Abstract
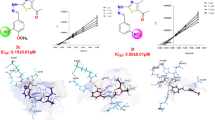
Effect of thiacalix[4]arene platform on inhibition of alkaline phosphatase by macrocyclic phosphonate is presented in this article. Using tetrakis(dihydroxyphosphorylmethyl) derivatives we have found that phosphonate inhibitor on thiacalix[4]arene platform has displayed stronger inhibition properties towards alkaline phosphatases from bovine intestine mucosa, shrimp and human placenta than its structural calix[4]arene analogue. For elucidation of the molecular mechanism of the inhibition the tested macrocyclic compounds were docked computationally to the active site of alkaline phosphatase from shrimp. The role of thiacalix[4]arene platform in formation of the enzyme-inhibitor complex is discussed.
Graphical Abstract
Thiacalix[4]arene as molecular platform for design of alkaline phosphatase inhibitors









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Engel, R.: Phosphonates as analogues of natural phosphates. Chem. Rev. 77, 349–367 (1977)
Hilderbrand, R.L.: The Role of Phosphonates in Living Systems. Boca Raton FL, CRC Press (1983)
Kukhar, V.P., Hudson, H.R. (eds.): Aminophosphonic and aminophosphinic acids: chemistry and biological activity. Wiley, LTD Inc., Chichester, UK (2000)
Rogers, M.J., Gordon, S., Benford, H.L., Coxon, F.P., Luckman, S.P., Monkkonen, J., Frith, J.C.: Cellular and molecular mechanisms of action of bisphosphonates. Cancer 88, 2961–2978 (2000)
Bergstrom, J.D., Bostedor, R.G., Masarachia, P.J., Reszka, A.A., Rodan, G.: Alendronate is a specific, nanomolar inhibitor of farnesyl diphosphate synthase. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 373, 231–241 (2000)
Bukowski, J.F., Dascher, C.C., Das, H.: Alternative bisphosphonate targets and mechanisms of action. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 328, 746–750 (2005)
Vovk, A.I., Kalchenko, V.I., Cherenok, S.A., Kukhar, V.P., Muzychka, O.V., Lozynsky, M.O.: Calix[4]arene methylenebisphosphonic acids as calf intestine alkaline phosphatase inhibitors. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2, 3162–3166 (2004)
Cherenok, S., Vovk, A., Muravyova, I., Shivanyuk, A., Kukhar, V., Lipkowski, J., Kalchenko, V.: Calix[4]arene α-aminophosphonic acids: asymmetric synthesis and enantioselective inhibition of an alkaline phosphatase. Org. Lett. 8, 549–552 (2006)
Le Du, M.H., Millan, J.L.: Structural evidence of functional divergence in human alkaline phosphatases. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 49808–49814 (2002)
Zhang, L., Balcerzak, M., Radisson, J., Thouverey, C., Pikula, S., Azzar, G., Buchet, R.: Phosphodiesterase activity of alkaline phosphatase in ATP-initiated Ca(2 +) and phosphate deposition in isolated chicken matrix vesicles. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 37289–37296 (2005)
Coburn, S.P., Mahuren, J.D., Jain, M., Zubovic, Y., Wortsman, J.: Alkaline phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.1) in serum is inhibited by physiological concentrations of inorganic phosphate. J. Clin. Endocrinology and Metabolism. 83, 3951–3957 (1998)
Mathieu, P., Voisine, P., Pepin, A., Shetty, R., Savard, N., Dagenais, F.: Calcification of human valve interstitial cells is dependent on alkaline phosphatase activity. J. Heart Valve Dis. 14, 353–357 (2005)
Sanchez de Medina, F., Martinez-Augustin, O., Gonzalez, R., Ballester, I., Nieto, A., Galvez, J., Zarzuelo, A.: Induction of alkaline phosphatase in the inflamed intestine: a novel pharmacological target for inflammatory bowel disease. Biochem. Pharmacol. 68, 2317–2326 (2004)
Tung, C.B., Tung, C.F., Yang, D.Y., Hu, W.H., Hung, D.Z., Peng, Y.C., Chang, C.S.: Extremely high levels of alkaline phosphatase in adult patients as a manifestation of bacteremia. Hepatogastroenterology 52, 1347–1350 (2005)
