Abstract
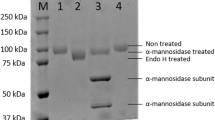
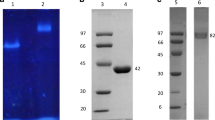
Dendryphiella arenaria TM94 is an obligate marine fungus. Fucoidanase expressed by TM94 by solid state fermentation was purified. The fermented solid medium was extracted with citric acid buffer, and the extracts were precipitated by acetone and separated on Sephadex G-100 chromatography. The specific fucoidanase activity of purified enzyme was 27-fold than that of the crude enzyme. The recovery of the enzyme was 17.69%. SDS-PAGE was used to identify the purity and the molecular weight of the fucoidanase. A single band appeared on SDS-PAGE gel which suggested that relatively pure fucoidanase has been obtained. The molecular weight of fucoidanase is 180 kDa and the isoelectric point was about pH 4.4. The purified fucoidanase appeared to have the maximum enzymatic activity at pH 6.0. KM and the maximum velocity of the enzyme was 6.56 mg·mL−1 and 6.55 mg·mL−1·min−1 by using fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus as substrate. The enzyme may be a type of endo-fucoidanase which could hydrolyze high molecular weight fucoidan to low molecular weight fucoidan rather than to fucose.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albuquerque IRL, Queiroz KCS, Alves LG, Santos EA, Leite EL, Rocha HAO (2004) Heterofucans from Dictyota menstrualis have anticoagulant activity. Braz J Med Biol Res 37:167–171. doi:10.1590/S0100-879X- 2004000200002
Bakunina IY, Nedashkovskaya OI, Alekseeva SA, Ivanova EP, Romanenko LA, Gorshkova NM, Sakov VV, Zvyagintseva TN, Mikhailov VV (2002) Degradation of fucoidan by the marine proteo-bacterium Pseudoalteromonas citrea. Microbiology 71:41–47
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chevolot L, Foucault A, Chaubet F, Kervarec N, Sinquin C, Fisher A, Boisson-Vidal C (1999) Further data on the structure of brown seaweed fucans: relationships with anticoagulant activity. Carbohydr Res 319:154–165
Daniel R, Berteau O, Jozefonvicz J, Goasdoue N (1999) Degradation of algal (Ascophyllum nodosum) fucoidan by an enzymatic activity contained in digestive glands of the marine mollusc Pecten maximus. Carbohydr Res 322:291–297
Descamps V, Colin S, Marc L, Jam M, Richard C, Potin P, Barbeyron T, Yvin J, Kloareg B (2006) Isolation and culture of a marine bacterium degrading the sulfated fucans from marine brown algae. Mar Biotechnol 8:27–39
Fujikawa T, Koyabu K, Wada M (1979) Enzymes in hepatopancreas of abalone active on fucoidan(1), crude enzyme and unabsorbed fraction on CM-cellulose. Nippon Nogei Kagakukaishi (In Japanese) 53:87–95
Furukawa S, FujikawaT KD, Ide A (1992a) Production of fucoidan-degrading enzymes, fucoidan- ase, and fucoidan sulfatase by Vibrio sp. N-5. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 58:1499–1503
Furukawa S, Fujikawa T, Koga D, Ide A (1992b) Purification and some properties of exo-type fucoidanase from Vibrio sp. N-5. Arch Biotech Biochem 56:1829–1834
Holtkamp AD, Kelly S, Ulber R, Lang S (2009) Fucoidans and fucoidanases—focus on techniques for molecular structure elucidation and modification of marine polysaccharides. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82:1–11
Kawai Y, Seno N, Anno K (1969) A modified method for chondrosulfatase assay. Anal Biochem 32:314–321
Kim WJ, Koo YK, Jung MK, Moon HR, Kim SM, Synytsya A, Yun-Choi HS, Kim YS, Park JK, Park Y (2010) Anticoagulating activities of low-molecular weight fuco-oligosaccharides prepared by enzymatic digestion of fucoidan from the sporophyll of Korean Undaria pinnatifida. Arch Pharm Res 33:125–131
Kitamura K, Masaru M, Yasui T (1992) Enzymic degradation of fucoidan by fucoidanase from the hepatopancreas of Patinopecten yessoensis. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 56:490–494
