Abstract
Purpose: To relate pronuclear patterns (PN) and zygote cytoplasmic appearance and embryo morphology.
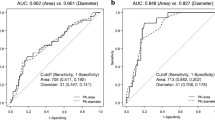
Methods: The usefulness of PN classification described by Tesarik et al. 1999 (patterns p0-5) and Scott et al. 2000 (Z1-4), for embryo selection is assessed.
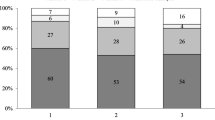
Results: Sinchrony on polarization and number of nucleolar precursor bodies (NPB) were associated with good quality embryos (p0 60.9% and p3 67.3%, and Z1 62.5% and Z2 64.7%; p<0.01). Pattern 4 zygotes were associated with small number of NPB developed into multinucleated embryos (14.3%) and poor quality embryos (61.9%). No significant differences were found in the pregnancy rate between transfer of at least one good prognosis PN pattern and transfer of poor prognosis PN patterns, although 75% of the transfers included at least one embryo derived from a pattern 0 zygote, and 55% included embryos from categories Z1 or Z2.
Conclusions: Sequential assessment involving the evaluation of oocyte quality, the classification of PN patterns and embryo morphology allows a more accurate evaluation of embryos to be selected for transfer.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gardner DK, Lane M. Towards a single embryo transfer. Reprod BioMed Online 2003;6:470–81.
Ludwig M, Schopper B, Al-Hasani S, Dietrich K. Clinical use of a pronuclear stage score following intracytoplasmatic sperm injection: impact on pregnancy rates under the conditions of the German embryo law. Hum Reprod 2000;15:325–29.
Zollner U, Zollner K-P, Hartl G, Dietl J, Steck T. The use of a detailed zygote score after IVF/ICSI to obtain good quality blastocysts: the German experience. Hum Reprod 2002;17:1327–33.
Tesarik J, Greco E. The probability of abnormal preimplantation development can be predicted by a single static observation on pronuclear stage morphology. Hum Reprod 1999;14:1318–23.
Scott L, Alvero R, Leondires M, Miller B. The morphology of human pronuclear embryos is positively related to blastocyst development and implantation. Hum Reprod 2000;15:2394–403.
Sadowy S, Tomkin G, Munné S, Ferrara-Congedo T, Cohen J. Impaired development of zygotes with uneven pronuclear size. Zygote 1998;6:137–41.
Wright G, Wiker S, Elsner C, Kort H, Massey J, Mitchell D, Toledo A, Cohen J. Observations on the morphology in human zygotes and implications for cryopreservation. Hum Reprod 1990;5:109–15.
Scott L, Smith S. The successful of pronuclear embryo transfers the day following oocyte retrieval. Hum Reprod 1998;13:1003–13.
Wittemer C, Bettahar-Lebugle K, Ohl J, Rongières C, Nisand I, Gerlinger P. Zygote evaluation: and efficient tool for embryo selection. Hum Reprod 2000;15:2591–7.
Payne D, Flaherty SP, Barry MF, Matthews CD. Preliminary observations on polar body extrusion and pronuclear formation in human oocytes using time-lapse cinematography. Hum Reprod 1997;12:532–41.
Scott, L. Pronuclear scoring as a predictor of embryo development. Reprod BioMedOnline 2003;6:470–81.
Nagy ZP, Liu J, Joris H, Devroey P, Van Steirteghem A. Time-course of oocyte activation, pronucleus formation and cleavage in human oocytes fertilized by intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Hum Reprod 1994;9:1743–8.
Tesarik J, Kopecny V. Developmental control of the human male pronucleus by ooplasmic factors. Hum Reprod 1989;4:962–8.
Tesarik J, Kopecny V. Development of human male pronucleous: ultrastructure and timing. Gamete Res 1989;24:135–49.
Capmany G, Taylor A, Braude PR, Bolton VN. The timing of pronuclear formation, DNA synthesis and cleavage in the human 1-cell embryo. Molec Hum Reprod 1996;2:299–306.
Balakier H, MacLusky NJ, Casper RF. Characterization of the first cell cycle in human zygotes. implications for cryopreservation. Fertil Steril 1993;59:359–65.
Tesarik J, Kopecny V. Assembly of the nucleolar precursor bodies in human male pronuclei is correlated with an early RNA synthetic activity. Experimental Cell Research 1990;191:153–56.
