Abstract
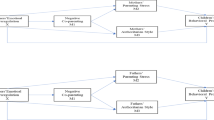
We examined perceived parental styles, emotion socialization practices and emotion dysregulation among fathers from a community sample in order to understand the intergenerational transmission of normative parenting behaviors. The sample consisted of 217 fathers of school-age children ranging in age from 6 to 12 years. We used a cross-sectional design. The fathers completed a set of self-report questionnaires including parental boding instrument, difficulties in emotion regulation scale, and coping with children’s negative emotion scale. The findings indicated that fathers’ perceived parental care of their own parents (G1) was negatively linked to fathers’ (G2) non-supportive responses to negative emotions shown by their children (G3) through its negative association with the father’s (G2) emotion regulation difficulties, whereas fathers’ perceived parental overprotection of their own parents (G1) was positively linked to fathers’ (G2) non-supportive responses to negative emotions shown by their children (G3) through its positive associations with the fathers’ (G2) emotion regulation difficulties. The current study contributed to the further understanding of individual differences in fathers’ emotion socialization practices. The findings potentially shed lights on prevention and intervention efforts regarding limiting the expansion of maladaptive emotional parenting behaviors across generations.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belsky, J. (1984). The determinants of parenting: A process model. Child Development, 1, 83–96.
Belsky, J., Conger, R., & Capaldi, D. M. (2009). The intergenerational transmission of parenting: Introduction to the special section. Developmental Psychology, 45, 1201–1204.
Belsky, J., Jaffee, S. R., Sligo, J., Woodward, L., & Silva, P. A. (2005). Intergenerational transmission of warm-sensitive-stimulating parenting: A prospective study of mothers and fathers of 3-year-olds. Child Development, 76, 384–396.
Bowlby, J. (1969). Attachment. Attachment and loss (Vol. I). London: Hogarth.
Bretherton, I., Lambert, J. D., & Golby, B. (2005). Involved fathers of preschool children as seen by themselves and their wives: Accounts of attachment, socialization, and companionship. Attachment & Human Development, 7, 229–251.
Buckholdt, K. E., Parra, G. R., & Jobe-Shields, L. (2014). Intergenerational transmission of emotion dysregulation through parental invalidation of emotions: Implications for adolescent internalizing and externalizing behaviors. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 23, 324–332.
Cassano, M., Perry-Parrish, C., & Zeman, J. (2007). Influence of gender on parental socialization of children’s sadness regulation. Social Development, 16, 210–231.
Cole, P. M., Hall, S. E., & Hajal, N. J. (2008). Emotion dysregulation as a risk factor for psychopathology. Child and Adolescent Psychopathology, 2, 341–373.
Coplan, R. J., Hastings, P. D., Lagacé-Séguin, D. G., & Moulton, C. E. (2002). Authoritative and authoritarian mothers’ parenting goals, attributions, and emotions across different childrearing contexts. Parenting, 2, 1–26.
Coplan, R. J., Reichel, M., & Rowan, K. (2009). Exploring the associations between maternal personality, child temperament, and parenting: A focus on emotions. Personality and Individual Differences, 46, 241–246.
Darling, N., & Steinberg, L. (1993). Parenting style as context: An integrative model. Psychological Bulletin, 113, 487.
DeBoard-Lucas, R. L., Fosco, G. M., Raynor, S. R., & Grych, J. H. (2010). Interparental conflict in context: Exploring relations between parenting processes and children’s conflict appraisals. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, 39, 163–175.
Denham, S. A., Bassett, H. H., & Wyatt, T. (2007). The socialization of emotional competence. In G. E. Grusec & P. D. Hastings (Eds.), Handbook of socialization: Theory and research, (pp. 614–637). NY: The Guilford Press.
Eisenberg, N., Cumberland, A., & Spinrad, T. L. (1998). Parental socialization of emotion. Psychological Inquiry, 9, 241–273.
Fabes, R. A., Eisenberg, N., & Bernzweig, J. (1990). Coping with children’s negative emotions scale (CCNES): Description and scoring. Tempe, AZ: Arizona State University.
Fletcher, K., Parker, G., Bayes, A., Paterson, A., & McClure, G. (2014). Emotion regulation strategies in bipolar II disorder and borderline personality disorder: Differences and relationships with perceived parental style. Journal of Affective Disorders, 157, 52–59.
Fivush, R., Brotman, M. A., Buckner, J. P., & Goodman, S. H. (2000). Gender differences in parent–child emotion narratives. Sex Roles, 42, 233–253.
Fox, R. (1967). Kinship and marriage: An anthropological perspective (No. 50). NY: Cambridge University Press.
