Abstract
Objectives
Bullying victimization increases the risk of displaying internalized and externalized symptoms and alexithymia traits among adolescents. The aim of this study is to examine the mediating role of Alexithymia in the relationships between bullying victimization and internalized and externalized symptoms.
Methods
A total of 1092 students and their teachers (N = 67) of 4th to 6th grade anonymously completed a series of measures about experiences of bullying victimization, internalizing and externalizing symptoms, and alexithymia.
Results
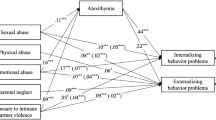
Our data suggest that three types of bullying victimization (verbal, physical and social) predicted internalized, externalized and alexithimic symptoms. Furthermore, alexithymia partially mediated the positive effect of all the three types of bullying victimization on both internalizing and externalizing symptoms.
Conclusions
This study provided empirical data about the mediating role of alexithimia in exacerbation of internalized and externalized symptoms among adolescents and pre-adolescents exposed to three types of bullying victimization.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aricak, O. T., & Ozbay, A. (2016). Investigation of the relationship between cyberbullying, cybervictimization, alexithymia and anger expression styles among adolescents. Computers in Human Behavior, 55, 278–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2015.09.015.
Arseneault, L., Bowes, L., & Shakoor, S. (2010). Bullying victimization in youths and mental health problems: “much ado about nothing”? Psychological Medicine, 40(5), 717–729. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291709991383.
Bagby, R. M., Parker, J. D., & Taylor, G. J. (1994). The twenty-item toronto alexithymia scale–I. Item selection and cross-validation of the factor structure. Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 38(1), 23–32.
Baldry, A. C. (2004). The impact of direct and indirect bullying on the mental and physical health of Italian youngsters. Aggressive Behavior, 30(5), 343–355. https://doi.org/10.1002/ab.20043.
Baldry, A. C., Farrington, D. P., & Sorrentino, A. (2017). School bullying and cyberbullying among boys and girls: roles and overlap. Journal of Aggression Maltreatment & Trauma, 26(9), 937–951. https://doi.org/10.1080/10926771.2017.1330793.
Baldry, A. C., Sorrentino, A., & Farrington, D. P. (2018). Post-traumatic stress symptoms among italian preadolescents involved in school and cyber bullying and victimization. Journal of Child and Family Studies, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-018-1122-4.
Casper, D. M., & Card, N. A. (2017). Overt and relational victimization: a meta-analytic review of their overlap and associations with social–psychological adjustment. Child Development, 88(2), 466–483. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdev.12621.
Di Trani, M., Tomassetti, N., Bonadies, M., Capozzi, F., De Gennaro, L., Presaghi, F., & Solano, L. (2009). Un Questionario Italiano per l’Alessitimia in Età Evolutiva: struttura fattoriale e attendibilità. Psicologia Della Salute, 2, 131–143. https://doi.org/10.3280/PDS2009-002009.
Di Trani, M., Tomassetti, N., Capozzi, F., Solano, L., Romani, M., & Levi, G. (2013). Alessitimia, sintomatologia internalizzante, esternalizzante ed ossesivo-compulsiva in pre-adolescenza: studio empirico su 160 soggetti. Rassegna Di Psicologia, 3, 77–94. https://doi.org/10.7379/75666.
Eastman, M., Foshee, V., Ennett, S., Sotres-Alvarez, D., Reyes, H. L. M., Faris, R., & North, K. (2018). Profiles of internalizing and externalizing symptoms associated with bullying victimization. Journal of Adolescence, 65, 101–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adolescence.2018.03.007.
Gaher, R. M., Arens, A. M., & Shishido, H. (2015). Alexithymia as a mediator between childhood maltreatment and impulsivity. Stress and Health, 31(4), 274–280. https://doi.org/10.1002/smi.2552.
Gilmartin, B. G. (1987). Peer group antecedents of severe love-shyness in males. Journal of Personality, 55(3), 467–489. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-6494.1987.tb00447.x.
Goodman, A., Lamping, D. L., & Ploubidis, G. B. (2010). When to use broader internalising and externalising subscales instead of the hypothesised five subscales on the strengths and difficulties questionnaire (SDQ): data from British parents, teachers and children. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 38(8), 1179–1191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-010-9434-x.
Goodman, R. (1997). The strengths and difficulties questionnaire: a research note. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 38(5), 581–586. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.1997.tb01545.x.
Guzzo, G., Pace, U., Lo Cascio, V., Craparo, G., & Schimmenti, A. (2014). Bullying victimization, post-traumatic symptoms, and the mediating role of alexithymia. Child Indicators Research, 7(1), 141–153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12187-013-9206-6.
