Abstract
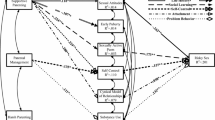
Research has documented social and developmental consequences for youth who experience an early pregnancy. Few studies, however, have examined predictors of teenage pregnancy other than participation in risky sexual behavior. The present study tests a social-contextual model predicting pregnancy among youth. Quality of parenting, affiliation with peers who engage in risky sexual behavior, and school engagement in early adolescence are examined as antecedents of pregnancy among youth. The model is tested using a using a prospective longitudinal design with a sample of 305 high-risk African American females. Results from structural equation modeling generally provide support for the model. Findings suggest that the association between quality of parenting and pregnancy among youth is mediated by affiliation with peers who engage in risky sex and risky sexual behaviors. Implications for education and intervention are discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akers, R. L., & Sellers, C. S. (2012). Social learning theory. In B. Feld & D. Bishop (Eds.), The oxford handbook of juvenile crime and juvenile justice. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Barber, B. K., Stolz, H. E., & Olsen, J. A. (2005). Parental support, psychological control, and behavioral control: Assessing relevance across time, culture, and method. Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development, 70, 1–137.
Baumrind, D. (1991). Effective parenting during the early adolescent transition. In P. A. Cowen & H. Hetherington (Eds.), Family transitions (pp. 111–164). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Bearman, P., & Bruckner, H. (1999). Power in numbers: Peer effects on adolescent girls’ sexual debut and pregnancy. Washington, DC: National Campaign to Prevent Teen Pregnancy.
Benda, B. B., & DiBlasio, F. A. (1991). Comparison of four theories of adolescent sexual exploration. Deviant Behavior, 12, 235–257.
Bonell, C., Allen, E., Strange, V., Copas, A., Oakley, A., Stephenson, J., et al. (2005). The effect of dislike of school on risk of teenage pregnancy: Testing of hypothesis using longitudinal data from a randomized trial of sex education. Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health, 59, 223–230.
Brody, G. H., Conger, R., Gibbons, F. X., Ge, X., McBride Murry, V., Gerrard, M., et al. (2001). The influence of neighborhood disadvantage, collective socialization, and parenting on African American children’s affiliation with deviant peers. Child Development, 72, 1231–1246.
Brody, G. H., Murry, V. M., Gerrard, M., Gibbons, F. X., Molgaard, V., McNair, L., et al. (2004). The Strong African American families program: Translating research into prevention programming. Child Development, 75, 900–917.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2009). YRBSS national youth risk behavior survey: 2005 health risk behaviors by race/ethnicity.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2012). Unintended Pregnancy statistics. US Department of Health and Human Services.
Chase-Landsdale, P. L., & Brooks-Gunn, J. (1994). Correlates of adolescent pregnancy and parenthood. In C. B. Fish & R. M. Lerner (Eds.), Applied developmental psychology (pp. 207–236). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Child Trends. (2009). Estimated percentage of females who will become teen mothers: Differences across states. Washington, DC: Author.
Conger, R. D., Conger, K. J., Elder, G. H., Lorenz, F. O., Simons, R. L., & Whitbeck, L. B. (1992). A family process model of economic hardship and adjustment of early adolescent boys. Child Development, 63, 526–541.
Conger, R. D., Wallace, L. E., Sun, Y., Simons, R. L., McLoyd, V. C., & Brody, G. H. (2002). Economic pressure in African American families: A replication and extension of the family stress model. Developmental Psychology, 38(2), 179.
DiClemente, R. J., Wingood, G. M., Crosby, R. A., et al. (2001). A prospective study of psychological distress and sexual risk behavior among black adolescent females. Pediatrics, 108, 1–6.
Dishion, T. J., & McMahon, R. J. (1998). Parental monitoring and the prevention of child and adolescent problem behavior. Clinical Child and Family Psychology, 1, 61–75.
Dishion, T. J., Capaldi, D., Spracklen, K. M., & Li, F. (1995). The development and ecology of substance use in adolescent boys. Development and Psychopathology, 7, 803–824.
Eaton, D. K., Kann, L., Kinchen, S., et al. (2005). Youth risk behavior surveillance—United States. Journal of School Health, 76, 353–372.
Fergusson, D. M., & Woodward, L. J. (2000). Teenage pregnancy and female educational under-achievement: A prospective study of a New Zealand birth cohort. Journal of Marriage and Family, 62, 147–161.
Fletcher, A. C., & Jefferies, B. C. (1999). Parental mediators of associations between parental authoritative parenting and early adolescent substance use. Journal of Early Adolescence, 19, 465–487.
Hockaday, C., Crase, S. J., Shelley, M. C., & Stockdale, D. F. (2000). A prospective study of adolescent pregnancy. Journal of Adolescence, 23, 423–438.
Hoffman, S. D., & Maynard, R. A. (Eds.). (2008). Kids having kids: Economic costs and social consequences of teen pregnancy (2nd ed.). Washington, DC: Urban Institute Press.
Hogan, D. P., Astone, N. M., & Kitagawa, E. M. (1985). Social and environmental factors influencing contraceptive use among black adolescents. Family Planning Perspectives, 17, 165–169.
Kan, M. L., Cheng, Y. A., Landale, N. S., & McHale, S. M. (2010). Longitudinal predictors of change in number of sexual partners across adolescence and early adulthood. Journal of Adolescent Health, 46, 25–31.
Kenny, D. A., Kashy, D. A., & Cook, W. L. (2006). Dyadic data analysis. New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Kline, R. B. (2011). Principles and practice of structural equation modeling (3rd ed.). New York: The Gilford Press.
