Abstract
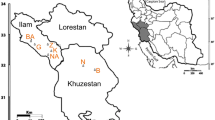
Simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers were developed for the brown alga Sargassum horneri (also known as “akamoku”) from an SSR-enriched genomic library. Of 22 SSR markers developed, 10 primer pairs produced clearly distinguishable DNA bands, indicating polymorphisms in S. horneri populations collected around Wakasa Bay, Kyoto, Japan. Ten primer pairs among the newly developed SSRs were also applicable to any of five other Sargassum species tested. To assess the utility of SSR markers for the classification of S. horneri, we genotyped 86 akamoku individuals from six populations (Naryu, Obase, Oshima, Satohami, Tai, and Taiza). We detected 148 alleles using 11 markers (10 new and 1 previously published). The allele number per locus ranged from 4 to 32 (average, 13.5). Based on the genotyping data for the 11 SSR markers, three of the six akamoku populations were separated on a phylogram. These results indicate that the SSR markers developed in this study are informative and useful for genetic analyses in Sargassum species.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bi Y, Yang X, Sun Z, Zhou Z (2015) Development and characterization of 12 polymorphic microsatellite markers in Sargassum vachellianum. Conserv Genet Resour 7:203–205
Excoffier L, Lischer HEL (2010) Arlequin suite ver 3.5: a new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol Ecol Resour 10:564–567
Guichoux E, Lagache L, Wagner S, Chaumeil P, Léger P, Lepais O, Lepoittevin C, Malausa T, Revardel E, Salin F, Petit RJ (2011) Current trends in microsatellite genotyping. Mol Ecol Resour 11:591–611
Hu ZM, Uwai S, Yu SH, Komatsu T, Ajisaka T, Duan DL (2011) Phylogeographic heterogeneity of the brown macroalga Sargassum horneri (Fucaceae) in the northwestern Pacific in relation to late Pleistocene glaciation and tectonic configurations. Mol Ecol 20:3894–3909
Kogame K, Uwai S, Shimada S, Masuda M (2005) A study of sexual and asexual populations of Scytosiphon lomentaria (Scytosiphonaceae, Phaeophyceae) in Hokkaido, northern Japan, using molecular markers. Eur J Phycol 40:313–322
Kubo N, Hirai M, Kaneko A, Tanaka D, Kasumi K (2009) Development and characterization of simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers in the water lotus (Nelumbo nucifera). Aquat Bot 90:191–194
Langella O (2011) Populations 1.2.32: population genetic software (individuals or population distances, phylogenetic trees). http://www.bioinformatics.org/project/?group_id=84. Accessed 22 Aug 2016
Liu F, Hu Z, Liu W, Li J, Wang W, Liang Z, Wang F, Sun X (2016) Distribution, function and evolution characterization of microsatellite in Sargassum thunbergii (Fucales, Phaeophyta) transcriptome and their application in marker development. Sci Rep 6:18947
Merritt BJ, Culley TM, Avanesyan A, Stokes R, Brzyski J (2015) An empirical review: characteristics of plant microsatellite markers that confer higher levels of genetic variation. Appl Plant Sci 3:8. doi:10.3732/apps.1500025
Nei M, Tajima F, Tateno Y (1983) Accuracy of estimated phylogenetic trees from molecular data. II. Gene frequency data. J Mol Evol 19:153–170
Nishigaki T, Douke A (2014) Growth and maturation of two populations of Sargassum horneri (Sargassaceae, Phaeophyta) in western Wakasa Bay, the Sea of Japan. Bull Kyoto Inst Ocean Fish Sci 36:1–6
Nunome T, Negoro S, Miyatake K, Yamaguchi H, Fukuoka H (2006) A protocol for the construction of microsatellite enriched genomic library. Plant Mol Biol Rep 24:305–312
Peakall R, Smouse PE (2012) GenAlEx 6.5: genetic analysis in excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research-an update. Bioinformatics 28:2537–2539
Ren JR, Yang R, He YY, Sun QH (2015) Genetic variation of Sargassum horneri populations detected by inter-simple sequence repeats. Genet Mol Res 14:619–625
Rousset F (2008) GENEPOP '007: a complete reimplementation of the Genepop software for Windows and Linux. Mol Ecol Resour 8:103–106
Shan T, Pang S, Li J, Su L (2015) Isolation and characterization of eight novel microsatellite loci from the brown alga Sargassum horneri. J Appl Phycol 27:2419–2421
Thiel M, Gutow L (2005) The ecology of rafting in the marine environment. I. The floating substrata. In: Gibson RN, Atkinson RJA, Gordon JDM (eds) Oceanography and marine biology: an annual review, vol 42. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, pp. 181–264
Uwai S, Kogame K, Yoshida G, Kawai H, Ajisaka T (2009) Geographical genetic structure and phylogeography of the Sargassum horneri/filicinum complex in Japan, based on the mitochondrial cox3 haplotype. Mar Biol 156:901–911
Wada Y, Yamada H (1997) Flow patterns in Wakasa Bay, Japan Sea. Bull Jpn Sea Natl Fish Res Inst 47:1–12
Yoshida G, Yoshikawa K, Terawaki T (2001) Growth and maturation of two populations of Sargassum horneri (Fucales, Phaeophyta) in Hiroshima Bay, the Seto Inland Sea. Fish Sci 67:1023–1029
Yu S, Chong Z, Zhao F, Yao J, Duan D (2013) Population genetics of Sargassum horneri (Fucales, Phaeophyta) in China revealed by ISSR and SRAP markers. Chin J Oceanol Limn 31:609–616
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. S. Uwai for the helpful information for the marker analysis in S. horneri and Ms. H. Kasaoka for the technical assistance. This work was funded by the Academic Contribution To Region (ACTR) grant (grant no. A11) from Kyoto Prefectural University to G.T.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kubo, N., Douke, A., Nishigaki, T. et al. Development and characterization of simple sequence repeat markers for genetic analyses of Sargassum horneri (Sargassaceae, Phaeophyta) populations in Kyoto, Japan. J Appl Phycol 29, 1729–1733 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-016-1041-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-016-1041-y