Abstract
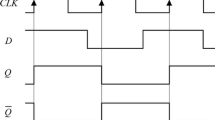
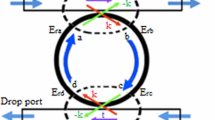
In this paper, a simple but novel scheme for all optical clocked D flip flop based on single micro-ring resonator with a feedback loop is proposed and prescribed. The GaAs-AlGaAs based micro-ring resonator is modulated through optical pump beam. The proposed clocked D flip flop presents two stable states determined by the phase shift in the ring and will allow synchronization of different optical devices by clock pulse (optical control pump beam). Theoretical model of clocked D flip flop has been developed using single micro-ring resonator and numerical simulation results confirming described methods are given in this paper. The design will be helpful in designing all optical integrated circuit.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal, G.P.: Lightwave Technology: Components and Devices. Wiley, New York (2004)
Belotitskii, V.I., Kuzin, E.A., Petrov, M.P., Spirin, V.V.: Demonstration of over 100 million round trips in recirculating fiber loop with all-optical regeneration. Electron. Lett. 29, 49–50 (1993)
Avramopoulos, H., Whitaker, N.A.: Addressable fiber-loop memory. Opt. Lett. 18(1), 22–24 (1993)
Doerr, C.R., W’ong, W.S., Haus, H.A., Ippen, E.P.: Additive-pulse mode-locking/limiting storage ring. Opt. Lett. 19(21), 1747–1749 (1994)
Moores, J.D., et al.: 20-GHz optical storage loop/laser using amplitude modulation, filtering, and artificial fast saturable absorption. IEEE Photonica Tech. Lett. 7(9), 1096–1098 (1995)
Poustie, A.: Semiconductor devices for all-optical signal processing. In: 31st European Conference on Optical Communication 2005 (ECOC 2005), vol. 3, pp. 475–478. IEEE Press, New York (2005)
Nagarajan, R., Kato, M., Dominic, V.G., et al.: Wide temperature (25 °C–85 °C), coolerless operation of 100 Gb/s DWDM transmitter photonic integrated circuit. Electron. Lett. 41, 347 (2005)
Dorren, H.J.S., Hill, M.T., et al.: Optical packet switching and buffering by using all-optical signal processing methods. IEEE J. Lightwave Technol. 21(1), 2–12 (2003)
Hill, M.T., de Waardt, H., Khoe, G.D., et al.: All-optical flip-flop based on coupled laser diodes. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 37(3), 405–413 (2001)
Maity, G.K., Chattopadhyay, T., et al.: All-optical binary flip-flop with the help of terahertz optical asymmetric demultiplexer. Nat. Comput. 9, 903–916 (2010)
Zoiros, K.E., et al.: All-optical pseudorandom binary sequence generator with TOAD-based D flip-flops. Opt. Commun. 284, 4297–4306 (2011)
Chattopadhyay, T.: All-optical clocked delay flip-flop using a single terahertz optical asymmetric demultiplexer-based switch: a theoretical study. Appl. Opt. 49(28), 5226–5235 (2010)
Liu, Y., Hill, M.T., de Waardt, H., et al.: All-optical flip-flop memory based on two coupled polarization switches. IEE Electron. Lett. 38(16), 904–906 (2002)
Chattopadhyay, T., Roy, J.N., Chakraborty, A.K.: Polarization encoded all-optical quaternary R–S flip-flop using binary latch. Opt. Commun. 282(7), 1287–1293 (2009)
Hill, M.T., de Waardt, H., Khoe, G.D., et al.: Fast optical flip-flop by use of Mach-Zehnder interferometers. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 31(6), 411–415 (2001)
Le Minh, H., Ghassemlooy, Z., Pang Ng, W.: All-optical flip flop based on a symmetric Mach-Zehnder switch with a feedback loop and multiple forward set/reset signals. Opt. Eng. 46(4), 040501 (2007)
Clavero, R., Ramos, F., Martí, J.: All-optical flip-flop based on an active Mach–Zehnder interferometer with a feedback loop. Opt. Lett. 30(21), 2861–2863 (2005)
Gayen, D.K., Bhattachryya, A., Chattopadhyay, T., Roy, J.N.: Ultrafast all-optical half adder using quantum-dot semiconductor optical amplifier-based Mach-Zehnder interferometer. J. Lightwave Technol. 30(21), 3387–3393 (2012)
Chattopadhyay, T., Reis, C., André, P., Teixeira, A.: Theoretical analysis of all-optical clocked D flip-flop using a single SOA assisted symmetric MZI. Opt. Commun. 285(9), 2266–2275 (2012)
Clavero, R., Ramos, F., Martinez, J.M., Marti, J.: All-optical flip-flop based on a single SOA-MZI. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 17(4), 843–845 (2005)
Reis, C., Costa, L., Bogoni, A., Maziotis, A., Teixeira, A., Kouloumentas, C., Apostolopoulos, D., Erasme, D., Berrettini, G., Meloni, G., Parca, G., Brahmi, H., Tomkos, I., Poti, L., Bougioukos, M., André, P.S., Zakynthinos, P., Dionisio, R., Chattopadhyay, T., Avramoupoulos, H.: Evolution of all-optical flip-flops and their applications in optical communication networks. IET Optoelectronics 6(6), 263–276 (2012)
Reis, C., Maziotis, A., Kouloumentas, C., Chattopadhyay, T., Calabretta, N., André, P., Berrettini, G., Meloni, G., Bogoni, A., Dorren, H.J.S., Avramopoulos, H., Teixeira, A.: Performance comparison of all-optical clocked S-R and D type flip-flops. Optik 124(16), 2327–2333 (2013)