Edwards RG, Beard K. Oocyte polarity and cell determination in early mammalian embryos. Molec Hum Reprod 1997;3:863–905.
Staessen C, Janssenswillen C, Devroey P, Van Steirteghem AC. Cytogenetic and morphological observations of single pronucleated human oocytes after in-vitro fertilization. Hum Reprod 1993;8:221–3.
Van Blerkom J, Davis P, Alexander S. Differential mitochondrial distribution in human pronuclear embryos leads to disproportionate inheritance between blastomeres: relationship to microtubular organization, ATP contents and competence. Hum Reprod 2000;15:2621–33.
Salumets, A, Hydén-Granskog, C, Suikkari, A-M, Tiitinen, A, Tuuri, T. The predective value of pronuclear morphology of zygotes in the assessment of human embryo quality. Hum Reprod 2001;16:2177–81.
Demirel LC, Evirgen O, Aydos K, Ünlü C. The impact of the source of spermatozoa used for ICSI on pronuclear morphology. Hum Reprod 2001;16:2327–32.
Ebner T, Moser M, Sommergruber M, Gaiswinkler U, Wiesinger R, Puchner M, Tews G. Presence, but not type or degree of extension, of a cytoplasmic halo has a significant influence on preimplantation development and implantation behavior. Hum Reprod 2003;18:2406–12.
Plachot M, Crozet N. Fertilization abnormalities in human in vitro fertilization. Hum Reprod 1992;7(Suppl 1):89–94.
Ebner T, Yaman C, Moser M. Prognostic value of first polar body morphology on fertilization rate and embryo quality in intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Hum Reprod 2000;15:427–30.
Van Blerkom J, Henry G. Oocyte dysmorphism and aneuploidy in meiotically mature human oocytes after ovarian stimulation. Hum Reprod 1992;3:379–90.
Alikani M, Palermo G, Adler A, Bertoli M, Blake M, Cohen J. Intracytoplasmic sperm injection in dysmorphic human oocytes. Zygote 1995;3:283–88.
Tesarik J, Junca AM, Hazout A, Aubriot FX, Nathan C, Cohen-Bacrie P, Dumont-Hassan. Embryos with high implantation potential after intracytoplasmic sperm injection can be recognized by a simple, non-invasive examination of pronuclear morphology. Hum Reprod 2000;15:1396–99.
Balaban B, Urman B, Isiklar A, Alatas C, Aksoy S, Mercan R, Mumcu A, Nuhoglu A. The effect of pronuclear morphology on embryo quality parameters and blastocyst transfer outcome. Hum Reprod 2001;16:2357–61.
Balaban B. Pronuclear morphology predicts embryo development and chromosome constitution. Reprod BioMed Online 2004;8(6):695–700.
Gmiz P, Rubio C, de los Santos MJ, Mercader A, Simón C, Remohí J, Pellicer A. The effect of pronuclear morphology on early development and chromosomal abnormalities in cleavage-stage embryos. Hum Reprod 2003;18:2413–9.
Kahraman S, Kumtepe Y, Sertyel S, Dönmez E, Benkhalifa M, Findikli N, Vanderzwalmen P. Pronuclear morphology scoring and chromosomal status of embryos in severe male infertility. Hum Reprod 2002;17:3193–3200.
Tur R, Barri PN, Coroleu B, Buxaderas R, Parera N, Balasch J. Use of a prediction model for a high-order multiple implantation after ovarian stimulation with gonadotrophins. Fertil Steril 2005;83(1):116–21.
Neuber E, Rinaudo P, Trimarchi JR, Sakkas D. Sequential assessment of individually cultured human embryos as an indicator of subsequent good quality blastocyst development. Hum Reprod 2003;18:1307–12.
Van Blerkom J, Antczak M, Schrader R. The developmental potential of the human oocyte to the dissolved oxygen content of follicular fluid: association with vascular endothelial growth factor levels and perifollicular blood flow characteristics. Hum Reprod 1997;12:1047–55.
Acknowledgements
This work was carried out under the auspices of the Catedra de Investigación de Obstetricia y Ginecología del Institut Universitari Dexeus
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arroyo, G., Veiga, A., Santaló, J. et al. Developmental prognosis for zygotes based on pronuclear pattern: Usefulness of pronuclear scoring. J Assist Reprod Genet 24, 173–181 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-006-9099-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-006-9099-0