Abstract
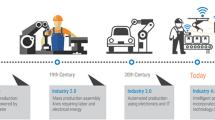
Traditional job shop scheduling is concentrated on centralized scheduling or semi-distributed scheduling. Under the Industry 4.0, the scheduling should deal with a smart and distributed manufacturing system supported by novel and emerging manufacturing technologies such as mass customization, Cyber-Physics Systems, Digital Twin, and SMAC (Social, Mobile, Analytics, Cloud). The scheduling research needs to shift its focus to smart distributed scheduling modeling and optimization. In order to transferring traditional scheduling into smart distributed scheduling (SDS), we aim to answer two questions: (1) what traditional scheduling methods and techniques can be combined and reused in SDS and (2) what are new methods and techniques required for SDS. In this paper, we first review existing researches from over 120 papers and answer the first question and then we explore a future research direction in SDS and discuss the new techniques for developing future new JSP scheduling models and constructing a framework on solving the JSP problem under Industry 4.0.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarts, E. H. L., & Lenstra, J. K. (Eds.). (1997). Local search in combinatorial optimization. London: Wiley.
Adams, J., Balas, E., & Zawack, D. (1988). The shifting bottleneck procedure for job shop scheduling. Management Science, 34(3), 391–401.
Adibi, M. A., Zandieh, M., & Amiri, M. (2010). Multi-objective scheduling of dynamic job shop using variable neighborhood search. Expert Systems with Applications, 37(1), 282–287.
Akyol, D. E., & Bayhan, G. M. (2007). A review on evolution of production scheduling with neural networks. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 53(1), 95–122.
Apt, K. (2003). Principles of constraint programming. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Balas, E., & Vazacopoulos, A. (1998). Guided local search with shifting bottleneck for job shop scheduling. Management Science, 44(2), 262–275.
Barker, J. R., & McMahon, G. B. (1985). Scheduling the general job-shop. Management Science, 31(5), 594–598.
Barták, R., Salido, M. A., & Rossi, F. (2010). Constraint satisfaction techniques in planning and scheduling. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 21(1), 5–15.
Baykasoğlu, A., Hamzadayi, A., & Köse, S. Y. (2014). Testing the performance of teaching-learning based optimization (TLBO) algorithm on combinatorial problems: Flow shop and job shop scheduling cases. Information Sciences, 276, 204–218.
Blum, C. (2005). Beam-ACO—Hybridizing ant colony optimization with beam search: An application to open shop scheduling. Computers & Operations Research, 32(6), 1565–1591.
Blum, C., & Sampels, M. (2004). An ant colony optimization algorithm for shop scheduling problems. Journal of Mathematical Modelling and Algorithms, 3(3), 285–308.
Brooks, G. H., & White, C. R. (1965). An algorithm for finding optimal or near optimal solutions to production scheduling problem. Journal of Industrial Engineering, 16(1), 34–40. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/284046228.
Bullnheimer, B., Hartl, R. F., & Strauss, C. (1999). An improved ant system algorithm for the vehicle routing problem. Annals of Operations Research, 89, 319–328.
Çaliş, B., & Bulkan, S. (2015). A research survey: Review of AI solution strategies of job shop scheduling problem. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 26(5), 961–973.
Canbolat, Y. B., & Gundogar, E. (2004). Fuzzy priority rule for job shop scheduling. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 15(4), 527–533.
Chen, Y. Y., Fu, L. C., & Chen, Y. C. (1998). Multi-agent based dynamic scheduling for a flexible assembly system. In Proceedings, 1998 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (Vol. 3, pp. 2122–2127). IEEE. doi:10.1109/ROBOT.1998.680634.
Chen, J. C., Wu, C. C., Chen, C. W., et al. (2012). Flexible job shop scheduling with parallel machines using genetic algorithm and grouping genetic algorithm. Expert Systems with Applications, 39(11), 10016–10021.
Cheng, R., Gen, M., & Tsujimura, Y. (1999). A tutorial survey of job-shop scheduling problems using genetic algorithms. Part II: Hybrid genetic search strategies. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 36(2), 343–364.
