Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the correlation between the ooplasmic volume and the number of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) copies in embryos and how they may affect fecundity.
Method
Using real-time PCR, mtDNA quantification was analyzed in unfertilized oocytes and uncleaved embryos. The size of the ovum was also assessed by calculating the ooplasmic volume at the time of granulosa cell removal for IVF or ICSI. Quantification analysis of the mtDNA in blastomeres was performed by real-time PCR at the 7–8 cell stage of the cleaved embryos at 72 h after oocyte retrieval. We calculated the cytoplasmic volume of the blastomeres.
Result
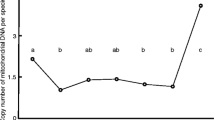
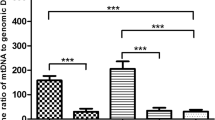
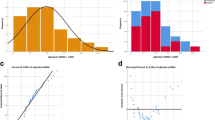
Our studies showed a significantly lower mtDNA copy number in unfertilized oocytes and uncleaved embryos in women who were older than 40 years of age (p < 0.05). The larger ooplasmic volume was also associated with earlier and more rapid cleavage (p < 0.05). The ooplasmic volume was also significantly larger in the group achieving pregnancy. We found a significant positive correlation between blastomere volume and the number of mtDNA copies (r = 0.76, p < 0.01, from Pearson product–moment correlation coefficient).
Conclusions
We have shown that blastomere volume is directly proportional to the number of mtDNA copies. Therefore, larger cytoplasmic volume, with earlier cleavage speed, implies more mtDNA copies. Evaluation of mtDNA quantification and the measurement of ooplasmic and blastomere volume may be useful for selection of high quality embryo and pregnancy outcome.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hill GA, Freeman M, Bastias MC, Rogers BJ, Herbert CM 3rd, Osteen KG, Wentz AC (1989) The influence of oocyte maturity and embryo quality on pregnancy rate in a program for in vitro fertilization–embryo transfer. Fertil Steril 52(5):801–806
Shulman A, Ben Nun I, Ghetler Y, Kaneti H, Shilon M, Beyth Y (1993) Relationship between embryo morphology and implantation rate after in vitro fertilization treatment in conception cycles. Fertil Steril 60(1):123–126
Cohen J, Inge KL, Suzman M, Wiker SR, Wright G (1989) Videocinematography of fresh and cryopreserved embryos: a retrospective analysis of embryonic morphology and implantation. Fertil Steril 51(5):820–827
Pelinck MJ, De Vos M, Dekens M, Van der Elst J, De Sutter P, Dhont M (1998) Embryos cultured in vitro with multinucleated blastomeres have poor implantation potential in human in vitro fertilization and intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Hum Reprod 13(4):960–963
Wilding M, Di Matteo L, D’Andretti S, Montanaro N, Capobianco C, Dale B (2007) An oocyte score for use in assisted reproduction. J Assist Reprod Genet 24(8):350–358
Nagy ZP, Dozortsev D, Diamond M, Rienzi L, Ubaldi F, Abdelmassih R, Greco E (2003) Pronuclear morphology evaluation with subsequentincreases implantation rates. Fertil Steril 80(1):67–74
Muggleton-Harris A, Whittingham DG, Wilson L (1982) Cytoplasmic control of preimplantation development in vitro in the mouse. Nature 299(5882):460–462
Battaglia DE, Goodwin P, Klein NA, Soules MR (1996) Influence of maternal age on meiotic spindle assembly in oocytes from naturally cycling women. Hum Reprod 11(10):2217–2222
Huang CC, Cheng TC, Chan HH, Chang CC, Chen CI, Liu J, Lee MS (1999) Birth after the injection of sperm and the cytoplasm of tripronucleate zygotes into metaphase II oocytes in patients with repeated implantation failure after assisted fertilization procedures. Fertil Steril 72(4):702–706
Cohen J, Scott R, Schimmel T, Levron J, Willadsen S (1997) Birth of infant after transfer of anucleate donor oocyte cytoplasm into recipient eggs. Lancet 350(9072):186–187
Anderson S, Bankier AT, Barrell BG, de Bruijn MH, Coulson AR, Drouin J, Eperon IC, Nierlich DP, Roe BA, Sanger F, Schreier PH, Smith AJ, Staden R, Young IG (1981) Sequence and organization of the human mitochondrial genome. Nature 290(5806):457–465
