205 (2004)
Rodriguez-Perez, A.I., Rodriguez-Tenreiro, C., Alvarez-Lorenzo, C., Concheiro, A., Torres-Labandeira, J.J.: Drug solubilization and delivery from cyclodextrin-pluronic aggregates. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 6(9–10), 3179–3186 (2006)
Zeng, P.Y., Zhang, G.F., Rao, A., Bowles, W., Wiedmann, T.S.: Concentration dependent aggregation properties of chlorhexidine salts. Int J Pharm 367(1–2), 73–78 (2009)
Duan, M.S., Zhao, N., Ossurardóttir, I.B., Thorsteinsson, T., Loftsson, T.: Cyclodextrin solubilization of the antibacterial agents triclosan and triclocarban: formation of aggregates and higher-order complexes. Int J Pharm 297(1–2), 213–222 (2005)
Roos, C., Buss, V.: Evidence for the cyclodextrin mediated aggregation of cyanine dyes into oligomers. J Incl Phenom Mol Recognit Chem 27(1), 49–56 (1997)
Khan, M.S.: Aggregate formation in poly(ethylene oxide) solutions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 102(3), 2578–2583 (2006)
Rossi, S., Bonini, M., Lo Nostro, P., Baglioni, P.: Self-assembly of β-cyclodextrin in water. 2. Electron spin resonance. Langmuir 23(22), 10959–10967 (2007)
Jansook, P., Kurkov, S.V., Loftsson, T.: Cyclodextrins as solubilizers: formation of complex aggregates. J. Pharm. Sci. 99(2), 719–729 (2010)
Loftsson, T., Hreinsdóttir, D., Másson, M.: Evaluation of cyclodextrin solubilization of drugs. Int J Pharm 302(1–2), 18–28 (2005)
Jarho, P., Pate, D.W., Brenneisen, R., Jarvinen, T.: Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin and its combination with hydroxypropyl-methylcellulose increases aqueous solubility of Δ(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol. Life Sci 63(26), Pl381–Pl384 (1998)
Kristinsson, J.K., Fridriksdóttir, H., Thorisdóttir, S., Sigurdardóttir, A.M., Stefánsson, E., Loftsson, T.: Dexamethasone-cyclodextrin-polymer co-complexes in aqueous eye drops—aqueous humor pharmacokinetics in humans. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 37(6), 1199–1203 (1996)
Loftsson, T., Frioriksdóttir, H.: The effect of water-soluble polymers on the aqueous solubility and complexing abilities of β-cyclodextrin. Int J Pharm 163(1–2), 115–121 (1998)
Loftsson, T., Jarvinen, T.: Cyclodextrins in ophthalmic drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 36(1), 59–79 (1999)
Mura, P., Faucci, M.T., Bettinetti, G.P.: The influence of polyvinylpyrrolidone on naproxen complexation with hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin. Eur J Pharm Sci 13(2), 187–194 (2001)
Valero, M., Tejedor, J., Rodriguez, L.J.: Encapsulation of nabumetone by means of -drug: (β-cyclodextrin)2: polyvinylpyrrolidone ternary complex formation. J Lumin 126(2), 297–302 (2007)
Jansook, P., Loftsson, T.: CDs as solubilizers: effects of excipients and competing drugs. Int J Pharm 379(1), 32–40 (2009)
Forgo, P., Göndös, G.: A study of β-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes with progesterone and hydrocortisone using rotating frame Overhauser spectroscopy. Monatsh Chem 133, 101–106 (2002)
Loftsson, T., Másson, M., Brewster, M.E.: Self-association of cyclodextrins and cyclodextrin complexes. J. Pharm. Sci. 93(5), 1091–1099 (2004)
Loftsson, T., Magnusdóttir, A., Másson, M., Sigurjonsdóttir, J.F.: Self-association and cyclodextrin solubilization of drugs. J. Pharm. Sci. 91(11), 2307–2316 (2002)
Acknowledgements
The financial support provided by the Eimskip fund and the Icelandic Center For Research (RANNÍS) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jansook, P., Moya-Ortega, M.D. & Loftsson, T. Effect of self-aggregation of γ-cyclodextrin on drug solubilization. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 68, 229–236 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-010-9779-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-010-9779-3