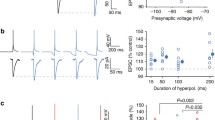
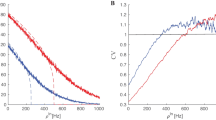
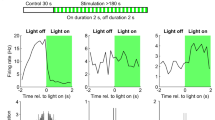
Abstract
Inhibitory interactions play a crucial role in the synchronization of neuronal activity. Here we investigate the effect of GABAergic PSPs on spike timing in cortical neurons that exhibit an oscillatory modulation of their membrane potential. To this end we combined numerical simulations with in-vitro patch-clamp recordings from layer II/III pyramidal cells of the rat visual cortex. Special emphasis was placed on exploring how the reversal potential of the GABAergic synaptic currents (EGABA) and the phase relations of the PSPs relative to the oscillation cycles affect the timing of spikes riding on the depolarizing peaks of the oscillations. The simulations predicted: (1) With EGABA more negative than the oscillation minima PSPs are hyperpolarizing at all phases and thus delay or prevent spikes. (2) With EGABA being more positive than the oscillation maxima PSPs are depolarizing in a phase-independent way and lead to a phase advance of spikes. (3) In the intermediate case where EGABA lies within oscillation maxima and minima PSPs are either hyper- or depolarizing depending on their phase relations to the V m oscillations and can therefore either delay or advance spikes. Experiments conducted in this most interesting last configuration with biphasic PSPs agreed with the model predictions. Additional theoretical investigations revealed the effect of these PSP induced shifts in spike timing on synchronization in neuronal circuits. The results suggest that GABAergic mechanisms can assume highly specific timing functions in oscillatory networks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abeles M (1991) Corticotronics. Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge.
Alonso JM, Usrey WM, Reid RC (1996) Precisely correlated firing in cells of the lateral geniculate nucleus. Nature 383: 815–819.
Artola A, Brocher S, Singer W (1990) Different voltage-dependent thresholds for inducing long-term depression and long-term potentiation in slices of rat visual cortex. Nature 347: 69–72.
Borg-Graham L, Monier C, Fregnac Y (1996) Voltage-clamp measurement of visually-evoked conductances with whole-cell patch recordings in primary visual cortex. J Physiol Paris 90: 185–188.
Brecht M, Singer W, Engel AK (1999) Patterns of synchronization in the superior colliculus of anesthetized cats. J Neurosci 19: 3567–3579.
Buhl EH, Tamas G, Fisahn A (1998) Cholinergic activation and tonic excitation induce persistent gamma oscillations in mouse somatosensory cortex in vitro. J Physiol (Lond) 513(Pt 1): 117–126.
Bush P, Sejnowski T (1996) Inhibition synchronizes sparsely connected cortical neurons within and between columns in realistic network models. J Comput Neurosci 3: 91–110.
Bush PC, Sejnowski TJ (1993) Reduced compartmental models of neocortical pyramidal cells. J Neurosci Methods 46: 159–166.
Chen Z, Ermentrout B, Wang XJ (1998) Wave propagation mediated by GABAB synapse and rebound excitation in an inhibitory network: A reduced model approach. J Comput Neurosci 5: 53–69.
Dallwig R, Deitmer JW, Backus KH (1999) On the mechanism of GABA-induced currents in cultured rat cortical neurons. Pflugers Arch 437: 289–297.
Destexhe A, Mainen ZF, Sejnowski TJ (1994) Synthesis of models for excitable membranes, synaptic transmission and neuromodulation using a common kinetic formalism. J Comput Neurosci 1: 195–230.
Dodt HU, Zieglgansberger W (1990) Visualizing unstained neurons in living brain slices by infrared DIC-videomicroscopy. Brain Res 537: 333–336.
Engel AK, Fries P, Singer W (2001) Dynamic predictions: oscillations and synchrony in top-down processing. Nat Rev Neurosci 2: 704–716.
Ermentrout B, Pascal M, Gutkin B (2001) The effects of spike frequency adaptation and negative feedback on the synchronization of neural oscillators. Neural Comput 13: 1285–1310.