Kaneda H, Hayashi J, Takahama S, Taya C, Lindahl KF, Yonekawa H (1995) Elimination of paternal mitochondrial DNA in intra specific crosses during early mouse embryogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92(10):4542–4546
Bitner-Glindzicz M (2002) Hereditary deafness and phenotyping in humans. Br Med Bull 63:73–94
Keefe DL, Niven-Fairchild T, Powell S, Buradagunta S (1995) Mitochondrial deoxyribonucleic acid deletions in oocytes and reproductive aging in women. Fertil Steril 64(3):577–583
Jansen RP (2000) Germline passage of mitochondria: quantitative considerations and possible embryological sequelae. Hum Reprod 15(Suppl 2):112–128
Wallace DC, Ye JH, Neckelmann SN, Singh G, Webster KA, Greenberg BD (1987) Sequence analysis of cDNAs for the human and bovine ATP synthase beta subunit: mitochondrial DNA genes sustain seventeen times more mutations. Curr Genet 12(2):81–90
Macmillan C, Lach B, Shoubridge EA (1993) Variable distribution of mutant mitochondrial DNAs (tRNA(Leu[3243])) in tissues of symptomatic relatives with MELAS: the role of mitotic segregation. Neurology 43(8):1586–1590
Schon EA, Bonilla E, DiMauro S (1997) Mitochondrial DNA mutations and pathogenesis. J Bioenerg Biomembr 29(2):131–149
Holt IJ, Harding AE, Morgan-Hughes JA (1988) Deletions of muscle mitochondrial DNA in patients with mitochondrial myopathies. Nature 331(6158):717–719
Holt IJ, Harding AE, Petty RK, Morgan-Hughes JA (1990) A new mitochondrial disease associated with mitochondrial DNA heteroplasmy. Am J Hum Genet 46(3):428–433
Mazat JP, Rossignol R, Malgat M, Rocher C, Faustin B, Letellier T (2001) What do mitochondrial diseases teach us about normal mitochondrial functions…that we already knew: threshold expression of mitochondrial defects. Biochim Biophys Acta 1504(1):20–30
Linnane AW, Marzuki S, Ozawa T, Tanaka M (1989) Mitochondrial DNA mutations as an important contributor to ageing and degenerative diseases. Lancet 1(8639):642–645
Chan CC, Liu VW, Lau EY, Yeung WS, Ng EH, Ho PC (2005) Mitochondrial DNA content and 4977 bp deletion in unfertilized oocytes. Mol Hum Reprod 11(12):843–846
Seifer DB, DeJesus V, Hubbard K (2002) Mitochondrial deletions in luteinized granulosa cells as a function of age in women undergoing in vitro fertilization. Fertil Steril 78(5):1046–1048
Chan CC, Liu VW, Lau EY, Yeung WS, Ng EH, Ho PC (2006) Mitochondrial DNA deletion in granulosa and cumulus oophorus cells. Fertil Steril 85(3):780–782
Sun X, Li Z, Yi Y, Ding W, Chen J, Engelhardt JF, Leno GH (2009) Chromatin configurations in the ferret germinal vesicle that reflect developmental competence for in vitro maturation. Reprod Domest Anim 44(2):320–325
Combelles CM, Cekleniak NA, Racowsky C, Albertini DF (2002) Assessment of nuclear and cytoplasmic maturation in in-vitro matured human oocytes. Hum Reprod 17(4):1006–1016
Raziel A, Schachter M, Strassburger D, Kasterstein E, Ron-El R, Friedler S (2006) In vivo maturation of oocytes by extending the interval between human chorionic gonadotropin administration and oocyte retrieval. Fertil Steril 86(3):583–587
Itskovitz J, Rubattu S, Rosenwaks Z, Liu HC, Sealey JE (1991) Relationship of follicular fluid prorenin to oocyte maturation, steroid levels, and outcome of in vitro fertilization. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 72:165–171
Yamamura Y, Tamano M, Iguchi T, Ohta Y (2001) Metallothionein expression and tumor growth in the transplantable pregnancy-independent mouse mammary tumor. J Vet Med Sci 63(6):687–689
Hofhaus G, Johns DR, Hurko O, Attardi G, Chomyn A (1996) Respiration and growth defects in transmitochondrial cell lines carrying the 11778 mutation associated with Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy. J Biol Chem 271(22):13155–13161
Tajima H, Sueoka K, Moon SY, Nakabayashi A, Sakurai T, Murakoshi Y, Watanabe H, Iwata S, Hashiba T, Kato S, Goto Y, Yoshimura Y (2007) The development of novel quantification assay for mitochondrial DNA heteroplasmy aimed at preimplantation genetic diagnosis of Leigh encephalopathy. J Assist Reprod Genet 24(6):227–232
Fu J, Wang XJ, Wang YW, Sun J, Gemzell-Danielsson K, Sun XX (2009) The influence of early cleavage on embryo developmental potential and IVF/ICSI outcome. J Assist Reprod Genet 26(8):437–441