Chong, C. S., Sivakumar, A. I., Low, M. Y. H., et al. (2006). A bee colony optimization algorithm to job shop scheduling. In Proceedings of the 38th conference on winter simulation. Winter simulation conference (pp. 1954–1961). http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1218469.
Colorni, A., Dorigo, M., & Maniezzo, V. (1991). Distributed optimization by ant colonies. In Proceedings of the first European conference on artificial life (Vol. 142, pp. 134–142). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/216300484.
Dauzere-Peres, S., & Lasserre, J. B. (1993). A modified shifting bottleneck procedure for job-shop scheduling. The International Journal of Production Research, 31(4), 923–932.
Davis, L. (1985). Job shop scheduling with genetic algorithms. In Proceedings of an international conference on genetic algorithms and their applications (p. 140). Carnegie-Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA.
Dorigo, M. (1992). Optimization, learning and natural algorithms. Ph.D. thesis, Politecnico di Milano, Italy.
Falkenauer, E., & Bouffouixm, S. (1991). A genetic algorithm for job shop. In IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, Proceedings, 1991 (pp. 824–829). IEEE. doi:10.1109/ROBOT.1991.131689.
Fausett, L. (1994). Fundamentals of neural networks: Architectures, algorithms, and applications. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall.
Floudas, C. A., & Lin, X. (2004). Continuous-time versus discrete-time approaches for scheduling of chemical processes: A review. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 28(11), 2109–2129.
Floudas, C. A., & Lin, X. (2005). Mixed integer linear programming in process scheduling: Modeling, algorithms, and applications. Annals of Operations Research, 139(1), 131–162.
Fnaiech, N., Hammami, H., Yahyaoui, A., et al. (2012). New Hopfield neural network for joint job shop scheduling of production and maintenance. In IECON 2012-38th Annual Conference on IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (pp. 5535–5541). IEEE. doi:10.1109/IECON.2012.6389511.
Fonseca, D. J., & Navaresse, D. (2002). Artificial neural networks for job shop simulation. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 16(4), 241–246.
French, S. (1982). Sequencing and scheduling: An introduction to the mathematics of the job-shop. New York: Ellis Horwood.
Garey, M. R., Johnson, D. S., & Sethi, R. (1976). The complexity of flowshop and job shops cheduling. Mathematics of Operations Research, 1(2), 117–129.
Gen, M., & Lin, L. (2014). Multiobjective evolutionary algorithm for manufacturing scheduling problems: State-of-the-art survey. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 25(5), 849–866.
Geyik, F., & Cedimoglu, I. H. (2004). The strategies and parameters of tabu search for job-shop scheduling. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 15(4), 439–448.
Glover, F. (1986). Future paths for integer programming and links to artificial intelligence. Computers & Operations Research, 13(5), 533–549.
Glover, F., & Laguna, M. (2013). Tabu search. New York: Springer.
Graves, S. C. (1981). A review of production scheduling. Operations Research, 29(4), 646–675.
Güçdemir, H., & Selim, H. (2017). Customer centric production planning and control in job shops: A simulation optimization approach. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 43, 100–116.
Harmanani, H. M., & Ghosn, S. B. (2016). An efficient method for the open-shop scheduling problem using simulated annealing (chapter). In Information technology: New generations (pp. 1183–1193). Berlin: Springer. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-32467-8_102.
Harrison, R. (2016) Engineering the smart factory. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 1. http://www.cjmenet.com/CN/article/downloadArticleFile.do?attachType=PDF&id=2905.
Hefetz, N., & Adiri, I. (1982). An efficient optimal algorithm for the two-machines unit-time jobshop schedule-length problem. Mathematics of Operations Research, 7(3), 354–360.
Hermann, M., Pentek, T., & Otto, B. (2016). Design principles for Industrie 4.0 scenarios. In 2016 49th Hawaii international conference on system sciences (HICSS) (pp. 3928–3937). IEEE. doi:10.1109/HICSS.2016.488.
Hino, R., & Moriwaki, T. (2002). Decentralized job shop scheduling by recursive propagation method. JSME International Journal Series C Mechanical Systems, Machine Elements and Manufacturing, 45(2), 551–557.
Huang, S., Tian, N., & Ji, Z. (2016). Particle swarm optimization with variable neighborhood search for multi objective flexible job shop scheduling problem. International Journal of Modeling, Simulation, and Scientific Computing.. doi:10.1142/S1793962316500240.
