Abstract
Background
Prior studies have suggested that left atrial (LA) volume and frequency of atrial fibrillation (AF) are associated with suboptimal outcomes in patients undergoing catheter ablation of AF. However, the interaction of these factors and their relative impact on outcome are not clear.
Methods
Seventy-nine consecutive patients underwent catheter ablation of persistent AF. LA volume was determined by echocardiography. Electrograms from the LA appendage (LAA), coronary sinus (CS), and lead V1 were obtained before ablation, and the dominant frequency (DF) was determined by fast Fourier transformation. The ablation strategy consisted of pulmonary vein isolation, electrogram-guided, and linear ablation.
Results
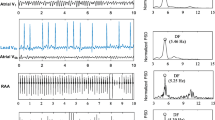
The mean LA volume indexed, LA voltage, and DF in the LAA were 48 ± 16 mL/m2, 0.58 ± 0.20 mV, and 6.3 ± 0.8 Hz, respectively. There was a significant inverse correlation between LA volume and DF in the CS (P < 0.0001, R = −0.51). The mean LA amplitude also correlated with DF in the LAA (P = 0.0008, R = 0.37). In 38 patients (48%), AF terminated during catheter ablation. Sixty-six of the 79 patients (84%) are arrhythmia-free without antiarrhythmic drugs at a mean follow-up of 14±7 months after the last procedure. Advancing age was associated with recurrence (odds ratio (OR), 1.2; 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.02 to 1.42; P = 0.02), and duration of radiofrequency energy delivery was associated with a favorable outcome (OR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.86 to 0.99; P = 0.04).
Conclusion
Atrial enlargement is associated with a lower AF frequency. Age and RF duration seem to be better predictors of outcome than LA volume or AF frequency.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oral, H., Pappone, C., Chugh, A., Good, E., Bogun, F., Pelosi, F., Jr., et al. (2006). Circumferential pulmonary-vein ablation for chronic atrial fibrillation. The New England Journal of Medicine, 354, 934–941.
Oakes, R. S., Badger, T. J., Kholmovski, E. G., Akoum, N., Burgon, N. S., Fish, E. N., et al. (2009). Detection and quantification of left atrial structural remodeling with delayed-enhancement magnetic resonance imaging in patients with atrial fibrillation. Circulation, 119, 1758–1767.
Verma, A., Wazni, O. M., Marrouche, N. F., Martin, D. O., Kilicaslan, F., Minor, S., et al. (2005). Pre-existent left atrial scarring in patients undergoing pulmonary vein antrum isolation: an independent predictor of procedural failure. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 45, 285–292.
Hof, I., Chilukuri, K., Arbab-Zadeh, A., Scherr, D., Dalal, D., Nazarian, S., et al. (2009). Does left atrial volume and pulmonary venous anatomy predict the outcome of catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation? Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 20, 1005–1010.
O'Neill, M. D., Wright, M., Knecht, S., Jais, P., Hocini, M., Takahashi, Y., et al. (2009). Long-term follow-up of persistent atrial fibrillation ablation using termination as a procedural endpoint. European Heart Journal, 30, 1105–1112.
Calkins, H., Brugada, J., Packer, D. L., Cappato, R., Chen, S. A., Crijns, H. J., et al. (2007). HRS/EHRA/ECAS expert Consensus Statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation: recommendations for personnel, policy, procedures and follow-up. A report of the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) Task Force on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm, 4, 816–861.
Lester, S. J., Ryan, E. W., Schiller, N. B., & Foster, E. (1999). Best method in clinical practice and in research studies to determine left atrial size. The American Journal of Cardiology, 84, 829–832.
Gottdiener, J. S., Bednarz, J., Devereux, R., Gardin, J., Klein, A., Manning, W. J., et al. (2004). American Society of Echocardiography recommendations for use of echocardiography in clinical trials. Journal of the American Society of Echocardiography, 17, 1086–1119.
Ruby, R. S., Wells, D., Sankaran, S., Good, E., Jongnarangsin, K., Ebinger, M., et al. (2009). Prevalence of fever in patients undergoing left atrial ablation of atrial fibrillation guided by barium esophagraphy. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 20, 883–887.
Nademanee, K., McKenzie, J., Kosar, E., Schwab, M., Sunsaneewitayakul, B., Vasavakul, T., et al. (2004). A new approach for catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: mapping of the electrophysiologic substrate. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 43, 2044–2053.
Oral, H., Chugh, A., Yoshida, K., Sarrazin, J. F., Kuhne, M., Crawford, T., et al. (2009). A randomized assessment of the incremental role of ablation of complex fractionated atrial electrograms after antral pulmonary vein isolation for long-lasting persistent atrial fibrillation. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 53, 782–789.
Haissaguerre, M., Sanders, P., Hocini, M., Takahashi, Y., Rotter, M., Sacher, F., et al. (2005). Catheter ablation of long-lasting persistent atrial fibrillation: critical structures for termination. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 16, 1125–1137.
