Abstract
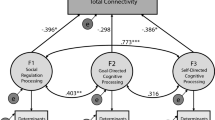
Atypical connectivity patterns have been observed for individuals with autism spectrum disorders (ASD), particularly across the triple-network model. The current study investigated brain-behavior relationships in the context of social skills and executive function profiles for ASD youth. We calculated connectivity measures from diffusion tensor imaging using Bayesian estimation and probabilistic tractography. We replicated prior structural equation modeling of behavioral measures with total default mode network (DMN) connectivity to include comparisons with central executive network (CEN) connectivity and CEN-DMN connectivity. Increased within-CEN connectivity was related to metacognitive strengths. Our findings indicate behavior regulation difficulties in youth with ASD may be attributable to impaired connectivity between the CEN and DMN and social skill difficulties may be exacerbated by impaired within-DMN connectivity.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott, A. E., Linke, A. C., Nair, A., Jahedi, A., Alba, L. A., Keown, C. L., Fishman, I., & Muller, R. A. (2018). Repetitive behaviors in autism are linked to imbalance of corticostriatal connectivity: A functional connectivity MRI study. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 13(1), 32–42.
Addis, D. R., Wong, A. T., & Schacter, D. L. (2007). Remembering the past and imagining the future: Common and distinct neural substrates during event construction and elaboration. Neuropsychologia, 45, 1363–1377.
Ahmed, S. F., Kuhfeld, M., Watts, T. W., Davis-Kean, P. E., & Vandell, D. L. (2021). Preschool executive function and adult outcomes: A developmental cascade model. Developmental Psychology, 57(12), 2234–2249. https://doi.org/10.1037/dev0001270
Ahmed, S. F., Tang, S., Waters, N. E., & Davis-Kean, P. (2019). Executive function and academic achievement: Longitudinal relations from early childhood to adolescence. Journal of Educational Psychology, 111(3), 446–458. https://doi.org/10.1037/edu0000296
Andersen, P. N., Skogli, E. W., Hovik, K. T., Egeland, J., & Øie, M. (2015). Associations among symptoms of autism, symptoms of depression, and executive functions in children with high-functioning autism: A 2 year follow-up study. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 45(8), 2497–2507.
Anderson, D. K., Liang, J. W., & Lord, C. (2014). Predicting young adult outcome among more and less cognitively able individuals with autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Child Psychology & Psychiatry, 55(5), 485–494.
Assaf, M., Jagannathan, K., Calhoun, V. D., Miller, L., Stevens, M. C., Sahl, R., O’Boyle, J. G., Schultz, R. T., & Pearlson, G. D. (2010). Abnormal functional connectivity of default mode sub-networks in autism spectrum disorder patients. NeuroImage, 53(1), 247–256.
Azad, G. F., Dillon, E., Feuerstein, J., Kalb, L., Neely, J., & Landa, R. (2020). Quality of life in school-aged youth referred to an autism specialty clinic: A latent profile analysis. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 50(4), 1269–1280.
Bednarz, H. M., Trapani, J. A., & Kana, R. K. (2020). Metacognition and behavioral regulation predict distinct aspects of social functioning in autism spectrum disorder. Child Neuropsychology, 26(7), 953–981.
Behrens, T. E. J., Johansen-Berg, H., Jbabdi, S., Rushworth, M. F. S., & Woolrich, M. W. (2007). Probablistic diffusion tractography with multiple fibre orientations: What can we gain? NeuroImage, 34(1), 144–155.
Behrens, T. E. J., Woolrich, M. W., Jenkinson, M., Johansen-Berg, H., Nunes, R. G., Clare, S., Matthews, P. M., Brady, J. M., & Smith, S. M. (2003). Characterization and propagation of uncertainty in diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 50(5), 1077–1088.
Belmonte, M. K., Allen, G., Beckel-Mitchener, A., Boulanger, L. M., Carper, R. A., & Webb, S. J. (2004). Autism and abnormal development of brain connectivity. Journal of Neuroscience, 24(42), 9228–9231.
Bertollo, J. R., Strang, J. F., Anthony, L. G., Kenworthy, L., Wallace, G. L., & Yerys, B. E. (2020). Adaptive behavior in youth with autism spectrum disorder: The role of flexibility. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 50(1), 42–50.
Bertollo, J. R., & Yerys, B. E. (2019). More than IQ: Executive function explains adaptive behavior above and beyond nonverbal IQ in youth with autism and lower IQ. American Journal on Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities, 124(3), 191–205.
