Abstract
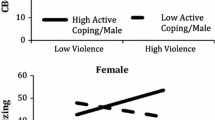
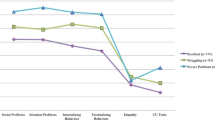
Relations among exposure to violence, coping, and adjustment were examined in three urban samples. In study 1, which took place in a southeastern city, children ages 6–16 (N = 35; M age = 10.7 years) completed measures of adjustment, exposure to violence, and coping with violence. In study 2, which took place in one southern Midwestern city and one Northeastern city, children ages 8–15 (N = 70; M age = 11.3 years) completed similar measures with the addition of a measure assessing normative beliefs about aggression. Results are in line with the pathologic adaptation model and provide preliminary evidence for two hypothesized pathways explaining the effects of exposure to violence on adjustment: a normalization pathway in which exposure leads to more aggression-supporting beliefs and in turn to greater aggression, and a distress pathway in which exposure leads to avoidant coping and in turn to emotional symptoms.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bentler, P. M., & Chou, C. (1987). Practical issues in structural equation modeling. Sociological Methods & Research, 16, 78–117.
Boxer, P., Edwards-Leeper, L., Goldstein, S. E., Musher-Eizenman, D., & Dubow, E. F. (2003). Exposure to “low-level” aggression in school: Associations with aggressive behavior, future expectations, and perceived safety. Violence and Victims, 18, 691–704.
Boxer, P., & Tisak, M. S. (2003). Adolescent attributions about aggression: An initial investigation. Journal of Adolescence, 26, 559–573.
Brandt, R., Ward, C. L., Dawes, A., & Flisher, A. J. (2005). Epidemiological measurement of children’s and adolescents’ exposure to community violence: Working with the state of the science. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 8, 327–342.
Buka, S. L., Stichik, T. L., Birdthistle, I., & Earls, F. J. (2001). Youth exposure to violence: Prevalence, risks, and consequences. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 71, 298–310.
Bureau of Justice Statistics. (2004). Results from the National Crime Victimization Survey, 1973–2003. Downloaded from http://www.ojp.usdoj.gov/bjs/cvict.htm.
Byrne, B. M. (2001). Structural equation modeling with AMOS: Basic concepts, applications, and programming. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Causey, D. L., & Dubow, E. F. (1992). Development of a self-report coping measure for elementary school children. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 21, 47–59.
Cooley-Quille, M. R., Turner, S. M., & Beidel, D. C. (1995). Emotional impact of children’s exposure to community violence: A preliminary study. Journal of American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 34, 1362–1368.
Dempsey, M. (2002). Negative coping as mediator in the relation between violence and outcomes: Inner-city African American youth. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 72, 102–109.
Farrell, A. D., & Bruce, S. E. (1997). Impact of exposure to community violence on violent behavior and emotional distress among urban adolescents. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 26, 2–14.
Fitzpatrick, K. M. (1993). Exposure to violence and presence of depression among low-income, African-American youth. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 61, 528–531.
Folkman, S. (1984). Personal control and stress and coping processes: A theoretical analysis. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 46, 839–852.
Folkman, S., & Lazarus, R. S. (1980). An analysis of coping in a middle-aged community sample. Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 21, 219–239.
Frick, P., & Morris, A. S. (2004). Temperament and developmental pathways to severe conduct problems. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 33, 54–68.
Goodman, R. (2001). Psychometric properties of the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 40, 1337–1345.
Guerra, N. G., Huesmann, L. R., & Spindler, A. (2003). Community violence exposure, social cognition, and aggression among urban elementary school children. Child Development, 74, 1561–1576.
Horn, J. L., & Trickett, P. K. (1997). Community violence and child development: A review of research. In P. K. Trickett & C. J. Schellenbach (Eds.), Violence against children in the family and the community (pp. 103–138). New York: Free Press.
Huesmann, R. L., & Guerra, N. (1997). Children’s normative beliefs about aggression and aggressive behavior. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 72, 408–419.
Kliewer, W., Lepore, S. J., Oskin, D., & Johnson, P. D. (1998). The role of social and cognitive processes in children’s adjustment to community violence. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 66, 199–209.
Kliewer, W., Parrish, K. A., Taylor, K. W., Jackson, K., Walker, J. M., & Shivy, V. A. (2006). Socialization of coping with community violence: Influences of caregiver coaching, modeling, and family context. Child Development, 77, 605–623.
Kuther, T. L., & Wallace, S. A. (2003). Community violence and sociomoral development: An African American cultural perspective. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 73, 177–189.
Marini, Z. A., Dane, A. V., Bosacki, S. L., & YLC-CURA. (2006). Direct and indirect bully-victims: Differential psychosocial risk factors associated with adolescents involved in bullying and victimization. Aggressive Behavior, 32, 551–569.
Musher-Eizenman, D. R., Boxer, P., Danner, S., Dubow, E. F., Goldstein, S. E., & Heretick, D. M. L. (2004). Social-cognitive mediators of the relation of environmental and emotion regulation factors to children’s aggression. Aggressive Behavior, 30, 389–408.
Ng-Mak, D. S., Salzinger, S., Feldman, R. S., & Stueve, A. C. (2002). Normalization of violence among inner-city youth: A formulation of research. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 72, 92–101.
Ng-Mak, D. S., Salzinger, S., Feldman, R. S., & Stueve, A. C. (2004). Pathologic adaptation to community violence among inner-city youth. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 74, 196–208.
Richters, J. E., & Martinez, P. (1993). The NIMH community violence project I: Children as victims and witnesses to violence. Psychiatry, 56, 7–21.
Rosario, M., Salzinger, S., Feldman, R. S., & Ng-Mak, D. S. (2003). Community violence exposure and delinquent behaviors among youth: The moderating role of coping. Journal of Community Psychology, 31, 489–512.
Scarpa, A., & Haden, S. C. (2006). Community violence victimization and aggressive behavior: The moderating effects of coping and social support. Aggressive Behavior, 32, 502–515.
Schwab-Stone, M. E., Ayers, T. S., Kasprow, W., Voyce, C., Barone, C., Shriver, T., & Weissberg, R. P. (1995). No safe haven: A study of violence exposure in an urban community. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 34, 1343–1352.
Schwartz, D., & Proctor, L. J. (2000). Community violence exposure and children’s social adjustment in the school peer group: The mediating roles of emotion regulation and social cognition. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 68, 670–683.
SPSS. (2007). AMOS version 7. Chicago: SPSS, Inc.
Stein, B. D., Jaycox, L. H., Kataoka, S., Rhodes, H. J., & Vestal, K. D. (2003). Prevalence of child and adolescent exposure to community violence. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 6, 247–264.
Tolan, P. H., Gorman-Smith, D., Henry, D., Chung, K., & Hunt, M. (2002). The relation of patterns of coping of inner-city youth to psychopathology symptoms. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 12, 423–449.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boxer, P., Morris, A.S., Terranova, A.M. et al. Coping with Exposure to Violence: Relations to Emotional Symptoms and Aggression in Three Urban Samples. J Child Fam Stud 17, 881–893 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-008-9196-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-008-9196-z