Hahn, A. M., Simons, R. M., & Simons, J. S. (2016). Childhood maltreatment and sexual risk taking: the mediating role of alexithymia. Archives of Sexual Behavior, 45(1), 53–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10508-015-0591-4.
Hamilton, L. D., Newman, M. L., Delville, C. L., & Delville, Y. (2008). Physiological stress response of young adults exposed to bullying during adolescence. Physiology & Behavior, 95(5), 617–624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2008.09.001.
Hébert, M., Boisjoli, C., Blais, M., & Oussaïd, E. (2018). Alexithymia as a mediator of the relationship between child sexual abuse and psychological distress in adolescence: a short-term longitudinal study. Psychiatry Research, 260, 468–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2017.12.022.
Honkalampi, K., Tolmunen, T., Hintikka, J., Rissanen, M.-L., Kylmä, J., & Laukkanen, E. (2009). The prevalence of alexithymia and its relationship with youth self-report problem scales among finnish adolescents. Comprehensive Psychiatry, 50(3), 263–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comppsych.2008.08.007.
Longobardi, C., Iotti, N. O., Jungert, T., & Settanni, M. (2018). Student-teacher relationships and bullying: the role of student social status. Journal of Adolescence, 63, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adolescence.2017.12.001.
Longobardi, C., Prino, L. E., Fabris, M. A., & Settanni, M. (2017a). School violence in two Mediterranean countries: Italy and Albania. Children and Youth Services Review, 82, 254–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2017.09.037.
Longobardi, C., Prino, L. E., Fabris, M. A., & Settanni, M. (2017b). Muscle dysmorphia and psychopathology: findings from an Italian sample of male bodybuilders. Psychiatry Research, 256, 231–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2017.06.065.
Longobardi, C., Prino, L. E., Fabris, M. A., & Settanni, M. (2019). Violence in school: an investigation of physical, psychological, and sexual victimization reported by Italian adolescents. Journal of School Violence, 18(1), 49–61. https://doi.org/10.1080/15388220.2017.1387128.
Longobardi, C., Borello, L., Thornberg, R., & Settanni, M. (2019). Empathy and defending behaviours in school bullying: the mediating role of motivation to defend victims. British Journal of Educational Psychology. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjep.12289.
Mannarini, S., Balottin, L., Toldo, I., & Gatta, M. (2016). Alexithymia and psychosocial problems among Italian preadolescents. a latent class analysis approach. Scandinavian Journal of Psychology, 57(5), 473–481. https://doi.org/10.1111/sjop.12300.
Manninen, M., Therman, S., Suvisaari, J., Ebeling, H., Moilanen, I., Huttunen, M., & Joukamaa, M. (2011). Alexithymia is common among adolescents with severe disruptive behavior. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 199(7), 506–509. https://doi.org/10.1097/NMD.0b013e3182214281.
Marengo, D., Jungert, T., Iotti, N. O., Settanni, M., Thornberg, R., & Longobardi, C. (2018). Conflictual student–teacher relationship, emotional and behavioral problems, prosocial behavior, and their associations with bullies, victims, and bullies/victims. Educational Psychology, 38(9), 1201–1217. https://doi.org/10.1080/01443410.2018.1481199.
Marengo, D., Settanni, M., Prino, L. E., Parada, R. H., & Longobardi, C., (2019). Exploring the dimensional structure of bullying victimization among primary and lower-secondary school students: ? Frontiers in Psychology https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00770.
Marsh, H. W., Nagengast, B., Morin, A. J. S., Parada, R. H., Craven, R. G., & Hamilton, L. R. (2011). Construct validity of the multidimensional structure of bullying and victimization: an application of exploratory structural equation modeling. Journal of Educational Psychology, 103(3), 701–732. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0024122.
Modecki, K. L., Minchin, J., Harbaugh, A. G., Guerra, N. G., & Runions, K. C. (2014). Bullying prevalence across contexts: a meta-analysis measuring cyber and traditional bullying. The Journal of Adolescent Health, 55(5), 602–611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2014.06.007.
Nocentini, A., & Menesini, E. (2016). KiVa anti-bullying program in Italy: evidence of effectiveness in a randomized control trial. Prevention Science, 17(8), 1012–1023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-016-0690-z.
Olweus, D. (1994). Bullying at school. In L. R. Huesmann (Ed.), Aggressive behavior: current perspectives (pp. 97–130). New York, NY: Springer.
Olweus, D. (2013). School bullying: development and some important challenges. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 9(1), 751–780. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-050212-185516.
Olweus, D., Limber, S. P., & Breivik, K. (2019). Addressing specific forms of bullying: a large-scale evaluation of the olweus bullying prevention program. International Journal of Bullying Prevention, 1(1), 70–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42380-019-00009-7.