Bi, X., Zhao, J., Xu, Q., Sun, Q., & Wang, Z. (2018). Abnormal functional connectivity of resting state network detection based on linear ICA analysis in autism spectrum disorder. Frontiers in Psychology, 9, 475.
Bieleninik, L., Posserud, M. B., Geretsegger, M., Thompson, G., Elefant, C., & Gold, C. (2017). Tracing the temporal stability of autism spectrum diagnosis and severity as measured by the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE, 12(9), e0183160.
Blume, J., Kahathuduwa, C. K., & Mastergeorge, A. M. (2022). Intrinsic structural connectivity of the default mode network and behavioral correlates of executive function and social skills in youth with autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-022-05460-y
Bressler, S. L., & Menon, V. (2010). Large-scale brain networks in cognition: Emerging methods and principles. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 14, 277–290.
Buckner, R. L., & Wheeler, M. E. (2001). The cognitive neuroscience of remembering. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 2, 624–634.
Bzdok, D., Schilbach, L., Vogeley, K., Schneider, K., Laird, A. R., Langner, R., & Eickhoff, S. B. (2012). Parsing the neural correlates of moral cognition: ALE meta-analysis on morality, theory of mind, and empathy. Brain Structure & Function, 217(4), 783–796.
Cai, W., Chen, T., Szegletes, L., Supekar, K., & Menon, V. (2013). Aberrant time-varying cross-network interactions in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and the relation to attention deficits. Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging, 3(3), 263–273.
Calhoun, V. D., Adali, T., Pearlson, G. D., & Pekar, J. J. (2001). A method for making group inferences from functional MRI data using independent component analysis. Human Brain Mapping, 14(3), 140–151.
Chand, G. B., & Dhamala, M. (2016). Interactions among the brain default-mod, salience, and central-executive networks during perceptual decision-making of moving dots. Brain Connect, 6, 249–254.
Chang, C., & Glover, G. H. (2009). Relationship between respiration, end-tidal CO2, and BOLD signals in resting-state fMRI. NeuroImage, 47(4), 1381–1393.
Chen, A. C., Oathes, D. J., Chang, C., Bradley, T., Zhou, Z. W., Williams, L. M., Glover, G. H., Deisseroth, K., & Etkiin, A. (2013). Causal interactions between fronto-parietal central executive and default-mode networks in humans. PNAS, 110(49), 19944–19949.
Chiong, W., Wilson, S. M., D’Esposito, M., Kayser, A. S., Grossman, S. N., Poorzand, P., Seeley, W. W., Miller, B. L., & Rankin, K. P. (2013). The salience network causally influences default mode network activity during moral reasoning. Brain, 136(6), 1929–1941.
Cibralic, S., Kohlhoff, J., Wallace, N., McMahon, C., & Eapen, V. (2019). A systematic review of emotion regulation in children with autism spectrum disorder. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 68, 101422.
Constantino, J. N., & Gruber, C. P. (2005). Social responsiveness scale (SRS). Western Psychological Services.
Crone, E. A., & Steinbeis, N. (2017). Neural perspectives on cognitive control development during childhood and adolescence. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 21(3), 205–215.
De Lacy, N., Doherty, D., King, B. H., Rachakonda, S., & Calhoun, V. D. (2017). Disruption to control network function correlates with altered dynamic connectivity in the wider autism spectrum. NeuroImage: Clinical, 15, 513–524.
de Vries, M., & Geurts, H. (2015). Influence of autism traits and executive functioning on quality of life in children with an autism spectrum disorder. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 45(9), 2734–2743.
DeMayo, M. M., Young, L. J., Hickie, I. B., Song, Y. J. C., & Guastella, A. J. (2019). Circuits for social learning: A unified model and application too autism spectrum disorder. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 107, 388–398.
Descoteaux, M., Deriche, R., Knosche, T. R., & Anwander, A. (2009). Deterministic and probabilistic tractography based on complex fibre orientation distributions. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 28(2), 269–286.
Di Norcia, A., Pecorar, G., Bombi, A. S., Baumgartner, E., & Laghi, F. (2015). Hot and cool inhibitory control in Italian toddlers: Associations with social competence and behavioral problems. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 24, 909–914.
Diener, M. L., & Kim, D.-Y. (2004). Maternal and child predictors of preschool children’s social competence. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 25(1), 3–24.