Kogan, S. M., Simons, L. G., Chen, Y., Burwell, S., & Brody, G. H. (2013). Protective parenting, relationship power equity, and condom use among rural African American emerging adult women. Family Relations, 62, 341–353.
Landor, A., Simons, L. G., Simons, R. L., Brody, G. H., & Gibbons, F. X. (2011). The influence of religion on adolescent sexual behavior. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 40, 296–309.
Li, X., Stanton, B., & Feigelman, S. (2000). Impact of perceived parental monitoring on adolescent risk behavior over 4 years. Journal of Adolescent Health, 27, 49–56.
Longmore, M. A., Manning, W. D., & Giordano, P. C. (2001). Preadolescent parenting strategies and teen’s dating and sexual initiation: A longitudinal analysis. Journal of Marriage and Family, 63, 322–335.
Luster, T., & Small, S. A. (1994). Factors associated with sexual risk-taking behaviors among adolescents. Journal of Marriage and Family, 56, 622–632.
Maccoby, E. E., & Martin, J. A. (1983). Socialization in the context of the family: Parent–child interaction. In P. H. Mussen (Ed.), Handbook of child psychology (Vol. 4, pp. 1–101). New York: Wiley.
Manlove, J., Terry-Humen, E., Papillo, A. R., Franzetta, K., Williams, S., & Ryan, S. (2002). Preventing teenage pregnancy, childbearing, and sexually transmitted diseases: What the research shows. In Child trends research brief (pp. 1–10).
Martin, J. A., Hamilton, B. E., & Sutton, P. D, et al. (2009). Births: Final data for 2006. National vital statistics reports, 57. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics.
Miller, K. S., Forehand, R., & Kotchick, B. A. (1999). Adolescent sexual behavior in two ethnic minority samples: The role of family variables. Journal of Marriage and the Family, 61, 85–98.
Mollborn, S., & Morningstar, E. (2009). Investigating the relationship between teenage childbearing and psychological distress using longitudinal evidence. Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 50, 310–326.
Muthen, L. K., & Muthen, B. O. (2004). Mplus: The comprehensive modeling program for applied researchers. User’s guide (3rd ed.). Los Angeles: Muthen and Muthen.
O’Connor, M. L. (1999). Academically oriented teenage women have reduced pregnancy risk. Family Planning Perspectives, 31, 105–106.
Pogarsky, G., Thornberry, T. P., & Lizotte, A. J. (2006). Developmental outcomes for children of young mothers. Journal of Marriage and Family, 68, 332–344.
Rainey, D. Y., Stevens-Simon, C., & Kaplan, D. W. (1995). Are adolescents who report prior sexual abuse at higher risk for pregnancy? Child Abuse and Neglect, 19, 1283–1288.
Roberts, M. E., Gibbons, F. X., Gerrard, M., Weng, C. Y., Murry, V. M., Simons, L. G., et al. (2012). From racial discrimination to risky sex: Prospective relations involving peers and parents. Developmental Psychology, 48, 89.
Scaramella, L. V., Conger, R. D., Simons, R. L., & Whitbeck, L. B. (1998). Predicting risk for pregnancy by late adolescence: A social contextual perspective. Developmental Psychology, 34, 1233–1245.
Sieving, R., McNeely, C., & Blum, R. (2000). Maternal expectations, mother–child connectedness, and adolescent sexual debut. Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine, 154, 809–816.
Simons, L. G., & Conger, R. D. (2007). Linking gender differences in parenting to a typology of family parenting styles and adolescent developmental outcomes. Journal of Family Issues, 28, 212–241.
Simons, L. G., Burt, C. H., & Tambling, R. (2012). Identifying mediators for the influence of family factors on risky sexual behavior. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 22, 460–470.
Simons, R. L., Lin, K., Gordon, L. C., Brody, G. H., Murry, V., & Conger, R. D. (2002). Community differences in the association between parenting practices and child conduct problems. Journal of Marriage and Family, 64, 331–345.
Simons, L. G., Su, X., & Simons, R. L. (2013). Consequences of corporal punishment for African Americans: The importance of context and outcome. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 42, 1273–1285.
Smith, C. (2003). Religious participation and network closure among American adolescents. Journal for the Scientific Study of Religion, 42, 259–267.
South, S. J., & Crowder, K. (2009). Neighborhood poverty and nonmarital fertility: Spatial and temporal dimensions. Journal of Marriage and Family, 72, 89–104.
Stanton, B., Li, X., Pack, R., Cottrell, L., Harris, C., & Burns, J. (2002). Longitudinal influence of perceptions of peer and parental factors on African American adolescent risk involvement. Journal of Urban Health, 79, 536–548.
Steinberg, L. (2001). We know some things: Parent-adolescent relationships in retrospect and prospect. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 11, 1–19.
Steinberg, L., Blatt-Eisengart, I., & Cauffman, E. (2006). Patterns of competence and adjustment among adolescents from authoritative, authoritarian, indulgent, and neglectful homes: A replication in a sample of serious juvenile offenders. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 16, 47–58.
The National Campaign to Prevent Teen and Unplanned Pregnancy. (2012). http://www.thenationalcampaign.org/national-data/default.aspx. Accessed Feb 1, 2012.
Wallace, S. A., Miller, K. S., & Forehand, R. (2008). Perceived peer norms and sexual intentions among African American preadolescents. AIDS Education and Prevention, 20, 360–369.
Wickrama, K. A. S., Conger, R. D., Wallace, L. E., & Elder, G. H. (2003). Linking early social risks to impaired physical health during the transition to adulthood. Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 44, 61–74.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoskins, D.H., Simons, L.G. Predicting the Risk of Pregnancy Among African American Youth: Testing a Social Contextual Model. J Child Fam Stud 24, 1163–1174 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-014-9925-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-014-9925-4