Abstract
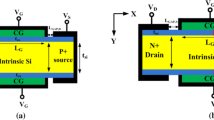
In this paper, we propose a new gate engineered dopingless tunnel field effect transistor (GEDL-TFET). GEDL-TFET has double gate and uses metals of different work functions to realize source and drain regions in undoped silicon; a charge plasma concept. The novelty of the device is the use of dual material top gate and thus two gates appear at the top, main gate 1 and a tunneling gate (TG). The use of TG has enhanced the performance of the device significantly and it acts as a performance booster. The simulation study has shown that the \(\hbox {I}_{\mathrm{ON}}\) and \(\hbox {I}_{\mathrm{ON}}/\hbox {I}_{\mathrm{OFF}}\) ratio in the proposed GEDL-TFET device have increased by \(\sim \)53 times and \(\sim \)68 times in comparison to a double gate doped TFET (D-TFET) and a double gate dopingless TFET (DL-TFET) devices respectively. Further, a significant improvement in average subthreshold slope of \(\sim \)57% has been achieved in the proposed GEDL-TFET device in comparison to the other two devices. Besides, the cutoff frequency \((f_{\mathrm{T}})\) of GEDL-TFET (90.77 GHZ) has increased by \(\sim \)12 times in comparison to D-FET (\(\sim \)7.77 GHZ) and DL-TFET (\(\sim \)7.77 GHZ) devices respectively. The transient analyses have shown that a reduction of 47 and 44.11 % in switching ON-delay and 21.1 and 16.23 % in switching OFF delay is obtained in the GEDL-TFET device based inverting amplifier in comparison to DL-TFET and D-TFET based inverters amplifiers respectively.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dennard, R.H., Gaensslen, F.H., Yu, H.-N., Rideout, V.L., Bassous, E., Leblanc, A.R.: Design of ion-implanted MOSFETs with very small physical dimensions. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits SSC-9(5), 256–268 (1974)
Baccarani, G., Wordeman, M.R., Dennard, R.: Generalized scaling theory and its application to a 1/4 micrometer MOSFET design. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices ED-31(4), 452–462 (1984)
Ellinger, F., Claus, M., Schroeter, M., Carta, C.: Review of advanced and beyond CMOS FET technologies for radio frequency circuit design. In: Proceedings of SBMO/IEEE MTT-S IMOC, pp. 347–351 (2011)
Skotnicki, T.: Heading for decananometer CMOS—Is navigation among icebergs still a viable strategy. In: Proceedings of ESSDERC, Gif-sur-Yvette pp. 19–33 (2000)
Loan, S.A., Qureshi, S., Iyer, S.S.K.: A novel partial ground plane based MOSFET on selective buried oxide: 2D simulation study. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 57, 671–680 (2010)
Nagavarapu, V., Jhaveri, R.: Woo, Jason C.S.: The tunnel source (PNPN) n-MOSFET: a novel high performance transistor. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 4(55), 1013–1019 (2008)
Ionescu, A.M., Riel, H.: Tunnel field effect transistors as energy efficient electronic switches. Nature 479, 329–337 (2011)
Kim, D., et al.: Heterojunction tunneling transistor (HETT)-based extremely low power applications. Proceedings of IEEE/ACM design international symposium on low power electron, New York, pp. 219–224 (2009)
Hisamoto, D., Lee, W.-C., Kedzierski, J., Takeuchi, H., Asano, K., Kuo, C., Anderson, E., King, T.-J., Bokor, J., Hu, C.: FinFET—a self-aligned double-gate MOSFET scalable to 20 nm. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 47(12), 2320–2325 (2000)
Kimura, S., Noda, H., Hisamoto, D., Takeda, E.: A 0.1 \(\mu \)m-gate elevated source and drain MOSFET fabricated by phase-shifted lithography. In: IEDM technical digest, pp. 950–952 (1991)
Mizuno, T., et al.: High velocity electron injection MOSFETs for ballistic transistors using SiGe/strained-Si heterojunction source structures. In: VLSI symposium technology digest, pp. 202–203 (2004)
Nayak, D.K., Woo, J.C.S., Park, J.S., Wang, K., McWilliams, K.P.: Enhancement-mode quantum-well Ge\(x\)SiGe1-\(x\) PMOS. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 12(4), 154–156 (1991)
Kim, Y., et al.: Conventional n-channel MOSFET devices using single layer HfO\(_2\) and ZrO\(_2 as\) high \(k\) gate dielectrics with polysilicon gate electrode. In: IEDM technical digest, pp. 20.2.1-20.2.4 (2001)
Gopalakrishnan, K., Griffin, P.B., Plummer, J. D.: I-MOS: a novel semiconductor device with subthreshold slope lower than \(kT/q\). In: Technical digest—IEEE international electron devices meet, pp. 289–292 (2002)
Salahuddin, S., Datta, S.: Use of negative capacitance to provide voltage amplification for low power nanoscale devices. Nano Lett. 8, 405–410 (2008)
Nathanson, H., Newell, W., Wickstro, R., Davis, J.: Resonant gate transistor. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices ED-14(3), 117–133 (1967)
Rusu, A., Salvatore, G. A., Jimenez, D., Ionescu, A. M.: Metal-ferroelectric-metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistor with sub-60mV/decade subthreshold swing and internal voltage amplification. In: IEEE international electron devices meeting, pp. 16.3.1-16.3.4 (2010)
Abele, N., et al.: Suspended-gate MOSFET: bringing new MEMS functionality into solid-state MOS transistor. Technical digest IEEE international electron devices meeting, pp. 479–481 (2005)
Chen, F., et al.: Integrated circuit design with NEM relays. In: IEEE/ACM international conference on computer-aided design, San Jose, pp. 750–757 (2008)