Bos-Mikich A, Mattos AL, Ferrari AN (2001) Early cleavage of human embryos: an effective method for predicting successful IVF/ICSI outcome. Hum Reprod 16(12):2658–2661
Dunson DB, Colombo B, Baird DD (2002) Changes with age in the level and duration of fertility in the menstrual cycle. Hum Reprod 17(5):1399–1403
Van Blerkom J, Sinclair J, Davis P (1998) Mitochondrial transfer between oocytes: potential applications of mitochondrial donation and the issue of heteroplasmy. Hum Reprod 13(1O):2857–2868
Eichenlaub-Ritter U, Vogt E, Yin H, Gosden R (2004) Spindles, mitochondria and redox potential in ageing oocytes. Reprod Biomed Online 8(1):45–58
Hamatani T, Falco G, Carter MG, Akutsu H, Stagg CA, Sharov AA, Dudekula DB, VanBuren V, Ko M (2004) Age-associated alteration of gene expression patterns in mouse oocytes. Hum Mol Genet 13(19):2263–2278
Thouas GA, Trounson AO, Jones GM (2005) Effect of female age on mouse oocyte developmental competence following mitochondrial injury. Biol Reprod 73(2):366–373
Steuerwald NM, Bermúdez MG, Wells D, Munné S, Cohen J (2007) Maternal age-related differential global expression profiles observed in human oocytes. Reprod Biomed Online 14(6):700–708
Grøndahl ML, Yding Andersen C, Bogstad J, Nielsen FC, Meinertz H, Borup R (2010) Gene expression profiles of single human mature oocytes in relation to age. Hum Reprod 25(4):957–968
Steuerwald N, Barritt JA, Adler R, Malter H, Schimmel T, Cohen J, Brenner CA (2000) Quantification of mtDNA in single oocytes, polar bodies and subcellular components by real-time rapid cycle fluorescence monitored PCR. Zygote 8(3):209–215
Barritt JA, Kokot M, Cohen J, Steuerwald N, Brenner CA (2002) Quantification of human ooplasmic mitochondria. Reprod Biomed 4(3):243–247
Chen X, Prosser R, Simonetti S, Sadlock J, Jagiello G, Schon EA (1995) Rearranged mitochondrial genomes are present in human oocytes. Am J Hum Genet 57(2):239–247
Wai T, Ao A, Zhang X, Cyr D, Dufort D, Shoubridge EA (2010) The role of mitochondrial DNA copy number in mammalian fertility. Biol Reprod 83(1):52–62
Dumollard R, Duchen M, Carroll J (2007) The role of mitochondrial function in the oocyte and embryo. Curr Top Dev Biol 77:21–49
Crozet N, Dahirel M, Gall L (2000) Meiotic competence of in vitro grown goat oocytes. J Reprod Fertil 118(2):367–373
El Shourbagy SH, Spikings EC, Freitas M, St John JC (2006) Mitochondria directly influence fertilisation outcome in the pig. Reproduction 131(2):233–245
Kameyama Y, Ohnishi H, Shimoi G, Hashizume R, Ito M, Smith LC (2010) Asymmetrical allocation of mitochondrial DNA to blastomeres during the first two cleavages in mouse embryos. Reprod Fertil Dev 22(8):1247–1253
Smith LC, Alcivar AA (1993) Cytoplasmic inheritance and its effects on development and performance. J Reprod Fertil Suppl 48:31–43
Van Blerkom J (2000) Intrafollicular influences on human oocyte developmental competence: perifollicular vascularity, oocyte metabolism and mitochondrial function. Hum Reprod 15(Suppl 2):173–188
Nayudu PL, Lopata A, Jones GM, Gook DA, Bourne HM, Sheather SJ, Brown TC, Johnston WI (1989) An analysis of human oocytes and follicles from stimulated cycles: oocyte morphology and associated follicular fluid characteristics. Hum Reprod 4(5):558–567
Acknowledgments
We appreciate our coworkers’ collaboration and advice on the study, especially Ms. Yoko Yasuda, Ms. Mariko Araga, Ms. Yoko Matumoto, and support from the mitochondrial disease working group of Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare in Japan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Capsule In our studies, higher ooplasmic volume was frequently associated with fecundity. And we found a significant positive correlation between blastomere volume and the number of mtDNA copies.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murakoshi, Y., Sueoka, K., Takahashi, K. et al. Embryo developmental capability and pregnancy outcome are related to the mitochondrial DNA copy number and ooplasmic volume. J Assist Reprod Genet 30, 1367–1375 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-013-0062-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-013-0062-6