Abstract
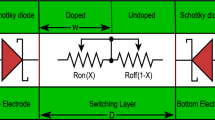
Since real memristor devices are still not commercially available to most researchers, modeling a memristor is an effective method to explore its properties. In this paper, a flux-controlled memristor emulator circuit that can correctly mimic the memristive behavior of a real nanoscale \(\mathrm{TiO}_2\) thin-film memristor device is presented. The mathematical equations for the proposed emulator are explicitly derived, and the design parameters for the circuit in which the emulator works as a passive memristor with positive memductance are discussed. In addition, the proposed emulator can produce various v–i hysteretic behaviors by controlling the nonlinear polynomial cubic function between the flux and charge inside. The results from numerical simulations in PSpice and MATLAB, as well as the measured results from an implemented emulator circuit on a printed circuit board using off-the-shelf electronics components, demonstrate that a controllable emulator can actually be constructed. This study serves as a foundation for understanding and designing different emulators for nanoscale \(\mathrm{TiO}_2\) thin-film memristors at the laboratory level.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chua, L.O.: Memristor: the missing circuit element. IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory CT-18, 507–519 (1971)
Strukov, D.B., Snider, G.S., Stewart, D.R., Williams, R.S.: The missing memristor found. Nature 453, 80–83 (2008)
Shraghian, K., Cho, K., Kavehel, O., Kang, S., Abbott, D., Kang, S.: Memristor MOS content addressable memory (MCAM): hybrid architecture for future high performance. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 19, 1407–1417 (2011)
Ontobel, P., Robinett, W., Kuekes, P., Stewart, D., Straznicky, I., Williams, R.: Writing to and reading from a nano-scale crossbar memory based on memristors. Nanotechnology 20, 425204 (2009)
Pershin, Y., Di Ventra, M.: Practical approach to programmable analog circuits with memristors. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 57, 1857–1864 (2010)
Shin, S., Kim, K., Kang, S.: Memristor applications for programmable analog ICs. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 10, 266–274 (2011)
Xia, Q., Robinett, W., Cumbie, M., Banerjee, N., Cardinali, T., Yang, J., Wu, W., Li, X., Tong, W., Strukov, D., et al.: Memristor CMOS hybrid integrated circuits for recongurable logic. Nano Lett. 9, 3640–3645 (2009)
Shaltoot, A., Madian, A.: A Memristor based carry look ahead adder architectures. IEEE International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), pp. 298–301 (2012)
Zidan, M.A., Omran, H., Radwan, A.G., Salam, K.N.: Memristor-based reactance-less oscillator. Electron. Lett. 47, 1220–1221 (2011)
Fouda, M.E., Khatib, M., Mosad, A., Radwan, A.: Generalized analysis of symmetric and asymmetric Memristive two-gate relaxation oscillators. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 60, 2701–2708 (2013)
Fouda, M., Radwan, A.: Memristor-based voltage controlled relaxation oscillators. Int. J. Circuit Theor. Appl. 42, 1092–1102 (2014)
Buscarino, A., Fortuna, L., Frasca, M., Gambuzza, L.V.: A gallery of chaotic oscillators based on HP memristor. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 23, 1330015 (2013)
Jo, S.H., Chang, T., Ebong, I., Bhadviya, B.B., Mazumder, P., Lu, W.: Nanoscale memristor device as synapse in neuromorphic systems. Nano Lett. 10, 1297–1301 (2010)
McDonald, N.R., Pino, R.E., Rozwood, P.J., Wysocki, B.T.: Analysis of dynamic linear and non-linear mem ristor device models for emerging neuromorphic computing hardware design. International Joint Conference on Neural networks (IJCNN), pp. 1–5 (2010)
Biolek, Z., Biolek, D., Biolkov, V.: SPICE model of memristor with nonlinear dopant drift. Radio Eng. 18, 210–214 (2009)
Benderli, S., Wey, T.A.: On SPICE macromodelling of TiO2 memristors. Electron. Lett. 45, 377–379 (2009)
Pershin, Y.V., Di Ventra, M.: SPICE model of memristive devices with threshold. Radio Eng. 22, 485–489 (2013)
Kvatinsky, S., Friedman, E.G., Kolodny, A., Weiser, U.C.: TEAM: threshold adaptive memristor model. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 60, 211–221 (2013)
Pershin, Y.V., Di Ventra, M.: Teaching memory circuit elements via experiment-based learning. IEEE Circuits Syst. Mag. 12, 64–74 (2012)
Bush, S.: HP nano device implements memristor. Electron. Wkly. (2008). http://www.electronicsweekly.com/news/products/memory/hp-nano-device-implements-memristor-2008-05/
Jo, K.H., Jung, C.M., Min, K.S., Kang, S.M.: Memristor models and circuits for controlling Process-VDD-Temperature variations. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 6, 675–678 (2010)
Mutlu, R., Karakulak, E.: Emulator circuit of TiO\(_2\) memristor with linear dopant drift made using analog multiplier. In: Proceedings of 2010 National Conference on Electrical, Electronic, Computer Engineering (ELECO), pp. 380–384 (2010)
Sodhi, A., Gandhi, G.: Circuit mimicking TiO2 memristor: a plug and play kit to understand the fourth passive element. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 20, 2537–2545 (2010)
Fouda, M.E., Radwan, A.G.: Charge controlled memristor-less memcapacitor emulator. Electron. Lett. 48, 1454–1455 (2012)
Wang, X.Y., Fitch, A.L., Iu, H.H.C., Qi, W.G.: Design of a memcapacitor emulator based on a memristor. Phys. Lett. A. 376, 394–399 (2012)
Wang, X.Y., Fitch, A.L., Iu, H.H.C., Sreeram, V., Qi, W.G.: Implementation of an analogue model of a memristor based on a light dependent resistor. Chin. Phys B. 21, 108501 (2012)
Shin, S.H., Choi, J.M., Cho, S., Min, K.S.: Small-area and compact CMOS emulator circuit for CMOS/nanoscale memristor co-design. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 8, 454 (2013)
Sanchez-Lopez, C., Mendoza-Lopez, J., Carrasco Aguilar, M.A., Muniz-Montero, C.: A oating analog mem ristor emulator circuit. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Br. 61, 309–313 (2014)
Yang, C., Choi, H., Park, S., Sah, M.P., Kim, H., Chua, L.O.: A memristor emulator as a replacement of a real memristor. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 30(19), 015007 (2015)
Muthuswamy, B.: Implementing memristor based chaotic circuits. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 20, 1335–1350 (2010)
Zhong, G.Q.: Implementation of Chuas circuit with a cubic nonlinearity. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Fundam. Theory Appl. 41, 994 (1994)
Chua, L.O., Kang, S.M.: Memristive devices and systems. Proc. IEEE 64, 209–224 (1976)
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Human Resource Training Program for Regional Innovation and Creativity through the Ministry of Education and National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2014H1C1A1066686). This research was also supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (NRF-2015R1D1A1A01057495).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, V.H., Sohn, K.Y. & Song, H. On-printed circuit board emulator with controllability of pinched hysteresis loop for nanoscale \(\mathrm{TiO}_2\) thin-film memristor device. J Comput Electron 15, 993–1002 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-016-0862-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-016-0862-x