Abstract
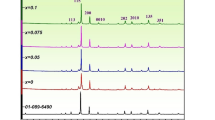
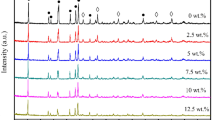
BaTi4O9 and B2O3-doped Ba2Ti9O20 ceramics powders have been prepared by a sol-gel route. The phase evolution, grain size and dielectric properties of the BaTi4O9 and Ba2Ti9O20-based ceramics powders have been investigated. These results show that the BaTi4O9 and 5 wt% B2O3-doped Ba2Ti9O20 ceramics powders calcined at 800∘C for 2 h with the grain sizes of 30–80 and 50–200 nm, respectively. Monophase sample of BaTi4O9 with orthorhombic symmetry could be obtained after the BaTi4O9 precursor was calcined at 1200∘C for 2 h, whereas, monophase sample of 5 wt% B2O3-doped Ba2Ti9O20 was obtained at 800∘C for 2 h. The BaTi4O9 and Ba2Ti9O20: 5 wt% B2O3 ceramics fabricated using the sol-gel powders were found to have microwave dielectric properties with ε r = 36.1, Q = 3220 at 5.31 GHz, and ε r = 34.5, Q = 2425 at 5.53 GHz, respectively. The effect of sintering temperatures on the microwave dielectric properties of the Ba2Ti9O20: 5 wt% B2O3 ceramics was studied.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.D. Richtmyer, J. Appl. Phys., 10, 391 (1939).
H.M. O’Bryan Jr., J. Thomson Jr., and J.K. Plourde, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 57(10), 450 (1974).
J.K. Plourde, D.F. Linn, H.M. O’Bryan Jr., and J. Thomson Jr., J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 58(9/10), 418 (1975).
C.M. Cheng, C.F. Yang, S.H. Lo, and T.Y. Tseng, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 20, 1061 (2000).
H.M. O’Bryan and J. Thomson, J. Am. Cerm. Soc., 66(1), 66 (1983).
J.J. Ritter, R.S. Roth, and J.E. Blendell, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 69(2), 155 (1986).
Y.B. Xu, X.M. Chen, and L.B. Wang, J. Am. Cerm. Soc., 84(3), 669 (2001).
H.C. Lu, L.E. Burkhart, and G.L. Schrader, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 74(5), 968 (1991).
B.W. Hakki and P.D. Coleman, IRE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech., 8, 402 (1960).
S.F. Wang, C.C. Chiang, and C.H. Wang, Mater. Chem. Phys., 79(2), 256 (2003).
S.F. Wang, T.C.K. Yang, C.C. Chiang, and S.H.Y. Tsai, Ceram. Int., 29, 77 (2003).
Y.C. Lee, W.H. Lee, and F.S. Shieu, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 41(10), 6049 (2002).
M. Cernea, E. Chirtop, D. Neacsu, I. Pasuk, and S. Iordanescu, J. Am. Cerm. Soc., 85(2), 499 (2002).
J.H. Choy, Y.S. Han, and S.H. Hwang, J. Am. Cerm. Soc., 81(12), 3197 (1998).
W.Y. Lin, R.F. Speyer, W.S. Hackenberger, and T.R. Shrout, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 82(5), 1207 (1999).
Y.C. Lee, W.H. Lee, and F.S. Shieu, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 42(3), 1311 (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, X.G., Liu, J.Z., Kwok, K.W. et al. Microwave Dielectric Properties of Sol-Gel Derived BaTi4O9 and Ba2Ti9O20:B2O3 Ceramics. J Electroceram 14, 119–122 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-005-0873-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-005-0873-7