Abstract
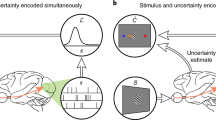
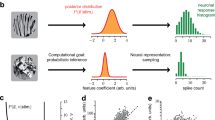
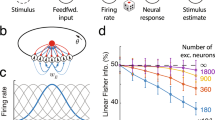
Bayesian models are often successful in describing perception and behavior, but the neural representation of probabilities remains in question. There are several distinct proposals for the neural representation of probabilities, but they have not been directly compared in an example system. Here we consider three models: a non-uniform population code where the stimulus-driven activity and distribution of preferred stimuli in the population represent a likelihood function and a prior, respectively; the sampling hypothesis which proposes that the stimulus-driven activity over time represents a posterior probability and that the spontaneous activity represents a prior; and the class of models which propose that a population of neurons represents a posterior probability in a distributed code. It has been shown that the non-uniform population code model matches the representation of auditory space generated in the owl’s external nucleus of the inferior colliculus (ICx). However, the alternative models have not been tested, nor have the three models been directly compared in any system. Here we tested the three models in the owl’s ICx. We found that spontaneous firing rate and the average stimulus-driven response of these neurons were not consistent with predictions of the sampling hypothesis. We also found that neural activity in ICx under varying levels of sensory noise did not reflect a posterior probability. On the other hand, the responses of ICx neurons were consistent with the non-uniform population code model. We further show that Bayesian inference can be implemented in the non-uniform population code model using one spike per neuron when the population is large and is thus able to support the rapid inference that is necessary for sound localization.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albeck, Y., & Konishi, M. (1995). Responses of neurons in the auditory pathway of the barn owl to partially correlated binaural signals. Journal of Neurophysiology, 74, 1689–1700.
Anderson, C.H., and Van Essen, D.C. (1994). Neurobiological computational systems. Computational Intelligence Imitating Life, 213–222.
Arthur, B. J. (2004). Sensitivity to spectral interaural intensity difference cues in space-specific neurons of the barn owl. Journal of Comparative Physiology A, 190, 91–104.
Bala, A. D. S., Spitzer, M. W., & Takahashi, T. T. (2003). Prediction of auditory spatial acuity from neural images on the owl’s auditory space map. Nature, 424, 771–774.
Barber, M. J., Clark, J. W., & Anderson, C. H. (2003). Neural representation of probabilistic information. Neural Computation, 15, 1843–1864.
Beck, J. M., Ma, W. J., Kiani, R., Hanks, T., Churchland, A. K., Roitman, J., Shadlen, M. N., Latham, P. E., & Pouget, A. (2008). Probabilistic population codes for Bayesian decision making. Neuron, 60, 1142–1152.
Berkes, P., Orbán, G., Lengyel, M., & Fiser, J. (2011). Spontaneous cortical activity reveals hallmarks of an optimal internal model of the environment. Science, 331, 83–87.
Deneve, S. (2008). Bayesian spiking neurons I: inference. Neural Computation, 20, 91–117.
Edut, S., & Eilam, D. (2004). Protean behavior under barn-owl attack: voles alternate between freezing and fleeing and spiny mice flee in alternating patterns. Behavioural Brain Research, 155, 207–216.
Eliasmith, C., & Anderson, C. C. H. (2004). Neural engineering: Computation, representation, and dynamics in neurobiological systems. Cambridge: MIT Press.
Fetsch, C. R., Pouget, A., DeAngelis, G. C., & Angelaki, D. E. (2011). Neural correlates of reliability-based cue weighting during multisensory integration. Nature Neuroscience, 15, 146–154.
Fischer, B. J., & Peña, J. L. (2011). Owl’s behavior and neural representation predicted by Bayesian inference. Nature Neuroscience, 14, 1061–1066.
Fiser, J., Berkes, P., Orbán, G., & Lengyel, M. (2010). Statistically optimal perception and learning: from behavior to neural representations. Trends in Cognitive Science, 14, 119–130.
