Abstract
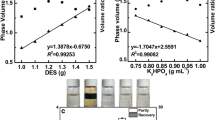
The cyanobacterium Spirulina (Arthrospira) platensis is a good source of phycobiliprotein purification. C-phycocyanin (C-PC) is the major phycobiliprotein, while allophycocyanin (APC) is less abundant in S. platensis. Previously reported methods for C-PC purification are only able to offer either high purity or high efficiency. This paper describes one-step anion exchange chromatography method with continuous pH gradient elution for simultaneous purification of C-PC and APC with high purity and high recovery. Crude C-PC and APC were extracted and concentrated by ammonium sulfate fractionation at saturation of 25% and 60%, then purified on a DEAE-Sepharose Fast Flow chromatography column with continuous pH gradient elution from pH 5.0 to 3.6. After this single-step chromatography, C-PC and APC with high purity and recovery were simultaneously obtained. The purity ratios of C-PC and APC reached 5.59 (A620/A280) and 5.19 (A650/A280), respectively. Their purity was further demonstrated by electrophoresis and fluorescence emission spectroscopy. Moreover, the total recovery yield of pure C-PC and APC were 67.04% and 80.0%, representing 111.83 and 29.28 mg·g−1 lyophilized weight, respectively. The obtained C-PC and APC remained stable over a pH range of 4–9. This purification method for high purity and recovery of C-PC and APC proved to be fairly efficient compared with previously reported methods.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benedetti S, Rinalducci S, Benvenuti F, Francogli S, Pagliarani S, Giorgi L, Micheloni M, D’Amici GM, Zolla L, Canestrari F (2006) Purification and characterization of phycocyanin from the blue-green alga Aphanizomenon flos-aquae. J Chromatogr B 833:12–18
Bennett A, Bogorad L (1973) Complementary chromatic adaptation in a filamentous blue-green alga. J Cell Biol 58:419–435
Bermejo R, Felipe MA, Talavera EM, Alvarez-Pez JM (2006) Expanded bed absorption chromatography for recovery of phycocyanins from the microalga Spirulina platensis. Chromatographia 63:59–66
Boussiba S, Richmond AE (1979) Isolation and characterization of phycocyanins from the blue-green alga Spirulina platensis. Arch Microbial 120:155–159
Chen F, Zhang Y, Guo S (1996) Growth and phycocyanin formation of Spirulina platensis in photoheterotrophic culture. Biotechnol Lett 18:603–608
Chen T, Wong YS, Zheng W (2006) Purification and characterization of selenium-containing phycocyanin from selenium-enriched Spirulina platensis. Phytochem 67:2424–2430
Glazer AN (1981) Photosynthetic accessory proteins with bilin prosthetic groups. In: Hatch MD, Boardman NK (eds) The biochemistry of plants, vol. 8, Photosynthesis. Academic, New York, pp 51–96
Glazer AN, Stryer L (1984) Phycofluor probes. Trends Biochem Sci 9:423–427
Haugland RP (1996) Handbook of fluorescent probes and research chemicals, 6th edn. Molecular Probes, Eugene
Liu LN, Chen XL, Zhang XY, Zhang YZ, Zhou BC (2005) One-step chromatography method for efficient separation and purification of R-phycoerythrin from Polysiphonia urceolata. J Biotechnol 116:91–100
MacColl R, Csatorday K, Berns DS, Traeger E (1980) Chromophore interactions in allophycocyanin. Biochem 19:2817–2820
Market Corporation (2005). http://www.marketbio.com (consult date: October 2005)
Minkova KM, Tchernov AA, Tchorbadjieva MI, Fournadjieva ST, Antova RE, Busheva MC (2003) Purification of C-phycocyanin from Spirulina (Arthrospira) fusiformis. J Biotechnol 102:55–59
Minkova K, Tchorbadjieva M, Tchernov A, Stojanova M, Gigova L, Busheva M (2007) Improved procedure for separation and purification of Arthronema africanum phycobiliproteins. Biotechnol Lett 29:647–651
Niu JF, Wang GC, Lin XZ, Zhou BC (2007) Large-scale recovery of C-phycocyanin from Spirulina platensis using expanded bed adsorption chromatography. J Chromatogr B 850:267–276
Padgett MP, Krogmann DW (1987) Large scale preparation of pure phycobiliproteins. Photosynth Res 11:225–235
Patel A, Mishra S, Pawar R, Ghosh PK (2005) Purification and characterization of C-phycocyanin from cyanobacterial species of marine and freshwater habitat. Protein Expr Purif 40:248–255
Patil G, Raghavarao KSMS (2007) Aqueous two phase extraction for purification of C-phycocyanin. Biochem Eng J 34:156–164
Patil G, Chethana S, Sridevi AS, Raghavarao KS (2006) Method to obtain C-phycocyanin of high purity. J Chromatogr A 1127:76–81
Qureshi MA, Garlich JD, Kidd MT (1996) Dietary Spirulina platensis enhances humoral and cell-mediated immune functions in chickens. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 18:465–476
Romay C, Gonzalez R (2000) Phycocyanin is an antioxidant protector of human erythrocytes against lysis by peroxyl radicals. J Pharm Pharmacol 52:367–368
Rito-Palomares M, Nunez L, Amador D (2001) Practical application of aqueous two-phase systems for the development of a prototype process for C-phycocyanin recovery from Spirulina maxima. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 76:1273–1280
Santiago-Santos MC, Ponce-Noyola T, Olvera-Ramirez R, Ortega-Lopez J, Canizares-Villanueva RO (2004) Extraction and purification of phycocyanin from Calothrix sp. Process Biochem 39:2047–2052
Siegelman HW, Kycia JH (1978) Algal biliproteins. In: Hellebust JA, Craigie JS (eds) Handbook of phycological methods. Physiological and biochemical methods. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 71–79
Silveira ST, Quines LKM, Burkert CAV, Kalil SJ (2008) Separation of phycocyanin from Spirulina platensis using ion exchange chromatography. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 31:477–482
Soni B, Trivedi U, Madamwar D (2008) A novel method of single step hydrophobic interaction chromatography for the purification of phycocyanin from Phormidium fragile and its characterization for antioxidant property. Bioresour Technol 99:188–194
Stewart DE, Farmer FH (1984) Extraction, identification, and quantitation of phycobiliprotein pigments from phototrophic plankton. Limnol Oceanogr 29:392–397
Su HN, Xie BB, Chen XL, Wang JX, Zhang XY, Zhou BC, Zhang YZ (2010) Efficient separation and purification of allophycocyanin from Spirulina (Arthrospira) platensis. J Appl Phycol 22:65–70
Wyman M (1992) An in vivo method for the estimation of phycoerythrin concentration in marine cyanobacteria (Synechococcus spp.). Limnol Oceanogr 37:1300–1306
Zhang YM, Chen F (1999) A simple method for efficient separation and purification of C-phycocyanin and allophycocyanin from Spirulina platensis. Biotechnol Tech 13:601–603
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by the Hi-Tech Research and Development program of China (2008AA09Z404), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (40676078), and the Scientific and Technological Development Program of Shandong Province (2006GG2205009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, SG., Zhu, LP., Su, HN. et al. Single-step chromatography for simultaneous purification of C-phycocyanin and allophycocyanin with high purity and recovery from Spirulina (Arthrospira) platensis . J Appl Phycol 23, 1–6 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-010-9525-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-010-9525-7