Maruyama H, Tamauchi H, Hashimoto M, Nakano T (2003) Antitumor activity and immune response of Mekabu fucoidan extracted from sporophyll of Undaria pinnatifida. In Vivo 17:245–249
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428
Mourao PAS (2004) Use of sulfated fucans as anticoagulant and antithrombotic agents: future perspectives. Curr Pharm Des 10:967–981
Nishino T, Nishioka C, Ura H, Nagumo T (1994) Isolation and partial characterization of a novel amino sugar-containing fucan sulfate from commercial Fucus vesiculosus fucoidan. Carbohydr Res 255:213–224
Nishino T, Yamauchi T, Horie M, Nagumo T, Suzuki H (2000) Effects of a fucoidan on the activation of plasminogen by u-PA and t-PA. Thromb Res 99:623–634
Rodríguez Jasso RM, Aguilar Gonzalez CN, Pastrana L, Teixeira JA (2008) Identification and evaluation of fungal strains with fucoidan degradation potential. Proceedings of the 10th International Chemical and Biological Engineering Conference-CHEMPOR 2008 E. C. Ferreira and M. Mota. Braga, Portugal, Universidade do Minho, pp 2106–2109
Sakai T, Kimura H, Kato I (2002) A marine strain of flavobacteriaceae utilizes brown seaweed fucoidan. Mar Biotechnol 4:399–405
Sakai T, Ishizuka K, Kato I (2003a) Isolation and characterization of a fucoidan-degrading marine bacterium. Mar Biotechnol 5:409–416
Sakai T, Ishizuka K, Shimanaka K, Ikai K, Kato I (2003b) Structures of oligosaccharides derived from Cladosiphon okamuranus fucoidan by digestion with marine bacterial enzymes. Mar Biotechnol 5:536–544
Sakai T, Kimura H, Kato I (2003c) Purification of sulfated fucoglucuronomannan lyase from bacterial strain of Fucobacter marina and study of appropriate conditions for its enzyme digestion. Mar Biotechnol 5:380–387
Sakai T, Kimura H, Kojima K, SK IK, Kato I (2003d) Marine bacterial sulfated fucoglucurono-mannan (SFGM) lyase digests brown algal SFGM into trisaccharides. Mar Biotechnol 5:70–78
Sakai T, Kawai T, Kato I (2004) Isolation and characterization of a fucoidan-degrading marine bacterial strain and its fucoidanase. Mar Biotechnol 6:335–346
Schaeffer DJ, Krylov VS (2000) Anti-HIV activity of extracts and compounds from algae and cyanobacteria. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 45:208–227
Urvantseva A, Bakunina I, Nedashkovskaya O, Kim S, Zvyagintseva T (2006) Distribution of intracellular fucoidan hydrolases among marine bacteria of the family Flavobacteriaceae. Appl Biochem Microbiol 42:484–491
Wang P, Cai J, Qin S, Wu Q, Wu K, Wang R, Xu D (2004) Fermentation of marine bacterium Bacillus sp. H-TP2 for fucoidanase and enzyme properties. Food and Fermentation Industry (In Chinese) 30(3):13–15
Wu K, Wu Q, Yan J, Liu B, Yang B, Zhang J, Qin S, Pan R, Cai J, Meiner M (2002) Production of fucoidanase from the marine fungus Dendryphiella arenaria TM94 by Solid Substrate Fermentation. European Meeting on Marine Biotechnology 5:12–14. Nantes, France
Wu Q, Cai J, Wu K, Qin S (2004) Solid state fermentation of fucoidanase of marine fungus LD8. Mar Sci (In Chinese) 28(6):23–27
Yaphe W, Morgan K (1959) Enzymic hydrolysis of fucoidin by Pseudomonas atlantica and Pseudomonas carrageenovora. Nature 183:761–762
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by funds from Anhui Provincial Nature Science Foundation (No: 03043104), Anhui Provincial Excellent Youth Science and Technology Foundation (No: 04043051), PRC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Min Zhang is co-first author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Q., Zhang, M., Wu, K. et al. Purification and characteristics of fucoidanase obtained from Dendryphiella arenaria TM94. J Appl Phycol 23, 197–203 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-010-9588-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-010-9588-5