Abstract
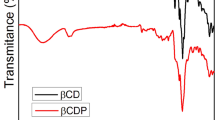
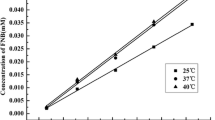
The present work investigates the possibility of improvement of the complexation efficiency of cyclodextrin towards a drug by adding a third auxiliary component (hydrophilic polymer). Phase solubility Analysis at 25 °C was used to investigate the interaction of the drug in both the binary systems (viz. Drug-Cyclodextrin and Drug-Polymer) and the ternary system (Drug-Cyclodextrin-Polymer). The combined use of polymer and cyclodextrin was clearly more effective in enhancing the aqueous solubility of the fenofibrate in comparison with the corresponding drug-cyclodextrin or drug-polymer binary systems. Hydrophilic polymers increased the complexation efficacy of cyclodextrin towards fenofibrate (as shown by the increased stability constants of the complexes). Polyvinyl Pyrollidone (PVP) was found to be most effective in enhancing the solubilization of fenofibrate by β-Cyclodextrin, the best results were obtained in ternary system with β-Cyclodextrin in presence of 1%w/v (PVP). Formulated ternary system with optimized drug:cyclodextrin:polymer ratio of 1:3.5:1 w/w resulted in a significant improvement in the dissolution rate of fenofibrate and showed 90% dissolution efficiency (D.E) as compared to around 15% and 83% of the plain drug and binary system respectively. DSC studies was carried out to characterize the ternary complex.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Loftsson, M. Masson, F. Sigurjonsdottir: In J.J. Torres and J.L. Vila-Jato (eds.), Proceedings of the Ninth International Symposium on Cyclodextrins, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Santiagode Compostela, Spain, 1998, p. 257
Loftsson T., Brewster M., J. Pharm. Sci. 85, 1017 (1996)
Devalina L., Wang W., Eric S., Yihong Q., Steven K., James F., J. Pharm. Sci. 92, 505 (2003)
Sheu M.-T., Yeh C.-M., Sokoloski T.D., Int. J. Pharm. 103, 137 (1994)
Palmeiri G.F., Antonini I., Martelli S., STP Pharm Sci. 6, 188 (1996)
Higuchi T., Connors K.A., Adv. Anal. Chem. Instr. 4, 117 (1965)
Acarturk F., Kislal O., Celebi N., Int. J. Pharm. 85, 1 (1992)
Loftsson T., Fridriksdottir F., Gudmundsdottir T.K., Int. J. Pharm. 127, 293 (1996)
Rekharshy M.Y., Inoue Y., Chem. Rev. 98, 1875, (1998)
Acknowledgement
We would like to thank University Grant Commission (UGC) for providing financial assistance. We are also thankful to Department of Science and Technology (DST) and Indian Pharmaceutical Association (IPA) for extending support through travel grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patel, A., Vavia, P. Effect of Hydrophilic Polymer on Solubilization of Fenofibrate by Cyclodextrin Complexation. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 56, 247–251 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-006-9091-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-006-9091-4