Abstract
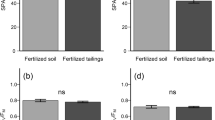
To aid in the restoration of coastal barren ground areas, it is important to clarify the effects of chelated iron on the growth of seaweed. In particular, for the further development of practical methods to promote seaweed growth, Fe-binding organic ligands, such as humic substances (HSs) composed of humus materials, rather than Fe-binding inorganic ligands, such as ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), should be investigated. In this study, the effects of an Fe fertilizer, made from HSs and steelmaking slag, on the growth of the brown alga Sargassum horneri at the germling and immature stages were examined. The addition of the Fe fertilizer eluate containing Fe organic ligand complexes clearly promoted the growth of S. horneri at the germling and immature stages. It was also clear that the effect of Fe concentration in the Fe fertilizer eluate on the growth rate was almost the same as that of Fe–EDTA. Moreover, the addition of the Fe fertilizer eluate had a great effect on the brown color of S. horneri thalli and promoted the increased content of photosynthetic pigments, such as chlorophyll a. Based on these experimental results, the application of the Fe fertilizer containing Fe organic ligand complexes is expected to become an effective method for the restoration of the barren ground phenomenon in Fe-deficient coastal areas.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choi HG, Lee KH, Yoo HL, Kang PJ, Kim YS, Nam KW (2008) Physiological differences in the growth of Sargassum horneri between the germling and adult stages. J Appl Phycol 20:729–735
Fujita D, Matumura W, Yamanaka M (2006) Seaweed. In: Fujita D, Takahashi M (eds) Kaiyoshinsosui riyougaku (Utilization of deep seawater resources). Seizando-Shoten, Tokyo, pp 61–65 (in Japanese)
Fujita D, Murase N, Kuwahara H (eds) (2010) Moba wo Mimamori Sodateru Tie to Gizyutu (Monitoring and maintenance of seaweed beds). Seizando-Shoten, Tokyo, 278 pp. (in Japanese)
Hwang EK, Park CS, Baek JM (2006) Artificial seed production and culture of the edible brown alga, Sargassum fulvellum (Turner) C. Agardh: developing a new species for seaweed culture in Korea. J Appl Phycol 18:251–257
Kato T, Kosugi C, Kiso E, Torii K (2014) Application of steelmaking slag to marine forest restoration. Nippon Steel Sumitomo Metal Tech Report 109:79–84
Martin JH, Fitzwater SE (1988) Iron deficiency limits phytoplankton growth in the north-east Pacific subarctic. Nature 331:341–342
Matsunaga K, Suzuki Y, Kuma K, Kudo I, Nakabayashi S (1991) Uptake rate of iron by macroalgae from the sea of Japan (Saccharina religiosa Miyabe and Undaria pinnatifida). Bull Jap Soc Fish Oceanogr 55:349–353
Matsunaga K (2003) Effect of land (forest) to the sea. J Jap Soc Water Env 26:614–620 (in Japanese)
Motomura T (2000) Culture medium. In: Aruga Y, Inoue I, Tanaka J, Yokohama Y, Yoshida T (eds) Souruigaku zikkenzisyu (Phycological experiments and methods). Kodansya, Tokyo, pp 170–171 (in Japanese)
Motomura T, Sakai Y (1981) Effect of chelated iron in culture media on oogenesis in Saccharina angustata. Bull Jap Soc Sci Fish 47:1535–1540
Motomura T, Sakai Y (1984) Regulation of gametogenesis of Saccharina and Desmarestia (Phaeophyta) by iron and boron. Jap J Phycol 32:209–215
Nagai T, Miki O, Okumura C (2014) Effects of chelated iron on the growth of Sargassaceae species at the germling and immature stages. Jo Water a Env Technol 12:285–294
Pang SJ, Liu F, Shan TF, Gao SQ, Zhang ZH (2009) Cultivation of the brown alga Sargassum horneri: sexual reproduction and seedling production in tank culture under reduced solar irradiance in ambient temperature. J Appl Phycol 21:413–422
Porra RJ (2002) The chequered history of the development and use of simultaneous equations for the accurate determination of chlorophylls a and b. Photosynth Res 73:149–156
Provasoli L (1968) Media and prospects for the cultivation of marine algae. In: Watanabe A, Hattori A (eds) Cultures and collections of algae. Proc. U.S.-Japan Conf, vol 1966, Hakone, Japan, September. Japanese Society of Plant Physiology, Tokyo, pp 63–75
Suzuki Y, Kuma K, Matsunaga K (1995a) Bioavailable iron species in seawater measured by macroalga (Laminaria japonica) uptake. Mar Biol 123:173–178
Suzuki Y, Kuma K, Kudo I, Matsunaga K (1995b) Iron requirement of the brown macroalgae Laminaria japonica, Undaria pinnatifida and the crustose coralline alga Lithophyllum yessoense and their competition in the northen Japan Sea. Phycologia 34:201–205
Suzuki Y, Kuma K, Matsunaga K (1994) Effect of iron on ogonium formation, growth rate and pigment synthesis of Laminaria japonica (Phaeophyta). Fish Sci 60:373–378
Turner DR, Hunter KA (eds) (2001) The biochemistry of iron in seawater. IUPAC Series on Analytical and Physical Chemistry of Environmental System, Volume 7. John Wiley d, UK, 396 pp
Ueki C, Murakami A, Kato T, Saga N, Motomura T (2010) Effects of nutrient deprivation on photosynthetic pigments and ultrastructure of chloroplasts in Porphyra yezoensis. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 76:375–382
Ueki C, Kato T, Miki O (2011) Mesocosm experiment for fertilizer made from steel-making slag and humus soil with growth of Porphyra yezoensis, nori. J Adv Mar Sci Technol Soc 17:49–55
Ueki C, Kumagai T, Fujita D (2012) Effects of iron-enriched fertilizer on marine algae in Toyama Bay deep seawater. Deep Ocean Water Res 13:7–16
Yamamoto M, Hamasuna M, Fukushima M, Okita S, Horiya S, Kiso S, Shibuya M, Sadakata M (2006) Recovery from barren grounds by supplying slag and humic substances. J Jap Inst Energy 85:971–978
Yamamoto M, Fukushima M, Kiso E, Kato T, Sibuya M, Horiya S, Nishida A, Otsuka K, Komai T (2010) Application of iron humates to barren ground in a coastal area for restoring seaweed beds. J Chem Eng Jpn 43:627–634
Yamamoto M, Fukushima M, Liu D (2011) Effect of humic substances on iron elusion in the method of restoration of seaweed beds with steelmaking slag. Tetsu-to-Hagane 97:159–164
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Kanazawa University and Nippon Steel & Sumitomo Metal Corporation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miki, O., Nagai, T., Marzuki, M. et al. Effects of Fe fertilizer eluate on the growth of Sargassum horneri at the germling and immature stages. J Appl Phycol 28, 1775–1782 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-015-0729-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-015-0729-8