Abstract
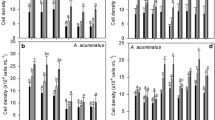
Cyanobacteria produce a wide spectrum of biologically active compounds such as microcystins, whose effects on photoautotrophic organisms and role in the aquatic ecosystems have been most intensively discussed and studied. In our study, we examined effects of semipurified Microcystis extract containing microcystins (0.2–20 nM corresponding to 0.2–20 μg L−1) on age-induced cell differentiation of filamentous cyanobacterium Trichormus variabilis. The heterocyst and akinete formation was significantly decreased after exposure to extract containing 2 or 20 nM of microcystins within 10 days of exposure. To our knowledge, this is the first information about effects of metabolites produced by planktonic cyanobacteria on cell differentiation in filamentous cyanobacteria. Since the effects were induced by environmentally relevant concentrations of microcystins, our observations may indicate not only that microcystins or other bioactive peptides could affect conservation, overwintering, and nitrogen-fixation in filamentous cyanobacteria under environmental conditions but also contribute to the understanding of possible signaling function of cyanobacterial metabolites.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams DG, Duggan PS (1999) Heterocyst and akinete differentiation in cyanobacteria. New Phytol 144:3–33
Babica P, Blaha L, Marsalek B (2006a) Exploring the natural role of microcystins—a review of effects on photoautotrophic organisms. J Phycol 42:9–20
Babica P, Kohoutek J, Blaha L, Adamovsky O, Marsalek B (2006b) Evaluation of extraction approaches linked to ELISA and HPLC for analyses of microcystin-LR, -RR and -YR in freshwater sediments with different organic material contents. Anal Bioanal Chem 385:1545–1551
Babica P, Hilscherová K, Bártová K, Bláha L, Maršálek B (2007) Effects of dissolved microcystins on growth of planktonic photoautotrophs. Phycologia 46:137–142
Blahova L, Babica P, Marsalkova E, Marsalek B, Blaha L (2007) Concentrations and seasonal trends of extracellular microcystins in freshwaters of the Czech Republic results of the national monitoring program. Clean Soil Air Water 35:348–354
Bubik A, Sedmak B, Novinec M, Lenarcic B, Lah TT (2008) Cytotoxic and peptidase inhibitory activities of selected non-hepatotoxic cyclic peptides from cyanobacteria. Biol Chem 389:1339–1346
Dasey M, Ryan N, Wilson J, McGregor G, Fabbro L, Neilan BA, Burns BP, Kankaanpaa H, Morrison LF, Codd GA, Rissik D, Bowling L (2005) Investigations into the taxonomy, toxicity and ecology of benthic cyanobacterial accumulations in Myall Lake, Australia. Mar Freshwater Res 56:45–55
Dong YQ, Huang X, Wu XY, Zhao JD (2000) Identification of the active site of HetR protease and its requirement for heterocyst differentiation in the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp strain PCC 7120. J Bacteriol 182:1575–1579
Dubey SK, Rai LC (1987) Effect of chromium and tin on survival, growth, carbon fixation, heterocyst differentiation, nitrogenase, nitrate reductase and glutamine synthetase activities of Anabaena doliolum. J Plant Physiol 130:165–172
Fay P, Van Baalen C (1987) The Cyanobacteria. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Fisher RW, Wolk CP (1976) Substance stimulating differentiation of spores of blue-green-alga Cylindrospermum licheniforme. Nature 259:394–395
Ghosh S, Bagchi D, Bagchi S (2008) Proteolytic activity in Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806 is inhibited by a trypsin-inhibitory cyanobacterial peptide with a partial structure of microviridin. J Appl Phycol 20:1045–1052
Golden JW, Yoon HS (1998) Heterocyst formation in Anabaena. Curr Opin Microbiol 1:623–629
Heath MW, Wood SA, Ryan KG (2010) Polyphasic assessment of fresh-water benthic mat-forming cyanobacteria isolated from New Zealand. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 73:95–109
Herdman M (1988) Cellular Differentiation—akinetes. Meth Enzymol 167:222–232
Hirosawa T, Wolk CP (1979) Isolation and characterization of a substance which stimulates the formation of akinetes in the cyanobacterium Cylindrospermum licheniforme Kutz. J Gen Microbiol 114:433–441
Hu ZQ, Liu YD, Li DH (2004) Physiological and biochemical microcystin-RR toxicity to the Synechococcus elongatus. Environ Toxicol 19:571–577
Hu ZQ, Liu YD, Li DH, Dauta A (2005) Growth and antioxidant system of the cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus in response to microcystin-RR. Hydrobiologia 534:23–29
Hu ZQ, Li DH, Xiao B, Dauta A, Liu YD (2008) Microcystin-RR induces physiological stress and cell death in the cyanobacterium Aphanizomenon sp DC01 isolated from Lake Dianchi, China. Fundam Appl Limnol 173:111–120
Ihle T, Jähnichen S, Benndorf J (2005) Wax and wane of Microcystis (Cyanophyceae) and microcystins in lake sediments: A case study in Quitzdorf Reservoir (Germany). J Phycol 41:479–488
Jiang F, Mannervik B, Bergman B (1997) Evidence for redox regulation of the transcription factor NtcA, acting both as an activator and a repressor, in the cyanobacterium Anabaena PCC 7120. Biochem J 327:513–517
Kearns KD, Hunter MD (2002) Algal extracellular products suppress Anabaena flos-aquae heterocyst spacing. Microb Ecol 43:174–180
Komárek, J. (1992) Diversity and modern classification of Cyanobacteria (Cyanoprokaryota). p. Dissertation thesis in Czech.