Fox, N. A., & Calkins, S. D. (2003). The development of self-control of emotion: Intrinsic and extrinsic influences. Motivation and Emotion, 27(1), 7–26.
Garside, R. B., & Klimes-Dougan, B. (2002). Socialization of discrete negative emotions: Gender differences and links with psychological distress. Sex Roles, 47, 115–128.
Gau, S. S., Shen, H. Y., Chou, M. C., Tang, C. S., Chiu, Y. N., & Gau, C. S. (2006). Determinants of adherence to methylphenidate and the impact of poor adherence on maternal and family measures. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology, 16, 286–297.
Gere, M. K., Villabø, M. A., Torgersen, S., & Kendall, P. C. (2012). Overprotective parenting and child anxiety: The role of co-occurring child behavior problems. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 26, 642–649.
Gerra, G., Angioni, L., Zaimovic, A., Moi, G., Bussandri, M., Bertacca, S., & Nicoli, M. A. (2004). Substance use among high-school students: Relationships with temperament, personality traits, and parental care perception. Substance Use and Misuse, 39, 345–367.
Gratz, K. L., & Roemer, L. (2004). Multidimensional assessment of emotion regulation and dysregulation: Development, factor structure, and initial validation of the difficulties in emotion regulation scale. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment, 26, 41–54.
Halberstadt, A. G. (1991). Toward an ecology of expressiveness: Family socialization in particular and a model in general. In R. S. Feldman & B. Rime (Eds.), Fundamentals of nonverbal behavior (pp. 106–160). NY: Cambridge University Press.
Halberstadt, A. G., Cassidy, J., Stifter, C. A., Parke, R. D., & Fox, N. A. (1995). Self-expressiveness within the family context: Psychometric support for a new measure. Psychological Assessment, 7, 93.
Hayes, A. F. (2012). PROCESS: A versatile computational tool for observed variable mediation, moderation, and conditional process modeling. Retrieved from http://www.afhayes.com/public/process2012.pdf.
Jaffe, M., Gullone, E., & Hughes, E. K. (2010). The roles of temperamental dispositions and perceived parenting behaviours in the use of two emotion regulation strategies in late childhood. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 31, 47–59.
Kiel, E. J., & Maack, D. J. (2012). Maternal BIS sensitivity, overprotective parenting, and children’s internalizing behaviors. Personality and Individual Differences, 53, 257–262.
Kitamura, T., Shikai, N., Uji, M., Hiramura, H., Tanaka, N., & Shono, M. (2009). Intergenerational transmission of parenting style and personality: Direct influence or mediation? Journal of Child and Family Studies, 18, 541–556.
Klimes-Dougan, B., Brand, A. E., Zahn-Waxler, C., Usher, B., Hastings, P. D., Kendziora, K., & Garside, R. B. (2007). Parental emotion socialization in adolescence: Differences in sex, age and problem status. Social Development, 16, 326–342.
Koszycki, D., Bilodeau, C., Zwanzger, P., Schneider, B. H., Flament, M. F., & Bradwejn, J. (2013). Parental bonds in children at high and low familial risk for panic disorder. Child Psychiatry and Human Development, 44, 278–289.
Kovan, N. M., Chung, A. L., & Sroufe, L. A. (2009). The intergenerational continuity of observed early parenting: A prospective, longitudinal study. Developmental Psychology, 45, 1205.
Lundberg, M., Perris, C., Schlette, P., & Adolfsson, R. (2000). Intergenerational transmission of perceived parenting. Personality and Individual Differences, 28, 865–877.
McDowell, D. J., & Parke, R. D. (2005). Parental control and affect as predictors of children’s display rule use and social competence with peers. Social Development, 14, 440–457.
Morelen, D., Shaffer, A., & Suveg, C. (2014). Maternal emotion regulation: Links to emotion parenting and child emotion regulation. Journal of Family Issues. doi:10.1177/0192513X14546720.
Morris, A. S., Silk, J. S., Steinberg, L., Myers, S. S., & Robinson, L. R. (2007). The role of the family context in the development of emotion regulation. Social Development, 16, 361–388.
Nelson, J. A., O’Brien, M., Blankson, A. N., Calkins, S. D., & Keane, S. P. (2009). Family stress and parental responses to children’s negative emotions: Tests of the spillover, crossover, and compensatory hypotheses. Journal of Family Psychology, 23, 671.
Nishikawa, S., Sundbom, E., & Hägglöf, B. (2010). Influence of perceived parental rearing on adolescent self-concept and internalizing and externalizing problems in Japan. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 19, 57–66.