Eisenberg, N., Fabes, R. A., & Spinirad, T. (2007). Prosocial development. In W. Damon & R. M. Lerner (Eds.), Handbook of child psychology: Social, emotional, and personality development. (Vol. 3). London: Wiley.
Freeman, L. M., Loocke, J., Rotheram-Fuller, E., & Mandell, D. (2017). Brief report: Examining executive and social functioning in elementary-aged children with autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 47(6), 1890–1895.
Gardiner, E., & Iarocci, G. (2018). Everyday executive function predicts adaptive and internalizing behavior among children with and without autism spectrum disorder. Autism Research, 11(2), 284–295.
Georgiades, S., Szatmari, P., & Boyle, M. (2013). Importance of studying heterogeneity in autism. Neuropsychiatry, 3(2), 123–125.
Gioa, G. A., Isquith, P. K., Guy, S. C., & Kenworthy, L. (2000). Behavior rating inventory of executive function (BRIEF). Psychological Assessment Resources.
Goulden, N., Khusnulina, A., Davis, N. J., Bracewell, R. M., Bokde, A. L., McNulty, J. P., & Mullins, P. G. (2014). The salience network is responsible for switching between the default mode network and the central executive network: Replication from DCM. NeuuroImage, 99, 180–190.
Green, S. A., Hernandez, L., Bookheimer, S. Y., & Dapretto, M. (2016). Salience network connectivity in autism is related to brain and behavioral markers of sensory overresponsivity. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 55(7), 618–626.
Grisot, G., Haber, S. N., & Yendiki, A. (2021). Diffusion MRI and anatomic tracing in the same brain reveal common failure modes of tractography. NeuroImage, 239, 118300.
Hassan, R., & Schmidt, L. A. (2021). Inhibitory control, dyadic social behavior, and mental health difficulties in preschoolers. Child Development, 93(3), e251–e265.
He, C., Chen, Y., Jian, T., Chen, H., Guo, X., Wang, J., Wu, L., Chen, H., & Duan, X. (2018). Dynamic functional connectivity analysis reveals decreased variability of the default-mode network in developing autistic brain. Autism Research, 11(11), 1479–1493.
Ho, N. S. P., Poerio, G., Konu, D., Turnbull, A., Sormaz, M., Leech, R., Bernhardt, B., Jefferies, E., & Smallwood, J. (2020). Facing up to why the wandering mind: Patterns of off-task laboratory thought are associated with stronger neural recruitment of right fusiform cortex while processing facial stimuli. NeuroImage, 214, 116765.
Hollocks, M. J., Jones, C. R. G., Pickles, A., Baird, G., Happe, F., Charman, T., & Simonoff, E. (2014). The association between social cognition and executive functioning and symptoms of anxiety and depression in adolescents with autism spectrum disorder. Autism Research, 7(2), 216–228.
Horn, A., Ostwald, D., Reisert, M., & Blankenburg, F. (2014). The structural-functional connectome and the default mode network of the human brain. NeuroImage, 15(102), 142–151.
Howlin, P., & Magiati, I. (2017). Autism spectrum disorder: Outcomes in adulthood. Current Opinion in Psychiatry, 30(2), 69–76.
Howlin, P., Moss, P., Savage, S., & Rutter, M. (2013). Social outcomes in mid- to later adulthood among individuals diagnosed with autism and average nonverbal IQ as children. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 52(6), 572–581.
Hu, L. T., & Bentler, P. M. (1999). Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Structural Equation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal, 6(1), 1–55.
Hutchison, L., Feder, M., Abar, B., & Winsler, A. (2016). Relations between parenting stress, parenting style, and child executive functioning for children with ADHD or autism. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 25(12), 3644–3656.
Jeste, S. S., & Geschwind, D. H. (2014). Disentangling the heterogeneity of autism spectrum disorder through genetic findings. Nature Reviews Neurology, 10(2), 74–81.
Kahathuduwa, C. N., Wakefield, S., West, B. D., Blume, J., Dassanayake, T. L., Weerasiinghe, V. S., & Mastergeorge, A. (2020). Effects of L-theanine-caffeine combination on sustained attention and inhibitory control among children with ADHD: A proof-of-concept neuroimaging RCT. Scientific Reports, 10, 13072.