Ortega-Ruiz, R., Del Rey, R., & Casas, J. A. (2016). Evaluar el bullying y el cyberbullying validación española del EBIP-Q y del ECIP-Q. Psicología Educativa, 22(1), 71–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pse.2016.01.004.
Paivio, S. C., & McCulloch, C. R. (2004). Alexithymia as a mediator between childhood trauma and self-injurious behaviors. Child Abuse & Neglect, 28(3), 339–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chiabu.2003.11.018.
Parker, J. D. A., Eastabrook, J. M., Keefer, K. V., & Wood, L. M. (2010). Can alexithymia be assessed in adolescents? Psychometric properties of the 20-item Toronto alexithymia scale in younger, middle, and older adolescents. Psychological Assessment, 22(4), 798–808. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0020256.
Rieffe, C., & De Rooij, M. (2012). The longitudinal relationship between emotion awareness and internalising symptoms during late childhood. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 21(6), 349–356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-012-0267-8.
Rieffe, C., Oosterveld, P., Meerum Terwogt, M., Novin, S., Nasiri, H., & Latifian, M. (2010). Relationship between alexithymia, mood and internalizing symptoms in children and young adolescents: evidence from an Iranian sample. Personality and Individual Differences, 48(4), 425–430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2009.11.010.
Rieffe, C., Oosterveld, P., & Terwogt, M. M. (2006). An alexithymia questionnaire for children: factorial and concurrent validation results. Personality and Individual Differences, 40(1), 123–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2005.05.013.
Schimmenti, A., Passanisi, A., Caretti, V., La Marca, L., Granieri, A., Iacolino, C., & Billieux, J. (2017). Traumatic experiences, alexithymia, and Internet addiction symptoms among late adolescents: a moderated mediation analysis. Addictive Behaviors, 64, 314–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2015.11.002.
Schoeler, T., Duncan, L., Cecil, C. M., Ploubidis, G. B., & Pingault, J.-B. (2018). Quasi-experimental evidence on short- and long-term consequences of bullying victimization: a meta-analysis. Psychological Bulletin, 144(12), 1229–1246. https://doi.org/10.1037/bul0000171.
Shetgiri, R., Lin, H., & Flores, G. (2013). Trends in risk and protective factors for child bullying perpetration in the United States. Child Psychiatry & Human Development, 44(1), 89–104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-012-0312-3.
Sifneos, P. E. (1973). The prevalence of ‘alexithymic’ characteristics in psychosomatic patients. Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics, 22(2–6), 255–262. https://doi.org/10.1159/000286529.
Taylor, G. J. (1984). Alexithymia: concept, measurement, and implications for treatment. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 141(6), 725–732. https://doi.org/10.1176/ajp.141.6.725.
Teten, A. L., Miller, L. A., Bailey, S. D., Dunn, N. J., & Kent, T. A. (2008). Empathic deficits and alexithymia in trauma-related impulsive aggression. Behavioral Sciences & the Law, 26(6), 823–832. https://doi.org/10.1002/bsl.843.
Thomas, R., DiLillo, D., Walsh, K., & Polusny, M. A. (2011). Pathways from child sexual abuse to adult depression: the role of parental socialization of emotions and alexithymia. Psychology of Violence, 1(2), 121–135. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0022469.
Tobia, V., Gabriele, M. A., & Marzocchi, G. M. (2011). Norme italiane dello strengths and difficulties questionnaire (SDQ): il comportamento dei bambini italiani valutato dai loro insegnanti. Disturbi di attenzione e iperattività, 6(2), 167–174.
Velotti, P., Garofalo, C., Petrocchi, C., Cavallo, F., Popolo, R., & Dimaggio, G. (2016). Alexithymia, emotion dysregulation, impulsivity and aggression: a multiple mediation model. Psychiatry Research, 237, 296–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2016.01.025.
Wachs, S., & Wright, M. F. (2018). Bullying and alexithymia: are there differences between traditional, cyber, combined bullies, and nonbullies in reading their own emotions? Criminal Behaviour and Mental Health, 28(5), 409–413. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbm.2083.
Funding
The author(s) received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Author Contributions
L.E.P. and C.L. designed and executed the study, assisted with the data analyses, and wrote the paper. M.S. and R.H.P. analyzed the data and wrote the results, collaborated with the design and writing of the study. M.A.F. collaborated in data collection, and in writing and editing the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prino, L.E., Longobardi, C., Fabris, M.A. et al. Effects of Bullying Victimization on Internalizing and Externalizing Symptoms: The Mediating Role of Alexithymia. J Child Fam Stud 28, 2586–2593 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-019-01484-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-019-01484-8