O’Brien, H. G. (2010). The intergenerational transmission of parenting styles of Irish immigrant mothers. Journal of Family Social Work, 13, 395–409.
Parke, R. D. (1996). Fatherhood. Harvard University Press.
Parker, G. (1983). Parental’affectionless control’as an antecedent to adult depression: A risk factor delineated. Archives of General Psychiatry, 40, 956–960.
Parker, G., Hadzi-Pavlovic, D., Greenwald, S., & Weissman, M. (1995). Low parental care as a risk factor to lifetime depression in a community sample. Journal of Affective Disorders, 33, 173–180.
Parker, G., Tupling, H., & Brown, L. B. (1979). Parental bonding instrument (PBI). British Journal of Medical Psychology, 52, 1–10.
Pears, K. C., & Capaldi, D. M. (2001). Intergenerational transmission of abuse: A two-generational prospective study of an at-risk sample. Child Abuse and Neglect, 25, 1439–1461.
Piotrowski, J. T., Lapierre, M. A., & Linebarger, D. L. (2013). Investigating correlates of self-regulation in early childhood with a representative sample of English-speaking American families. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 22, 423–436.
Preacher, K. J., Rucker, D. D., & Hayes, A. F. (2007). Addressing moderated mediation hypotheses: Theory, methods, and prescriptions. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 42, 185–227.
Ramsden, S. R., & Hubbard, J. A. (2002). Family expressiveness and parental emotion coaching: Their role in children’s emotion regulation and aggression. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 30, 657–667.
Reti, I. M., Samuels, J. F., Eaton, W. W., Bienvenu Iii, O. J., Costa, P. T, Jr, & Nestadt, G. (2002). Adult antisocial personality traits are associated with experiences of low parental care and maternal overprotection. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 106, 126–133.
Rubin, K. H., Burgess, K. B., & Hastings, P. D. (2002). Stability and social–behavioral consequences of toddlers’ inhibited temperament and parenting behaviors. Child Development, 73, 483–495.
Schofield, T. J., Lee, R. D., & Merrick, M. T. (2013). Safe, stable, nurturing relationships as a moderator of intergenerational continuity of child maltreatment: A meta-analysis. Journal of Adolescent Health, 53, S32–S38.
Simons, R. L., Whitbeck, L. B., Conger, R. D., & Wu, C. I. (1991). Intergenerational transmission of harsh parenting. Developmental Psychology, 27, 159.
Suveg, C., Shaffer, A., Morelen, D., & Thomassin, K. (2011). Links between maternal and child psychopathology symptoms: Mediation through child emotion regulation and moderation through maternal behavior. Child Psychiatry & Human Development, 42(5), 507–520.
Tanaka, M., Kitamura, T., Chen, Z., Murakami, M., & Goto, Y. (2009). Do parents rear their children as they were reared themselves? Intergenerational transmission of parental styles (warmth and control) and possible mediation by personality traits. The Open Family Studies Journal, 2, 82–90.
Tao, A., Zhou, Q., & Wang, Y. (2010). Parental reactions to children’s negative emotions: Prospective relations to Chinese children’s psychological adjustment. Journal of Family Psychology, 24, 135.
Thompson, R. A. (1994). Emotion regulation: A theme in search of definition. Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development, 59, 25–52.
Wong, M. S., McElwain, N. L., & Halberstadt, A. G. (2009). Parent, family, and child characteristics: Associations with mother-and father-reported emotion socialization practices. Journal of Family Psychology, 23(4), 452.
Yagmurlu, B., & Altan, O. (2010). Maternal socialization and child temperament as predictors of emotion regulation in Turkish preschoolers. Infant and Child Development, 19(3), 275–296.
Young, B. J., Wallace, D. P., Imig, M., Borgerding, L., Brown-Jacobsen, A. M., & Whiteside, S. P. (2013). Parenting behaviors and childhood anxiety: A psychometric investigation of the EMBU-C. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 22(8), 1138–1146.
Zeman, J., & Shipman, K. (1997). Social-contextual influences on expectancies for managing anger and sadness: The transition from middle childhood to adolescence. Developmental Psychology, 33(6), 917.
Zweig, F. H., & Paris, J. (1991). Parent’s emotional neglect and overprotection according to the recollections of patients with borderline personality disorder. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 148, 648–651.
Acknowledgments
This research received support from the Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars, Beijing Natural Science Foundation (5144028), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (SKZZX2013077).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, J., Han, Z.R. & Li, P. Intergenerational Transmission of Perceived Bonding Styles and Paternal Emotion Socialization: Mediation Through Paternal Emotion Dysregulation. J Child Fam Stud 25, 165–175 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-015-0199-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-015-0199-2