Kahathuduwa, C. N., West, B., & Mastergeorge, A. M. (2019). Effects of overweight or obesity on brain resting state functional connectivity of children with autism spectrum disorder. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 49(12), 4751–4760.
Ke, F., Whalon, K., & Yun, J. (2018). Social skill interventions for youth and adults with autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review. Review of Educational Research, 88(1), 3–42.
Keown, C. L., Shih, P., Nair, A., Peterson, N., Mulvey, M., & Muller, R. A. (2013). Local functional overconnectivity in posterior brain regions is associated with symptom severity in autism spectrum disorders. Cell Reports, 5(3), 567–572.
King, J. B., Prigge, M. B. D., King, C. K., Morgan, J., Weathersby, F., Fox, J. C., Dean, D. C., III., Freeman, A., Villaruz, J. A. M., Kane, K. L., Bigler, E. D., Alexander, A. L., Lange, N., Zielinski, B., Lainhart, J. E., & Anderson, J. S. (2019). Generalizability and reproducibility of functional connectivity in autism. Molecular Autism, 10(1), 27.
Kitzbichler, M. G., Khan, S., Ganesan, S., Vangel, M. G., Herbert, M. R., Hämäläinen, M. S., & Kenet, T. (2014). Altered development and multifaceted band-specific abnormalities of resting state networks in autism. Biological Psychiatry, 77(9), 794–804.
Kotila, A., Jarvela, M., Korhonen, V., Loukusa, S., Hurtig, T., Ebeling, H., & Kiviniemi, V. (2021). Atypical inter-network deactivation associated with the posterior default-mode network in autism spectrum disorder. Autism Research, 14(2), 248–264.
Kouklari, E. C., Tsermentseli, S., & Monks, C. P. (2019). Developmental trends of hot and cool executive function in school-aged children with and without autism spectrum disorder: Links with theory of mind. Development and Psychopathology, 31(2), 541–556.
Kuhlthau, K., Orlich, F., Hall, T. A., Sikora, D., Kovacs, E. A., Delahaye, J., & Clemons, T. E. (2010). Health-related quality of life in children with autism spectrum disorders: Results from the Autism Treatment Network. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 40(6), 721–729.
Kupis, L., Romero, C., Dirks, B., Hoang, S., Parladé, M. V., Beaumont, A. L., Cardona, S. M., Alessandri, M., Chang, C., Nomi, J. S., & Uddin, L. Q. (2020). Evoked and intrinsic brain network dynamics in children with autism spectrum disorder. NeuroImage: Clinical, 28, 102396.
Lai, C. L. E., Lau, Z., Lui, S. S., Lok, E., Tam, V., Chan, Q., Cheng, K. M., Lam, S. M., & Cheung, E. F. C. (2017). Meta-analysis of neuropsychological measures of executive functioning in children and adolescents with high-functioning autism spectrum disorder. Autism Research, 10(5), 911–939.
Lawrence, K. E., Hernandez, L. M., Bookheimer, S. Y., & Dipretto, M. (2018). Atypical longitudinal development of functional connectivity in adolescents with autism spectrum disorder. Autism Research, 12, 53–65.
Lin, L. Y., & Huang, P. C. (2019). Quality of life and its related factors for adults with autism spectrum disorder. Disability and Rehabilitation, 41(8), 896–903.
Lipszyc, J., & Schachar, R. (2010). Inhibitory control and psychopathology: A meta-analysis of studies using the stop signal task. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 16(6), 1064–1076.
Logan, G. D., Schachar, R. J., & Tannock, R. (1997). Impulsivity and inhibitory control. Psychological Science, 8(1), 60–64.
Lord, C., Risi, S., Lambrecht, L., Cook, E. H. J., Leventhal, B. L., DiLavore, P. C., Pickles, A., & Rutter, M. (2000). The autism diagnostic observation schedule - generic: A standard measure of social and communication deficits associated with the spectrum of autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 30(3), 205–223.
Lord, C., Rutter, M., & Couteur, A. L. (1994). Autism diagnostic interview - revised: A reviewed version of a diagnostic interview for caregivers of individuals with possible pervasive developmental disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 24(5), 659–685.
Lynch, C. J., Breeden, A. L., You, X., Ludlum, R., Gaillard, W. D., Kenworthy, L., & Vaidya, C. J. (2017). Executive dysfunction in autism spectrum disorder is associated with a failure to modulate frontoparietal-insular hub architecture. Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging, 2(6), 537–545.