Ermentrout GB (2002) Simulating, Analyzing, and Animating Dynamical Systems: A Guide to Xppaut for Researchers and Students (Software, Environments, Tools). Society for Industrial & Applied Mathematics.
Ermentrout GB, Kopell N (1984) Frequency plateaus in a chain of weakly coupled oscillators. I SIAM J Math Analysis 15: 215–237.
Fries P, Neuenschwander S, Engel AK, Goebel R, Singer W (2001) Rapid feature selective neuronal synchronization through correlated latency shifting. Nat Neurosci 4: 194–200.
Fries P, Reynolds JH, Rorie AE, Desimone R (2001) Modulation of oscillatory neuronal synchronization by selective visual attention. Science 291: 1560–1563.
Gray CM (1999) The temporal correlation hypothesis of visual feature integration: Still alive and well. Neuron 24: 31–25.
Gray CM, McCormick DA (1996) Chattering cells: Superficial pyramidal neurons contributing to the generation of synchronous oscillations in the visual cortex. Science 274: 109–113.
Gulledge AT, Stuart GJ (2003) Excitatory actions of GABA in the cortex. Neuron 37(2): 299–309.
Gupta A, Wang Y, Markram H (2000) Organizing principles for a diversity of GABAergic interneurons and synapses in the neocortex. Science 287: 273–278.
Hansel D, Mato G, Meunier C (1995) Synchrony in excitatory neural networks. Neural Comput 7: 307–337.
Hines ML, Carnevale NT (1997) The NEURON simulation environment. Neural Comput 9: 1179–1209.
Hines ML, Carnevale NT (2000) Expanding NEURON’s repertoire of mechanisms with NMODL. Neural Comput 12: 995–1007.
Huerta PT, Lisman JE (1995) Bidirectional synaptic plasticity induced by a single burst during cholinergic theta oscillation in CA1 in vitro. Neuron 15: 1053–1063.
Jeaong, HY, Gutkin, BS (2005) Study on the role of GABAergic synapses for synchronization, Neurocomputing (in press).
Lampl I, Reichova I, Ferster D (1999) Synchronous membrane potential fluctuations in neurons of the cat visual cortex. Neuron 22: 361–374.
Larkum ME, Zhu JJ, Sakmann B (1999) A new cellular mechanism for coupling inputs arriving at different cortical layers. Nature 398: 338–341.
Magee JC, Johnston D (1997) A synaptically controlled, associative signal for Hebbian plasticity in hippocampal neurons. Science 275: 209–213.
Mainen ZF, Joerges J, Huguenard JR, Sejnowski TJ (1995) A model of spike initiation in neocortical pyramidal neurons. Neuron 15: 1427–1439.
Markram H, Lubke J, Frotscher M, Sakmann B (1997) Regulation of synaptic efficacy by coincidence of postsynaptic APs and EPSPs. Science 275: 213–215.
Marsalek P, Koch C, Maunsell J (1997) On the relationship between synaptic input and spike output jitter in individual neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 735–740.
McCormick D, Contreras D (2001) On the cellular and network bases of epileptic seizures. Annu Rev Physiol 63: 815–846.
Michelson HB, Wong RK (1991) Excitatory synaptic responses mediated by GABAA receptors in the hippocampus. Science 253: 1420–1423.
Murthy VN, Fetz EE (1996) Synchronization of neurons during local field potential oscillations in sensorimotor cortex of awake monkeys. J Neurophysiol 76: 3968–3982.
Nakanishi K, Kukita F (2000) Intracellular [Cl(-)] modulates synchronous electrical activity in rat neocortical neurons in culture by way of GABAergic inputs. Brain Res 863: 192–204.
O’Keefe J (1993) Hippocampus, theta, and spatial memory. Curr Opin Neurobiol 3: 917–924.
Owens, DF, Boyce, LH, Davis, MB, Kriegstein, AR (1996). Excitatory GABA responses in embryonic and neonatal cortical slices demonstrated by gramicidin perforated-patch recordings and calcium imaging. J Neurosci 16(20): 6414–6423.
Penttonen M, Kamondi A, Acsady L, Buzsaki G (1998) Gamma frequency oscillation in the hippocampus of the rat: Intracellular analysis in vivo. Eur J Neurosci 10: 718–728.