Huang, K. L., & Liao, C. J. (2008). Ant colony optimization combined with taboo search for the job shop scheduling problem. Computers & Operations Research, 35(4), 1030–1046.
Huang, R. H., Yang, C. L., & Cheng, W. C. (2013). Flexible job shop scheduling with due window—A two-pheromone ant colony approach. International Journal of Production Economics, 141(2), 685–697.
Huang, R. H., & Yu, T. H. (2017). An effective ant colony optimization algorithm for multi-objective job-shop scheduling with equal-size lot-splitting. Applied Soft Computing, 57, 642–656.
Ingimundardottir, H., & Runarsson, T. P. (2011). Supervised learning linear priority dispatch rules for job-shop scheduling. In International conference on learning and intelligent optimization (pp. 263–277). Berlin: Springer. http://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007%2F978-3-642-25566-3_20.
Iwamura, K., & Sugimura, N. A. (2010). Study on real-time scheduling for autonomous distributed manufacturing systems. In 2010 IEEE international conference on systems man and cybernetics (SMC) (pp. 1352–1357). IEEE. doi:10.1109/ICSMC.2010.5642451.
Jain, A. S., & Meeran, S. (1998). A state-of-the-art review of job-shop scheduling techniques. http://ftp.bstu.by/ai/To-dom/My_research/Paper-0-again/For-courses/Job-SSP/jain.pdf. Technical report, Department of Applied Physics, Electronic and Mechanical Engineering, University of Dundee, Dundee, Scotland.
Jalilvand-Nejad, A., & Fattahi, P. (2015). A mathematical model and genetic algorithm to cyclic flexible job shop scheduling problem. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 26(6), 1085–1098.
Johnson, S. M. (1954). Optimal two and three stage production schedules with setup times included. Naval Research Logistics Quarterly, 1(1), 61–68. doi:10.1002/nav.3800010110/epdf.
Jones, D. F., Mirrazavi, S. K., & Tamiz, M. (2002). Multi-objective meta-heuristics: An overview of the current state-of-the-art. European Journal of Operational Research, 137(1), 1–9.
Ju, Q. Y. (2007). Planning and scheduling optimization of job-shop in intelligent manufacturing system (pp. 1–97). Doctoral dissertation of Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing, China.
Kagermann, H. (2015). Change through digitization—Value creation in the age of Industry 4.0. Management of permanent change (pp. 23–45). Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden, Wiesbaden. doi:10.1007/978-3-658-05014-6_2.
Kartam, N., & Tongthong, T. (1998). An artificial neural network for resource leveling problems. Ai Edam, 12(3), 273–287.
Karthikeyan, S., Asokan, P., Nickolas, S., et al. (2015). A hybrid discrete firefly algorithm for solving multi-objective flexible job shop scheduling problems. International Journal of Bio-Inspired Computation, 7(6), 386–401.
Kennedy, J., & Eberhart, R. (1995). Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of IEEE international conference on neural network (pp. 1942–1948), Perth. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-30164-8_630.
Khadwilard, A., Chansombat, S., Thepphakorn, T., Chainate, W., & Pongcharoen, P. (2012). Application of firefly algorithm and its parameter setting for job shop scheduling. The Journal of Industrial Technology, 8(1), 49–58. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/225274007.
Kirkpatrick, S., Gelatt, C. D., & Vecchi, M. P. (1983). Optimization by simulated annealing. Science, 220(4598), 671–680. http://www.jstor.org/stable/1690046.
Kuczapski, A. M., Micea, M. V., Maniu, L. A., et al. (2015). Efficient generation of near optimal initial populations to enhance genetic algorithms for job-shop scheduling. Information Technology and Control, 39(1). http://kalbos.ktu.lt/index.php/ITC/article/view/12091/6739.
Li, X., & Gao, L. (2016). An effective hybrid genetic algorithm and tabu search for flexible job shop scheduling problem. International Journal of Production Economics, 174, 93–110.
Lian, L., & Mesghouni, K. (2014). Comparative study of heuristics algorithms in solving flexible job shop scheduling problem with condition based maintenance. Journal of Industrial Engineering and Management, 7(2), 518–531.