Foldiak, P. (1993). The “Ideal Homunculus”: statistical inference from neural population responses. In Eeckman, F. & Bower, J. (eds), Computation and Neural Systems (pp. 55–60). Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Ganguli, D., & Simoncelli, E. P. (2014). Efficient sensory encoding and Bayesian inference with heterogeneous neural populations. Neural Comput, 26, 2103–2134.
Girshick, A. R., Landy, M. S., & Simoncelli, E. P. (2011). Cardinal rules: visual orientation perception reflects knowledge of environmental statistics. Nature Neuroscience, 14, 926–932.
Gold, J. I., & Shadlen, M. N. (2000). Representation of a perceptual decision in developing oculomotor commands. Nature, 404, 390–394.
Hausmann, L., von Campenhausen, M., Endler, F., Singheiser, M., & Wagner, H. (2009). Improvements of sound localization abilities by the facial ruff of the barn owl (Tyto alba) as demonstrated by virtual ruff removal. PLoS One, 4, e7721.
Kita, H., & Armstrong, W. (1991). A biotin-containing compound N-(2-aminoethyl)biotinamide for intracellular labeling and neuronal tracing studies: comparison with biocytin. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 37, 141–150.
Knudsen, E. I. (1982). Auditory and visual maps of space in the optic tectum of the owl. Journal of Neuroscience, 2, 1177–1194.
Knudsen, E. I. (1983). Subdivisions of the inferior colliculus in the barn owl (Tyto alba). Journal of Comparative Neurology, 218, 174–186.
Knudsen, E. I., Blasdel, G. G., & Konishi, M. (1979). Sound localization by the barn owl (Tyto alba) measured with the search coil technique. Journal of Comparative Physiology, 133, 1–11.
Konishi, M. (1973). How the owl tracks its prey: experiments with trained barn owls reveal how their acute sense of hearing enables them to catch prey in the dark. American Scientist, 61, 414–424.
Ma, W. J., Beck, J. M., Latham, P. E., & Pouget, A. (2006). Bayesian inference with probabilistic population codes. Nature Neuroscience, 9, 1432–1438.
Ma, W. J., Navalpakkam, V., Beck, J. M., van den Berg, R., & Pouget, A. (2011). Behavior and neural basis of near-optimal visual search. Nature Neuroscience, 14, 783–790.
Peña, J. L., & Konishi, M. (2002). From postsynaptic potentials to spikes in the genesis of auditory spatial receptive fields. Journal of Neuroscience, 22, 5652–5658.
Saberi, K., Takahashi, Y., Konishi, M., Albeck, Y., Arthur, B. J., & Farahbod, H. (1998). Effects of interaural decorrelation on neural and behavioral detection of spatial cues. Neuron, 21, 789–798.
Sahani, M., & Dayan, P. (2003). Doubly distributional population codes: simultaneous representation of uncertainty and multiplicity. Neural Computation, 15, 2255–2279.
Salinas, E. (2011). Prior and prejudice. Nature Neuroscience, 14, 943–945.
Sanger, T. D. (1996). Probability density estimation for the interpretation of neural population codes. Journal of Neurophysiology, 76, 2790–2793.
Shi, L., and Griffiths, T.L. (2009). Neural implementation of hierarchical Bayesian inference by importance sampling. In Advances in neural information processing systems, pp. 1669–1677.
Simoncelli, E.P. (2003). Local analysis of visual motion. Visual Neuroscience, 1616–1623.
Simoncelli, E.P. (2009). Optimal estimation in sensory systems. Cognitive Neuroscience, IV.
Wang, Y., Shanbhag, S. J., Fischer, B. J., & Peña, J. L. (2012). Population-wide bias of surround suppression in auditory spatial receptive fields of the owl’s midbrain. Journal of Neuroscience, 32, 10470–10478.
Weiss, Y., Simoncelli, E. P., & Adelson, E. H. (2002). Motion illusions as optimal percepts. Nature Neuroscience, 5, 598–604.
Acknowledgments
We thank W. Cox for comments on the manuscript. This work was funded by U.S. National Institutes of Health grant DC012949.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Action Editor: B. A. Olshausen
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rich, D., Cazettes, F., Wang, Y. et al. Neural representation of probabilities for Bayesian inference. J Comput Neurosci 38, 315–323 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10827-014-0545-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10827-014-0545-1