Bahrampour, A.R., et al.: All-optical set–reset flip–flop based on the passive microring-resonator bistability. Opt. Commun. 281, 5104–5113 (2008)
Luangxaysana, K., et al.: Novel all-optical flip-flop using dark-bright soliton conversion control. Inf. Technol. J. 11(10), 1470–1476 (2012)
Rakshit, J.K., Chattopadhyay, T., Roy, J.N.: All-optical clocked D flip-flop using a single micro-ring resonator. In: International conference on fiber optics and photonics (OSA 2012), WPo.29 (2012)
Reis, C., Maziotis, A., Kouloumentas, C., Stamatiadis, C., Bougioukos, M., Calabretta, N., André, P., Dionisio, R., Neto, B., Dorren, H.J.S., Avramopoulos, H., Teixeira, A.: All-optical clocked d flip-flop memory using a hybrid integrated S-R latch. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 53(6), 1201–1204 (2011)
Liu, L., Kumar, R., Huybrechts, K., Spuesens, T., Roelkens, G., Geluk, E.J., Vries, T.d., Regreny, P., Thourhout, D.V., Baets, R., Morthier, G.: An ultra-small, low-power, all-optical flip-flop memory on a silicon chip. Nat. Photonics 4, 182–187 (2010)
Ibrahim, T.A., Ritter, K., Absil, P.P., Johnson, F.G., Grover, R., Goldhar, J., Ho, P.T.: All optical nonlinear switching in GaAs-AlGaAs microring resonators. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 14(1), 74–76 (2002)
Li, L., Sun, J.: Theoretical investigation of phase-based all-optical logic gates based on AlGaAs microring resonators. J. Mod. Opt. 59(13), 1149–1153 (2012)
Rakshit, J.K., Roy, J.N., Chattopadhyay, T.: Design of micro-ring resonator based all-optical parity generator and checker circuit. Opt. Commun. 303, 30–37 (2013)
Rabus, D.G., Hamacher, M.: MMI-coupled ring resonators in GaInAsP–InP. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 13(8), 812–814 (2001)
Rabus, D.G., Hamacher, M., Heidrich, H.: Resonance frequency tuning of a double ring resonator in GaInAsP/InP: experiment and simulation. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 41, 1186–1189 (2002)
Chunpang, P., Piphithirankarn, P., Yupapin, P.P.: An investigation of quantum–chaotic signals generation using a fiber ring resonator and an add/drop multiplexer. Optik 121, 765–769 (2010)
Rakshit, J.K., Chattopadhyay, T., Roy, J.N.: Design of ring resonator based all optical switch for logic and arithmetic operations—a theoretical study. Optik 124(23), 6048–6057 (2013)
Tofighi, S., et al.: Optical bistability in fiber ring resonator containing an erbium doped fiber amplifier and quantum dot doped fiber saturable absorber. Appl. Opt. 51(29), 7016–7024 (2012)
Okamura, H., Iwatsuki, K.: Er-doped fibre ring resonator applied to optical spectrum analyser with less than 100 kHz resolution. Electron. Lett. 27(12), 1047–1049 (1991)
Ali, J., Yupapin, P.P.: An experimental investigation of multisoliton generation using an erbium-doped fiber amplifier and a fiber optic ring resonator. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 52(1), 70–72 (2010)
Xu, Q., Lipson, M.: All-optical logic based on silicon micro-ring resonators. Opt. Express 15(3), 924–929 (2007)
Thongmeea, S., Yupapin, P.P.: All optical half adder/subtractor using dark-bright soliton conversion control. Proc. Eng. 8, 217–222 (2011)
Phongsanama, P., Teekab, C., Jomtarakc, R., Mitathaa, S., Yupapin, P.P.: All-optical logic AND and OR gates generated by dark–bright soliton conversion. Optik 124(5), 406–410 (2013)
Saeung, P., Yupapin, P.P.: Generalized analysis of multiple ring resonator filters: modeling by using graphical approach. Optik 119, 465–472 (2008)
Zoiros, K.E., Papadopoulos, G., Houbavlis, T., Kanellos, G.T.: Theoretical analysis and performance investigation of ultrafast all-optical Boolean XOR gate with semiconductor optical amplifier-assisted Sagnac interferometer. Opt. Commun. 258(2), 114–134 (2006)
Houbavlis, T., Zoiros, K.E., Kanellos, G., Tsekrekos, C.: Performance analysis of ultrafast all-optical Boolean XOR gate using semiconductor optical amplifier-based Mach–Zehnder interferometer. Opt. Commun. 232(1–6), 179–199 (2004)
Taraphdar, C., Chattopadhyay, T., Roy, J.N.: Mach-Zehnder interferometer based all-optical reversible logic gate. Opt. Laser Technol. 42(2), 249–259 (2010)
Roy, J.N., Rakshit, J.K.: Design of micro-ring resonator-based all-optical logic shifter. Opt. Commun. 312, 73–79 (2014)
Vardakas, J.S., Zoiros, K.E.: Performance investigation of all-optical clock recovery circuit based on Fabry-Pérot filter and SOA-assisted Sagnac switch. Opt. Eng. 46(8), 085005 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rakshit, J.K., Roy, J.N. & Chattopadhyay, T. A theoretical study of all optical clocked D flip flop using single micro-ring resonator. J Comput Electron 13, 278–286 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-013-0519-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-013-0519-y