Lin, L., Hao, X. C., Gen, M., et al. (2012). Network modeling and evolutionary optimization for scheduling in manufacturing. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 23(6), 2237–2253.
Liu, S. Q., & Kozan, E. (2012). A hybrid shifting bottleneck procedure algorithm for the parallel-machine job-shop scheduling problem. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 63(2), 168–182.
Lomnicki, Z. A. (1965). A “branch-and-bound” algorithm for the exact solution of the three-machine scheduling problem. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 16(1), 89–100.
Łukasik, S., & Żak, S. (2009). Firefly algorithm for continuous constrained optimization tasks. In International conference on computational collective intelligence (pp. 97–106). Berlin: Springer. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-04441-0_8.
Manne, A. S. (1960). On the job-shop scheduling problem. Operations Research, 8(2), 219–223.
Marichelvam, M. K., & Geetha, M. (2016). A hybrid discrete firefly algorithm to solve flow shop scheduling problems to minimise total flow time. International Journal of Bio-Inspired Computation, 8(5), 318–325.
Marichelvam, M. K., Prabaharan, T., & Yang, X. S. (2014). A discrete firefly algorithm for the multi-objective hybrid flowshop scheduling problems. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 18(2), 301–305.
McMahon, G., & Florian, M. (1975). On scheduling with ready times and due dates to minimize maximum lateness. Operations Research, 23(3), 475–482.
Meeran, S., & Morshed, M. S. (2012). A hybrid genetic tabu search algorithm for solving job shop scheduling problems: A case study. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 23(4), 1063–1078.
Merkle, D., Middendorf, M., & Schmeck, H. (2002). Ant colony optimization for resource-constrained project scheduling. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 6(4), 333–346.
Min, H. S., & Yih, Y. (2003). Selection of dispatching rules on multiple dispatching decision points in real-time scheduling of a semiconductor wafer fabrication system. International Journal of Production Research, 41(16), 3921–3941.
Morton, T., & Pentico, D. W. (1993). Heuristic scheduling systems: With applications to production systems and project management. London: Wiley.
Muthiah, A., Rajkumar, A., & Rajkumar, R. (2016). Hybridization of artificial bee colony algorithm with particle swarm optimization algorithm for flexible job shop scheduling. In 2016 international conference on energy efficient technologies for sustainability (ICEETS) (pp. 896–903). IEEE.
Nawaz, M., Enscore, E. E., & Ham, I. (1983). A heuristic algorithm for the m-machine, n-job flow-shop sequencing problem. Omega, 11(1), 91–95.
Neto, R. F. T., & GodinhoFilho, M. (2013). Literature review regarding ant colony optimization applied to scheduling problems: Guidelines for implementation and directions for future research. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 26(1), 150–161.
Nouiri, M., Bekrar, A., Jemai, A., et al. (2015). An effective and distributed particle swarm optimization algorithm for flexible job-shop scheduling problem. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing. doi:10.1007/s10845-015-1039-3.
Nouiri, M., Bekrar, A., Jemai, A., et al. (2017). Two stage particle swarm optimization to solve the flexible job shop predictive scheduling problem considering possible machine breakdowns. Computers & Industrial Engineering. doi:10.1016/j.cie.2017.03.006.
Paul, M., Sridharan, R., & Ramanan, T. R. (2016). A multi-objective decision-making framework using preference selection index for assembly job shop scheduling problem. International Journal of Management Concepts and Philosophy, 9(4), 362–387.
Peng, B., Lü, Z., & Cheng, T. C. E. (2015). A tabu search/path relinking algorithm to solve the job shop scheduling problem. Computers & Operations Research, 53, 154–164.
Pesch, E., & Tetzlaff, U. A. W. (1996). Constraint propagation based scheduling of job shops. INFORMS Journal on Computing, 8(2), 144–157.
Pham, D. T., Ghanbarzadeh, A., Koc, E., Otri, S., Rahim, S., & Zaidi, M. (2005). The bees algorithm. Technical note, Manufacturing Engineering Center, Cardiff University.
Ponsich, A., & Coello, C. A. C. (2013). A hybrid differential evolution—Tabu search algorithm for the solution of job-shop scheduling problems. Applied Soft Computing, 13(1), 462–474.