Lynch, C. J., Uddin, L. Q., Supekar, K., Khouzam, A., Phillips, J., & Menon, V. (2013). Default mode network in childhood autism: Posteriomedial cortex heterogeneity and relationship with social deficits. Biological Psychiatry, 74(3), 212–219.
Magiati, I., Tay, X. W., & Howlin, P. (2014). Cognitive, language, social, and behavioral outcomes in adults with autism spectrum disorders: A systematic review of longitudinal follow-up studies in adulthood. Clinical Psychology Review, 34, 73–86.
Mandelberg, J., Frankel, F., Cunningham, T., Gorospe, C., & Laugeson, E. A. (2013). Long-term outcomes of parent-assiisted social skills intervention for high-functioning children with autism spectrum disorders. Autism, 18(3), 255–263.
Mandelberg, J., Laugeson, E. A., Cunningham, T. D., Elliingsen, R., Bates, S., & Frankel, F. (2014). Long-term treatment outcomes for parent-assisted social skills training for adolescents with autism spectrum disorders: The UCLA PEERS Program. Journal of Mental Health Research in Intellectual Disabilities, 7(1), 45–73.
Mars, R. B., Neubert, F. X., Noonan, M. A. P., Sallet, J., Toni, I., & Rushworth, M. F. S. (2012). On the relationship between the “default mode network” and the “social brain.” Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 6, 189.
Memari, A. H., Ziaee, V., Shayestehfar, M., Ghanouni, P., Mansournia, M. A., & Moshayedi, P. (2013). Cognitive flexibility impairments in children with autism spectrum disorders: Links to age, gender, and child outcomes. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 34(10), 3218–3225.
Menon, V. (2011). Large-scale brain networks and psychopathology: A unifying triple network model. Trends in Cognitive Science, 15(10), 483–506.
Moffitt, T. E., Arseneault, L., Belsky, D., & Caspi, A. (2011). A gradient of childhood self-control predicts health, wealth, and public safety. PNAS, 108(7), 2693–2698.
Mottron, L., & Bzdok, D. (2020). Autism spectrum heterogeneity: Fact or artifact? Molecular Psychiatry, 25, 3178–3185.
Munsell, E. G. S., Orsmond, G. I., Fulford, D., & Coster, W. J. (2021). Metacognition mediates the effect of social communication and internalizing behaviors on self-management of daily life tasks for diploma-track autistic youth. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-021-05306-z
Newman, L., Wagner, M., Knokey, A.-M., Marder, C., Nagle, K., Shaver, D., & Wei, X. (2011). The post-high school outcomes of young adults with disabilities up to 8 years after high school: A report from the National Longitudinal Transition Study-2 (NLTS2). SRI International.
Nimsky, C., Bauer, M., & Carl, B. (2016). Merits and limits of tractography techniques for the uninitiated. In J. Schramm (Ed.), Advances and technical standards in neurosurgery. (Vol. 43). Springer.
O’Reilly, C., Lewis, J. D., & Elsabbagh, M. (2017). Is functional brain connectivity atypical in autism? A systematic review of EEG and MEG studies. PLoS ONE, 12(5), e0175870.
Ochsner, K. N., & Gross, J. J. (2005). The cognitive control of emotion. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 9(5), 242–249.
Odriozoal, P., Dajan, D. R., Burrows, C. A., Gabard-Durnam, L. J., Goodman, E., Baez, A. C., Tottenham, N., Uddin, L. Q., & Gee, D. G. (2019). Atypical frontoamygdala functional connectivity in youth with autism. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 37, 100603.
Pekar, V. (2001). Specification in terms of interactional properties as a way to optimize semantic representation of spatial expressions. In Proceedings of the ACL 2001 Workshop on Temporal and Spatial Information Processing. Retrieved from https://aclanthology.org/W01-1302
Pellicano, E. (2012). The development of executive function in autism. Autism Research and Treatment, 2, 146132.
Peugh, J., & Feldon, D. F. (2020). “How well does your structural equation model fit your data?”: Is Marcoulides and Yuan’s equivalence test the answer? CBE Life Sciences Education, 19(3), es5.
Pfeiffer, B., Piller, A., Giazzoni-Fialko, T., & Chainaani, A. (2017). Meaningful outcomes for enhancing quality of life for individuals with autism spectrum disorder. Journal of Intellectual & Developmental Disability, 42(1), 90–100.