Rinzel J, Terman D, Wang X, Ermentrout B (1998) Propagating activity patterns in large-scale inhibitory neuronal networks. Science 279: 1351–1355.
Rivera C, Voipio J, Payne JA, Ruusuvuori E, Lahtinen H, Lamsa K, Pirvola U, Saarma M, Kaila K (1999) The +/Cl- co-transporter KCC2 renders GABA hyperpolarizing during neuronal maturation. Nature 397: 251–255.
Salinas E, Sejnowski TJ (2000) Impact of correlated synaptic input on output firing rate and variability in simple neuronal models [In Process Citation]. J Neurosci 20: 6193–6209.
Shadlen MN, Newsome WT (1998) The variable discharge of cortical neurons: Implications for connectivity, computation, and information coding. J Neurosci 18: 3870–3896.
Sherman SM (2001) Tonic and burst firing: Dual modes of thalamocortical relay. Trends Neurosci 24: 122–126.
Sillito AM, Grieve KL, Jones HE, Cudeiro J, Davis J (1995) Visual cortical mechanisms detecting focal orientation discontinuities. Nature 378: 492–496.
Singer W (1999a) Neuronal synchrony: A versatile code for the definition of relations? Neuron 24: 49–25.
Singer W (1999b) Time as coding space? Curr Opin Neurobiol 9: 189–194.
Staley KJ, Soldo BL, Proctor WR (1995) Ionic mechanisms of neuronal excitation by inhibitory GABAA receptors [see comments]. Science 269: 977–981.
Stevens CF, Zador AM (1998) Input synchrony and the irregular firing of cortical neurons. Nat Neurosci 1: 210–217.
Stuart GJ, Hausser M (2001) Dendritic coincidence detection of EPSPs and action potentials. Nat Neurosci 4: 63–71.
Sun MK, Nelson TJ, Xu H, Alkon DL (1999) Calexcitin transformation of GABAergic synapses: From excitation filter to amplifier. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 7023–7028.
Thomson AM, Destexhe A (1999) Dual intracellular recordings and computational models of slow inhibitory postsynaptic potentials in rat neocortical and hippocampal slices. Neuroscience 92: 1193–1215.
Thomson AM, Deuchars J (1997) Synaptic interactions in neocortical local circuits: Dual intracellular recordings in vitro. Cereb Cortex 7: 510–522.
Traub RD, Wong RK, Miles R, Michelson H (1991) A model of a CA3 hippocampal pyramidal neuron incorporating voltage-clamp data on intrinsic conductances. J Neurophysiol 66: 635–650.
Van Vreeswijk C, Abbott LF, Ermentrout GB (1994) When inhibition not excitation synchronizes neural firing. J Comput Neurosci 1: 313–321.
Volgushev M, Chistiakova M, Singer W (1998) Modification of discharge patterns of neocortical neurons by induced oscillations of the membrane potential. Neuroscience 83: 15–25.
Wespatat V, Tennigkeit F, Singer W (2004) Phase sensitivity of synaptic modifications in oscillating cells of rat visual cortex. J Neurosci 24(41): 9067–9075.
White JA, Chow CC, Ritt J, Soto-Trevino C, Kopell N (1998) Synchronization and oscillatory dynamics in heterogeneous, mutually inhibited neurons. J Comput Neurosci 5: 5–16.
Whittington MA, Traub RD, Kopell N, Ermentrout B, Buhl EH (2000) Inhibition-based rhythms: Experimental and mathematical observations on network dynamics. Int J Psychophysiol 38: 315–336.
Williams TL, Bowtell G (1997) The calculation of frequency-shift functions for chains of coupled oscillators, with application to a network model of the lamprey locomotor pattern generator. J Comput Neurosci 4: 47–55.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Action Editor: Alain Destexhe
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stiefel, K.M., Wespatat, V., Gutkin, B. et al. Phase Dependent Sign Changes of GABAergic Synaptic Input Explored In-Silicio and In-Vitro. J Comput Neurosci 19, 71–85 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10827-005-0188-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10827-005-0188-3