Ponsich, A., Tapia, M. G. C., & Coello, C. A. C. (2009). Solving permutation problems with differential evolution: An application to the jobshop scheduling problem. In ISDA (pp. 25–30). doi:10.1109/ISDA.2009.49.
Potts, C. N., & Van Wassenhove, L. N. (1985). A branch and bound algorithm for the total weighted tardiness problem. Operations Research, 33(2), 363–377.
Reeves, C. R. (1993). Modern heuristic techniques for combinatorial problems. London: Wiley.
Rosenkrantz, D. J., Stearns, R. E., & Lewis, P. M, I. I. (1977). An analysis of several heuristics for the traveling salesman problem. SIAM Journal on Computing, 6(3), 563–581.
Rossi, F., Van Beek, P., & Walsh, T. (2006). Handbook of constraint programming. Amsterdam: Elsevier. http://www.informatik.uni-ulm.de/pm/fileadmin/pm/home/fruehwirth/Papers/FAI.pdf.
Sadeh, N., & Fox, M. S. (1996). Variable and value ordering heuristics for the job shop scheduling constraint satisfaction problem. Artificial Intelligence, 86(1), 1–41.
Saidi-Mehrabad, M., Dehnavi-Arani, S., Evazabadian, F., et al. (2015). An ant colony algorithm (ACA) for solving the new integrated model of job shop scheduling and conflict-free routing of AGVs. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 86, 2–13.
Sakawa, M., & Kubota, R. (2000). Fuzzy programming for multiobjective job shop scheduling with fuzzy processing time and fuzzy duedate through genetic algorithms. European Journal of Operational Research, 120(2), 393–407.
Sarin, S. C., Ahn, S., & Bishop, A. B. (1988). An improved branching scheme for the branch and bound procedure of scheduling n jobs on m parallel machines to minimize total weighted flowtime. The International Journal of Production Research, 26(7), 1183–1191.
Sayadi, M., Ramezanian, R., & Ghaffari-Nasab, N. (2010). A discrete firefly meta-heuristic with local search for makespan minimization in permutation flow shop scheduling problems. International Journal of Industrial Engineering Computations, 1(1), 1–10.
Shivasankaran, N., Kumar, P. S., & Raja, K. V. (2015). Hybrid sorting immune simulated annealing algorithm for flexible job shop scheduling. International Journal of Computational Intelligence Systems, 8(3), 455–466.
Simon, F. Y. P., & Takefuji, Y. (1988). Stochastic neural networks for solving job-shop scheduling. I. Problem representation. In IEEE international conference on neural networks (pp. 275–282). IEEE. doi:10.1109/ICNN.1988.23939.
Singh, M. R., & Mahapatra, S. S. (2016). A quantum behaved particle swarm optimization for flexible job shop scheduling. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 93, 36–44.
Sotskov, Y. N., Tautenhahn, T., & Werner, F. (1999). On the application of insertion techniques for job shop problems with setup times. RAIRO-Operations Research, 33(2), 209–245.
Storn, R., & Price, K. (1995). Differential evolution—A simple and efficient adaptive scheme for global optimization over continuous spaces. Berkeley: ICSI.
Teekeng, W., Thammano, A., Unkaw, P., et al. (2016). A new algorithm for flexible job-shop scheduling problem based on particle swarm optimization. Artificial Life and Robotics, 21(1), 18–23.
Van Dyke Parunak, H., Irish, B. W., Kindrick, J., & Lozo, P. W. (1985). Fractal actors for distributed manufacturing control. In Second conference on artificial intelligence applications: The engineering of knowledge-based systems (pp. 653–660). Miami Beach, FL, USA.
Van Eck, M. (2003). Advanced planning and scheduling—Is logistics everything? Amsterdam: University of Amsterdam. http://www.docin.com/p-1372360378.html.
Wagner, H. M. (1959). An integer linearprogramming model for machine scheduling. Naval Research Logistics Quarterly, 6(2), 131–140.
Wang, L., Cai, J., Li, M., et al. (2017). Flexible job shop scheduling problem using an improved ant colony optimization. Scientific Programming. doi:10.1155/2017/9016303.