Quinn, J., Kawamoto, G., McCombe, B.: Subband spectroscopy by surface channel tunneling. Surf. Sci. 73, 190–196 (1978)
Banerjee, S., Richardson, W., Coleman, J., Chatterjee, A.: A new three-terminal tunnel device. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 8, 347–349 (1987)
Takeda, E., Matsuoka, H., Igura, Y., Asai, S.: A band to band tunneling MOS device B2T-MOSFET. In: Technical digest–international electron devices meeting, pp. 402–405 (1988)
Baba, T.: Proposal for surface tunnel transistors. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 31, L455–L457 (1992)
Seabaugh, A.C., Zhang, Q.: Low voltage tunnel transistors for beyond CMOS logic. Proc. IEEE 98, 2095–2110 (2010)
Chiang, M.-H., Lin, J.-N., Kim, K., Chuang, C.-T.: Random dopant fluctuation in limited-width FinFET technologies. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 54(8), 2055–2060 (2007)
Damrongplasit, N., Shin, C., Kim, S.H., Vega, R.A., Liu, T.J.K.: Study of random dopant fluctuation effects in germanium-source tunnel FETs. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 58(10), 3541–3548 (2011)
Damrongplasit, N., Kim, S.H., Liu, T.J.K.: Study of random dopant fluctuation induced variability in the raised-ge-source TFET. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 34(2), 184–186 (2013)
Kumar, M.J., Janardhanan, S.: Doping-less tunnel field effect transistor: design and investigation. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 60(10), 3285–3290 (2013)
Rajasekharan, B., Hueting, R.J.E., Salm, C., et al.: Fabrication and characterization of the charge-plasma diode. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 31(6), 528–530 (2010)
Hueting, R.J.E., Rajasekharan, B., Salm, C., et al.: Charge plasma P-N diode. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 29(12), 1367–1368 (2008)
Kumar, M.J., Nadda, K.: Bipolar charge-plasma transistor: a novel three terminal device. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 59(4), 962–967 (2012)
Loan, S.A., Bashir, F., Rafat, M., Alamoud, A.R., Abbasi, S.A.: A high performance charge plasma based lateral bipolar transistor on selective buried oxide. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 29, 015011 (2014)
Loan, S.A., Bashir, F., Rafat, M., Alamoud, A.R., Abbasi, S.A.: A high performance charge plasma PN-Schottky collector transistor on silicon-on-insulator. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 29, 095001 (2014)
Boucart, K., Ionescu, A.M.: Double gate tunnel FET with high-k gate dielectric. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 54(7), 1725–1733 (2007)
Saurabh, S., Kumar, M.J.: Investigation of the novel attributes of a dual material gate nanoscale tunnel field effect transistor. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 58(2), 404–410 (2011)
Washio, K., et al.: A 0.2 m 180 GHz f 6.7 ps ECL SOI/HRS self-aligned SEG SiGe HBT/CMOS technology for microwave and high speed digital applications. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 49, 271–278 (2002)
ATLAS Device Simulation Software: Silvaco Int., Santa Clara (2012)
Solomon, Paul M., et al.: Universal tunneling behavior in technologically relevant P/N junction diodes. J. Appl. Phys. 95(10), 5800–5812 (2004)
Mallik, A., Chattopadhyay, A.: Impact of a spacer-drain overlap on the characteristics of a silicon tunnel field-effect transistor based on vertical tunneling. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 60, 935–943 (2013)
Asra, R., Murali, K.V.R.M.: Rao, VRamgopal: A binary tunnel field effect transistor with a steep sub-threshold swing and increased ON current. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 49, 120203 (2010)
Mookerjea, S., Krishnan, R., Datta, S., Narayanan, V.: On enhanced Miller capacitance effect in interband tunnel transistors. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 30(10), 1102–1104 (2009)
Knoch, J., Appenzeller, J.: A novel concept for fi eld-effect transistors—the tunneling carbon nanotube FET. In: Proceedings of 63rd DRC 1, 153–156 (2005)
Guillaumot, B., Garros, X., Lime, F., Oshima, K., Tavel, B., Chrob-oczek, J.A., Masson, P., Truche, R., Papon, A.M., Martin, F., Dam-lencourt, J.F., Maitrejean, S., Rivoire, M., Leroux, C., Cristoloveanu, S., Ghibaudo, G., Autran, J.L., Skotnicki, T., Deleonibus, S.: 75 nm damascene metal gate and high-k integration for advanced CMOS devices. In: IEDM technical digest, pp. 355–358 (2002)
Wang, H., Chang, S., Hu, Y., He, H., He, J., Huang, Q., He, F., Wang, G.: A novel barrier controlled tunnel FET. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 35, 798 (2014)
Zhuge, J., Anne, S.: Digital-circuit analysis of short-gate tunnel FETs for low-voltage applications. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 26, 085001 (2011)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NSTIP strategic technologies programs, number (11_NAN-2118-02) in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bashir, F., Loan, S.A., Rafat, M. et al. A high performance gate engineered charge plasma based tunnel field effect transistor. J Comput Electron 14, 477–485 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-015-0665-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-015-0665-5