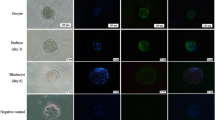
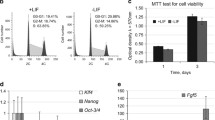
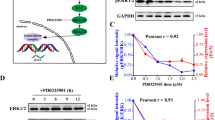
Abstract
Purpose
Stem cell factor (SCF)/c-Kit regulates the proliferation and survival of germ cells or stem cells; however, little is known about the role of SCF/c-Kit in pre-implantation embryo development.
Methods
Using exogenous SCF supplementation and c-Kit siRNA injection, we investigated the role and mechanism of SCF/c-Kit in pre-implantation mouse embryos.
Results
Addition of soluble SCF to the culture medium improved blastocyst formation. c-Kit gene silencing reduced the rate of blastocyst formation and delayed embryonic development. The number of proliferating cells in c-Kit gene-silenced blastocysts decreased, whereas the number of apoptotic cells in blastocysts obtained from both experimental and the control groups was not affected. RT-PCR, immunostaining and western blotting revealed that proliferation-related Akt downstream targets were substantially affected by c-Kit gene silencing.
Conclusion
SCF/c-Kit signaling through Akt downstream targets is likely involved in mediating the cleavage and proliferation of blastomeres during mouse pre-implantation embryogenesis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arceci RJ, Pampfer S, Pollard JW. Expression of CSF-1/c-fms and SF/c-kit mRNA during preimplantation mouse development. Dev Biol. 1992;151:1–8.
Paria BC, Dey SK. Preimplantation embryo development in vitro: cooperative interactions among embryos and role of growth factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1990;87:4756–60.
Rappolee DA, Brenner CA, Schultz R, Mark D, Werb Z. Developmental expression of PDGF, TGF-alpha, and TGF-beta genes in preimplantation mouse embryos. Science. 1988;241:1823–5.
Tartakovsky B, Ben-Yair E. Cytokines modulate preimplantation development and pregnancy. Dev Biol. 1991;146:345–52.
Sharkey AM, Dellow K, Blayney M, Macnamee M, Charnock-Jones S, Smith SK. Stage-specific expression of cytokine and receptor messenger ribonucleic acids in human preimplantation embryos. Biol Reprod. 1995;53:974–81.
Taniguchi F, Harada T, Nara M, Deura I, Mitsunari M, Terakawa N. Coculture with a human granulosa cell line enhanced the development of murine preimplantation embryos via SCF/c-kit system. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2004;21:223–8.
Linnekin D. Early signaling pathways activated by c-Kit in hematopoietic cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1999;31:1053–74.
Ronnstrand L. Signal transduction via the stem cell factor receptor/c-Kit. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004;61:2535–48.
van Dijk TB, van Den Akker E, Amelsvoort MP, Mano H, Lowenberg B, von Lindern M. Stem cell factor induces phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase-dependent Lyn/Tec/Dok-1 complex formation in hematopoietic cells. Blood. 2000;96:3406–13.
Brunet A, Datta SR, Greenberg ME. Transcription-dependent and -independent control of neuronal survival by the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2001;11:297–305.
Mitsunari M, Harada T, Tanikawa M, Iwabe T, Taniguchi F, Terakawa N. The potential role of stem cell factor and its receptor c-kit in the mouse blastocyst implantation. Mol Hum Reprod. 1999;5:874–9.
Glabowski W. The protective effect of stem cell factor (SCF) on in vitro development of preimplantation mouse embryos. Ann Acad Med Stetin. 2005;51:83–93.
Glabowski W, Kurzawa R, Wiszniewska B, Baczkowski T, Marchlewicz M, Brelik P. Growth factors effects on preimplantation development of mouse embryos exposed to tumor necrosis factor alpha. Reprod Biol. 2005;5:83–99.
Hamilton AJ, Baulcombe DC. A species of small antisense RNA in posttranscriptional gene silencing in plants. Science (New York, NY). 1999;286:950–2.
Elbashir SM, Harborth J, Lendeckel W, Yalcin A, Weber K, Tuschl T. Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature. 2001;411:494–8.
Bernstein E, Denli AM, Hannon GJ. The rest is silence. Rna. 2001;7:1509–21.
Khang I, Sonn S, Park JH, Rhee K, Park D, Kim K. Expression of epithin in mouse preimplantation development: its functional role in compaction. Dev Biol. 2005;281:134–44.