Hocini, M., Jais, P., Sanders, P., Takahashi, Y., Rotter, M., Rostock, T., et al. (2005). Techniques, evaluation, and consequences of linear block at the left atrial roof in paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: a prospective randomized study. Circulation, 112, 3688–3696.
Jais, P., Hocini, M., Hsu, L. F., Sanders, P., Scavee, C., Weerasooriya, R., et al. (2004). Technique and results of linear ablation at the mitral isthmus. Circulation, 110, 2996–3002.
Chae, S., Oral, H., Good, E., Dey, S., Wimmer, A., Crawford, T., et al. (2007). Atrial tachycardia after circumferential pulmonary vein ablation of atrial fibrillation: mechanistic insights, results of catheter ablation, and risk factors for recurrence. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 50, 1781–1787.
Lemola, K., Ting, M., Gupta, P., Anker, J. N., Chugh, A., Good, E., et al. (2006). Effects of two different catheter ablation techniques on spectral characteristics of atrial fibrillation. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 48, 340–348.
Ng, J., Kadish, A. H., & Goldberger, J. J. (2006). Effect of electrogram characteristics on the relationship of dominant frequency to atrial activation rate in atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm, 3, 1295–1305.
Matsuo, S., Lellouche, N., Wright, M., Bevilacqua, M., Knecht, S., Nault, I., et al. (2009). Clinical predictors of termination and clinical outcome of catheter ablation for persistent atrial fibrillation. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 54, 788–795.
Yoshida, K., Chugh, A., Good, E., Crawford, T., Myles, J., Veerareddy, S., et al. (2010). A critical decrease in dominant frequency and clinical outcome after catheter ablation of persistent atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm, 7, 295–302.
Stiles, M. K., John, B., Wong, C. X., Kuklik, P., Brooks, A. G., Lau, D. H., et al. (2009). Paroxysmal lone atrial fibrillation is associated with an abnormal atrial substrate: characterizing the "second factor". Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 53, 1182–1191.
Tanaka, K., Zlochiver, S., Vikstrom, K. L., Yamazaki, M., Moreno, J., Klos, M., et al. (2007). Spatial distribution of fibrosis governs fibrillation wave dynamics in the posterior left atrium during heart failure. Circulation Research, 101, 839–847.
Swartz, M. F., Fink, G. W., Lutz, C. J., Taffet, S. M., Berenfeld, O., Vikstrom, K. L., et al. (2009). Left versus right atrial difference in dominant frequency, K(+) channel transcripts, and fibrosis in patients developing atrial fibrillation after cardiac surgery. Heart Rhythm, 6, 1415–1422.
Roberts-Thomson, K. C., Kistler, P. M., Sanders, P., Morton, J. B., Haqqani, H. M., Stevenson, I., et al. (2009). Fractionated atrial electrograms during sinus rhythm: relationship to age, voltage, and conduction velocity. Heart Rhythm, 6, 587–591.
Kojodjojo, P., Kanagaratnam, P., Markides, V., Davies, D. W., & Peters, N. (2006). Age-related changes in human left and right atrial conduction. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 17, 120–127.
Kistler, P. M., Sanders, P., Fynn, S. P., Stevenson, I. H., Spence, S. J., Vohra, J. K., et al. (2004). Electrophysiologic and electroanatomic changes in the human atrium associated with age. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 44, 109–116.
Anyukhovsky, E. P., Sosunov, E. A., Plotnikov, A., Gainullin, R. Z., Jhang, J. S., Marboe, C. C., et al. (2002). Cellular electrophysiologic properties of old canine atria provide a substrate for arrhythmogenesis. Cardiovascular Research, 54, 462–469.
Vaquero, M., Calvo, D., & Jalife, J. (2008). Cardiac fibrillation: from ion channels to rotors in the human heart. Heart Rhythm, 5, 872–879.
Chan, C. P., Wong, W. S., Pumprueg, S., Veerareddy, S., Billakanty, S., Ellis, C., et al. (2010). Inadvertent electrical isolation of the left atrial appendage during catheter ablation of persistent atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm, 7, 173–180.
Kamata, J., Kawazoe, K., Izumoto, H., Kitahara, H., Shiina, Y., Sato, Y., et al. (1997). Predictors of sinus rhythm restoration after Cox maze procedure concomitant with other cardiac operations. The Annals of Thoracic Surgery, 64, 394–398.
Kim, K. B., Rodefeld, M. D., Schuessler, R. B., Cox, J. L., & Boineau, J. P. (1996). Relationship between local atrial fibrillation interval and refractory period in the isolated canine atrium. Circulation, 94, 2961–2967.
Misier, A. R., Opthof, T., van Hemel, N. M., Defauw, J. J., de Bakker, J. M., Janse, M. J., et al. (1992). Increased dispersion of "refractoriness" in patients with idiopathic paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 19, 1531–1535.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their gratitude to Dr. Jose Jalife for his helpful comments.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was supported in part by a grant from the Leducq Transatlantic Network.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshida, K., Rabbani, A.B., Oral, H. et al. Left atrial volume and dominant frequency of atrial fibrillation in patients undergoing catheter ablation of persistent atrial fibrillation. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 32, 155–161 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-011-9590-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-011-9590-0