Wang, C., & Jiang, P. (2016). Manifold learning based rescheduling decision mechanism for recessive disturbances in RFID-driven job shops. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing. doi:10.1007/s10845-016-1194-1.
Wenqi, H., & Aihua, Y. (2004). An improved shifting bottleneck procedure for the job shop scheduling problem. Computers & Operations Research, 31(12), 2093–2110.
Werner, F., & Winkler, A. (1995). Insertion techniques for the heuristic solution of the job shop problem. Discrete Applied Mathematics, 58(2), 191–211.
Xanthopoulos, A. S., & Koulouriotis, D. E. (2015). Cluster analysis and neural network-based metamodeling of priority rules for dynamic sequencing. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing. doi:10.1007/s10845-015-1090-0.
Xia, W., & Wu, Z. (2005). An effective hybrid optimization approach for multi-objective flexible job-shop scheduling problems. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 48(2), 409–425.
Xing, L. N., Chen, Y. W., Wang, P., et al. (2010). A knowledge-based ant colony optimization for flexible job shop scheduling problems. Applied Soft Computing, 10(3), 888–896.
Xue, H., Zhang, P., & Wei, S. (2015). Applying a hybrid algorithm of immunity and ant colony in job-shop scheduling. In Industrial engineering and manufacturing technology: Proceedings of the 2014 international conference on industrial engineering and manufacturing technology (ICIEMT 2014) (Vol. 4, p. 91), Shanghai, China. CRC Press, 10–11 July 2014.
Yang, X. S. (2008). Nature-inspired metaheuristic algorithms. Bristol: Luniver Press.
Yin, L., Yang, L., & Hu, M. (2015). Job shop scheduling based on improved discrete particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the 21st international conference on industrial engineering and engineering management 2014 (pp. 99–101). Amsterdam: Atlantis Press. doi:10.2991/978-94-6239-102-4_21.
Zahmani, M. H., Atmani, B., Bekrar, A., et al. (2015). Multiple priority dispatching rules for the job shop scheduling problem. In 2015 3rd international conference on control, engineering and information technology (CEIT) (pp. 1–6). IEEE. doi:10.1109/CEIT.2015.7232991.
Zandieh, M., Khatami, A. R., & Rahmati, S. H. A. (2017). Flexible job shop scheduling under condition-based maintenance: Improved version of imperialist competitive algorithm. Applied Soft Computing, 58, 449–464.
Zhang, R., & Chong, R. (2016). Solving the energy-efficient job shop scheduling problem: A multi-objective genetic algorithm with enhanced local search for minimizing the total weighted tardiness and total energy consumption. Journal of Cleaner Production, 112, 3361–3375.
Zhang, W., Wen, J. B., Zhu, Y. C., et al. (2017). Multi-objective scheduling simulation of flexible job-shop based on multi-population genetic algorithm. International Journal of Simulation Modelling (IJSIMM). doi:10.2507/IJSIMM16(2)CO6.
Zhang, H., Yan, Q., Zhang, G., et al. (2016). A chaotic differential evolution algorithm for flexible job shop scheduling. In Asian simulation conference (pp. 79–88). Singapore: Springer.
Zhao, B., Gao, J., Chen, K., et al. (2015). Two-generation Pareto ant colony algorithm for multi-objective job shop scheduling problem with alternative process plans and unrelated parallel machines. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing. doi:10.1007/s10845-015-1091-z.
Zhao, F., Shao, Z., Wang, J., et al. (2016). A hybrid differential evolution and estimation of distribution algorithm based on neighbourhood search for job shop scheduling problems. International Journal of Production Research, 54(4), 1039–1060.
Zorin, D. A., & Kostenko, V. A. (2014). Simulated annealing algorithm for job shop scheduling on reliable real-time systems. In International conference on operations research and enterprise systems (pp. 31–46). Berlin: Springer. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-17509-6_3.
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by the Aircraft Digital Workshop of Large-Scale Complex Structure Parts, Intelligent Manufacturing Special Project of Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of China (2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Ding, G., Zou, Y. et al. Review of job shop scheduling research and its new perspectives under Industry 4.0. J Intell Manuf 30, 1809–1830 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-017-1350-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-017-1350-2