Leao PN, Vasconcelos M, Vasconcelos VM (2009) Allelopathy in freshwater cyanobacteria. Crit Rev Microbiol 35:271–282
Li HY, Xie P, Zhang DW, Chen J (2009) The first study on the effects of microcystin-RR on gene expression profiles of antioxidant enzymes and heat shock protein-70 in Synechocystis sp PCC6803. Toxicon 53:595–601
Orr PT, Jones GJ (1998) Relationship between microcystin production and cell division rates in nitrogen-limited Microcystis aeruginosa cultures. Limnol Oceanogr 43:1604–1614
Potts M, Sun H, Mockaitis K, Kennelly PJ, Reed D, Tonks NK (1993) A protein-tyrosine serine phosphatase encoded by the genome of the cyanobacterium Nostoc commune UTEX-584. J Biol Chem 268:7632–7635
Rantala A, Fewer DP, Hisbergues M, Rouhiainen L, Vaitomaa J, Borner T, Sivonen K (2004) Phylogenetic evidence for the early evolution of microcystin synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:568–573
Saito K, Sei Y, Miki S, Yamaguchi K (2008) Detection of microcystin-metal complexes by using cryospray ionization-Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Toxicon 51:1496–1498
Sedmak B, Elersek T (2005) Microcystins induce morphological and physiological changes in selected representative phytoplanktons. Microb Ecol 50:298–305
Sedmak B, Kosi G (1998) The role of microcystin in heavy cyanobacterial bloom formation. J Plankton Res 20:691–708
Sedmak B, Carmeli S, Elersek T (2008) “Non-Toxic” cyclic peptides induce lysis of cyanobacteria—An effective cell population density control mechanism in cyanobacterial blooms. Microb Ecol 56:201–209
Sedmak B, Carmeli S, Pompe-Novak M, Tusek-Znidaric M, Grach-Pogrebinsky O, Elersek T, Zuzek MC, Bubik A, Frangez R (2009) Cyanobacterial cytoskeleton immunostaining: the detection of cyanobacterial cell lysis induced by planktopeptin BL1125. J Plankton Res 31:1321–1330
Shi L, Carmichael WW, Kennelly PJ (1999) Cyanobacterial PPP family protein phosphatases possess multifunctional capabilities and are resistant to microcystin-LR. J Biol Chem 274:10039–10046
Schatz D, Keren Y, Vardi A, Sukenik A, Carmeli S, Borner T, Dittmann E, Kaplan A (2007) Towards clarification of the biological role of microcystins, a family of cyanobacterial toxins. Environ Microbiol 9:965–970
Schlosser UG (1994) SAG—Sammlung von Algenkulturen at the University of Gottingen- Catalog of strains 1994. Bot Acta 107:113–186
Schmidtkunz C, Stich HB, Welsch T (2009) Improving the selectivity and confidence in the HPLC analysis of microcystins in lake sediments. J Liq Chromatogr Related Technol 32:801–821
Singh DP, Tyagi MB, Kumar A, Thakur JK, Kumar A (2001) Antialgal activity of a hepatotoxin producing cyanobacterium, Microcystis aeruginosa. World J Microbiol Biotech 17:15–22
Sivonen K, Jones G (1999) Cyanobacterial Toxins. In: Chorus I, Bertram J (eds) Toxic cyanobacteria in water—A guide to public health, conseqences, monitoring and management, London, New York. E & FN Spon, London, pp 41–111
Smith RJ, Hobson S, Ellis IR (1987) The effect of abscisic-acid on calcium-mediated regulation of heterocyst frequency and nitrogenase activity in Nostoc 6720. New Phytol 105:543–549
Stein J (1973) Handbook of phycological methods. Culture methods and growth measurements. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Valdor R, Aboal M (2007) Effects of living cyanobacteria, cyanobacterial extracts and pure microcystins on growth and ultrastructure of microalgae and bacteria. Toxicon 49:769–779
Vassilakaki M, Pflugmacher S (2008) Oxidative stress response of Synechocystis sp (PCC 6803) due to exposure to microcystin-LR and cell-free cyanobacterial crude extract containing microcystin-LR. J Appl Phycol 20:219–225
Wolk CP (1996) Heterocyst formation. Annu Rev Genet 30:59–78
Zhang CC, Gonzalez L, Phalip V (1998) Survey, analysis and genetic organization of genes encoding eukaryotic-like signaling proteins on a cyanobacterial genome. Nucleic Acids Res 26:3619–3625
Acknowledgements
Research has been supported by project AVOZ60050516 granted to Institute of Botany (Academy of Science, Czech Republic), project INCHEMBIOL MSM0021622412 and CETOCOEN CZ.1.05/2.1.00/01.0001 (project granted by the European Union and administred by the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bártová, K., Hilscherová, K., Babica, P. et al. Extract of Microcystis water bloom affects cellular differentiation in filamentous cyanobacterium Trichormus variabilis (Nostocales, Cyanobacteria). J Appl Phycol 23, 967–973 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-010-9624-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-010-9624-5