Besmer P, Manova K, Duttlinger R, Huang EJ, Packer A, Gyssler C, et al. Development (Cambridge, England). 1993;125:37.
Eppig JJ. Oocyte control of ovarian follicular development and function in mammals. Reproduction. 2001;122:829–38.
Horie K, Takakura K, Taii S, Narimoto K, Noda Y, Nishikawa S, et al. The expression of c-kit protein during oogenesis and early embryonic development. Biol Reprod. 1991;45:547–52.
Driancourt MA, Reynaud K, Cortvrindt R, Smitz J. Roles of KIT and KIT LIGAND in ovarian function. Rev Reprod. 2000;5:143–52.
Ismail RS, Okawara Y, Fryer JN, Vanderhyden BC. Hormonal regulation of the ligand for c-kit in the rat ovary and its effects on spontaneous oocyte meiotic maturation. Mol Reprod Dev. 1996;43:458–69.
Packer AI, Hsu YC, Besmer P, Bachvarova RF. The ligand of the c-kit receptor promotes oocyte growth. Dev Biol. 1994;161:194–205.
Yoshida H, Takakura N, Kataoka H, Kunisada T, Okamura H, Nishikawa SI. Stepwise requirement of c-kit tyrosine kinase in mouse ovarian follicle development. Dev Biol. 1997;184:122–37.
Cantley LC. The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science. 2002;296:1655–7.
Stokoe D. The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway and cancer. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2005;7:1–22.
Chan TO, Rittenhouse SE, Tsichlis PN. AKT/PKB and other D3 phosphoinositide-regulated kinases: kinase activation by phosphoinositide-dependent phosphorylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1999;68:965–1014.
Kandel ES, Hay N. The regulation and activities of the multifunctional serine/threonine kinase Akt/PKB. Exp Cell Res. 1999;253:210–29.
Obenauer JC, Cantley LC, Yaffe MB. Scansite 2.0: Proteome-wide prediction of cell signaling interactions using short sequence motifs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31:3635–41.
Datta SR, Dudek H, Tao X, Masters S, Fu H, Gotoh Y, et al. Akt phosphorylation of BAD couples survival signals to the cell-intrinsic death machinery. Cell. 1997;91:231–41.
Ozes ON, Mayo LD, Gustin JA, Pfeffer SR, Pfeffer LM, Donner DB. NF-kappaB activation by tumour necrosis factor requires the Akt serine-threonine kinase. Nature. 1999;401:82–5.
Verdu J, Buratovich MA, Wilder EL, Birnbaum MJ. Cell-autonomous regulation of cell and organ growth in Drosophila by Akt/PKB. Nat Cell Biol. 1999;1:500–6.
Kurzawa R, Glabowski W, Baczkowski T, Wiszniewska B, Marchlewicz M. Growth factors protect in vitro cultured embryos from the consequences of oxidative stress. Zygote. 2004;12:231–40.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by a grant (2009-0093821) from Priority Research Centers Program funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Capsule
c-Kit siRNA inhibited development of preimplantation-stage mouse embryo and changed the mRNA expression of Akt target gene (upregulation of Tuberin and downregulation of mTOR). Tuberin normally inhibited mTOR which modulates cell proliferlation.
Jung Jin Lim and Jin Hee Eum contributed equally to this study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplemental Figure 1
Effect of SCF supplementation on the development of mouse one-cell embryos at 96 h post-hCG. The data are expressed as the mean±SEM. a,b Values within the same column with different superscripts are significantly different (P < 0.05). Note: KSOM (only): 139 zygotes, serum-free KSOM media, KSOM (100 ng/ml SCF): 138 zygotes, serum-free KSOM media with 100 ng/ml soluble SCF, KSOM (3 mg/ml BSA): 144 zygotes, KSOM media with 3 mg/ml BSA. Early Bla: early blastocyst (less than 50% cavity), Bla: blastocyst (greater than 50% cavity), Expanded Bla: expanded blastocyst, Hatching Bla: hatching blastocyst. (GIF 170 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, J.J., Eum, J.H., Lee, J.E. et al. Stem cell factor/c-Kit signaling in in vitro cultures supports early mouse embryonic development by accelerating proliferation via a mechanism involving Akt-downstream genes. J Assist Reprod Genet 27, 619–627 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-010-9449-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-010-9449-9