Holtz, K.M., Stec, B., Kantrowitz, E.R.: A model of the transition state in the alkaline phosphatase reaction. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 8351–8354 (1999)
Holtz, K.M., Stec, B., Myers, J.K., Antonelli, S.M., Widlanski, T.S., Kantrowitz, E.R.: Alternate modes of binding in two crystal structures of alkaline phosphatase-inhibitor complexes. Protein Sci. 9, 907–915 (2000)
Llinas, P., Stura, E.A., Menez, A., Kiss, Z., Stigbrand, T., Millan, J.L., Le Du, M.H.: Structural studies of human placental alkaline phosphatase in complex with functional ligands. J. Mol. Biol. 350, 441–451 (2005)
Almi, M., Arduini, A., Casnati, A., Pochini, A., Ungaro, R.: Chloromethylation of calixarenes and synthesis of new water soluble macrocyclic hosts. Tetrahedron 45, 2177–2182 (1989)
Kasyan, O., Swierczynski, D., Drapailo, A., Suwinska, K., Lipkowski, J., Kalchenko, V.: Upper rim substituted thiacalix[4]arenes. Tetrahedron Lett. 44, 7167–7170 (2003)
Dixon, M., Webb, E.C.: Enzymes. Longman, London (1982). (in Russian, Mir, Moscow)
Morris, G.M., Goodsell, D.S., Huey, R., Olson, A.J.: Distributed automated docking of flexible ligands to proteins: parallel applications of AutoDock 2.4. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 10, 293–304 (1996)
Morris, G.M., Goodsel, D.S., Halliday, R.S., Huey, R., Hart, W.E., Belew, R.K., Olson, A.J.: Automated docking using a Lamarckian genetic algorithm and empirical binding free energy function. J. Comput. Chem. 19, 1639–1662 (1998)
de Backer, M.M., McSweeney, S., Lindley, P.F., Hough, E.: Ligand-binding and metal-exchange crystallographic studies on shrimp alkaline phosphatase. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 60, 1555–1561 (2004)
Stote, R.H., Karplus, M.: Zinc binding in proteins and solution: a simple but accurate nonbonded representation. Proteins 23, 12–31 (1995)
Case, D.A., Pearlman, D.A., Caldwell, J.W., et al.: AMBER 7. University of California, San Francisco (2002)
Guex, N., Peitsch, M.C.: SWISS-MODEL and the Swiss-PdbViewer: an environment for comparative protein modeling. Electrophoresis 18, 2714–2723 (1997)
Iki, N., Miyano, S.: Can thiacalixarene surpass calixarene? J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 41, 99–105 (2001)
Grootenhuis, P.D.J., Kollman, P.A., Groenen, L.G., Reinhoudt, D.N., van Hummel, G.J., Ugozzoli, F., Andreetti, G.D.: Computational study of the structural, energetical, and acid-base properties of calix[4]arenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 112, 4165–4176 (1990)
Groenen, L.G., Steinwender, E., Lutz, B.T.G., van der Maas, J.H., Reinhoudt, D.N.: Solvents effects on the conformations and hydrogen bond structure of partially methylated p-tret-butylcalix[4]arenes. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 2, 1893–1898 (1992)
Manes, T., Hoylaerts, M.F., Muller, R., Lottspeich, F., Holke, W., Millan, J.L.: Genetic complexity, structure, and characterization of highly active bovine intestinal alkaline phosphatases. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 23353–23360 (1998)
Hong, J., Ham, S.: Comparative study of calix[4]arene derivatives: implications for ligand design. Tetrahedron Lett. 49, 2393–2396 (2008)
Acknowledgments
The authors greatly appreciate the possibility of using the calculation cluster of the Kyiv National Taras Shevchenko University. This research was supported by the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine (A.I.V., L.A.K., V.P.K., grant 01/03-08). A.B.D. and V·I.K. thank the NASU-RFBR grant for partial support of the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vovk, A.I., Kononets, L.A., Tanchuk, V.Y. et al. Thiacalix[4]arene as molecular platform for design of alkaline phosphatase inhibitors. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 66, 271–277 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-009-9607-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-009-9607-9