Picci, G., & Scherf, K. S. (2014). A two-hit model of autism: Adolescence as the second hit. Clinical Psychological Science, 3(3), 349–371.
Posar, A., & Visconti, P. (2019). Long-term outcome of autism spectrum disorder. Turkish Archives of Pediatrics, 54(4), 2017–2212.
Pugliese, C. E., Anthony, L., Strang, J. F., Dudley, K., Wallace, G. L., & Kenworthy, L. (2015). Increasing adaptive behavior skill deficits from childhood to adolescence in autism spectrum disorder: Role of executive function. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 45(6), 1579–1587.
Radley, K. C., Dart, E. H., Brennan, K. J., Helbig, K. A., Lehmank, E. L., Silberman, M., & Mendanhall, K. (2020). Social skills teaching for individuals with autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review. Advances in Neurodevelopmental Disorders, 4(3), 215–226.
Raichle, M. E. (2015). The brain’s default mode network. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 38, 433–437.
Ratnarajah, N., Simmons, A., Davydov, O., & Hojjatoleslami, A. (2012). A novel approach for improved tractography and quantitative analysis of probabilistic fibre tracking curves. Medical Image Analysis, 16(1), 227–238.
Reniers, R. L. E. P., Corcoran, R., Völm, B. A., Mashru, A., Howard, R., & Liiddle, P. F. (2012). Moral decision-making, ToM, empathy, and the default mode network. Biological Psychology, 90(3), 202–210.
Rosen, B. Q., & Halgren, E. (2021). A whole-cortex probabilistic diffusion tractography connectome. eNeuro. https://doi.org/10.1523/enuro.0416-20.2020
Rosenthal, M., Wallace, G. L., Lawson, R., Wills, M. C., Dixon, E., Yerys, B. E., & Kenworthy, L. (2013). Impairments in real-world executive function increase from childhood to adolescence in autism spectrum disorders. Neuropsychology, 27(1), 13–18.
Roth, R. M., Isquith, P. K., & Gioia, G. A. (2014). Assessment of executive functioning using the Behavior Rating Inventory of Executive Function (BRIEF). In S. Goldstein & J. Naglieri (Eds.), Handbook of executive functioning. Springer.
Ryali, S., Supekar, K., Chen, T., Kochalka, J., Cai, W., Nicholas, J., Padmanabhan, A., & Menon, V. (2018). Temporal dynamics and developmental maturation of salience, default, and central-executive network interactions revealed by variational Bayes hidden Markov modeling. PLoS Computational Biology, 12(12), e1005138.
Shaw, S. B., McKinnon, M. C., Heisz, J., & Becker, S. (2021). Dynamic task-linked switching between brain networks: A tri-network perspective. Brain and Cognition, 151, 105725.
Sherman, L. E., Rudie, J. D., Pfeifer, J. H., Masten, C. L., McNealy, K., & Dapretto, M. (2014). Development of the default mode and central executive networks across early adolescence: A longitudinal study. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 10, 148–159.
Shumway, S., Thurm, A., Swedo, S. E., Deprey, L., Barnett, L. A., Amaral, D. G., Rogers, S. J., & Ozonoff, S. (2011). Brief report: Symptom onset patterns and functional outcomes in young children with autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorderrs, 41, 1727–1732.
Sivo, S. A., Fan, X., Witta, E. L., & Willse, J. T. (2006). The search for “optimal” cutoff properties: Fit index criteria in structural equation modeling. The Journal of Experimental Education, 74(3), 267–288.
Smallwood, J., Bernhardt, B. C., Leech, R., Bzdok, D., Jefferies, E., & Margulies, D. S. (2021). The default mode network in cognition: A topographical perspective. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 22, 503–513.
Smith, S. M., Jenkinson, M., Woolrich, M. W., Beckmann, C. F., Behrens, T. E. J., Johansen-Berg, H., Bannister, P. R., De Luca, M., Drobnjak, I., Flitney, D. E., Niazy, R. K., Saunders, J., Vickers, J., Zhang, Y., De Stefano, N., Brady, J. M., & Matthews, P. M. (2004). Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. NeuroImage, 23, S208-219.
Sridharan, D., Levitin, D. J., & Menon, V. (2008). A critical role for the right fronto-insular cortex in switching between central-executive and default-mode networks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 105(34), 12569–12574.
Thomason, M. E., Dennis, E. L., Joshi, A. A., Hoshi, S. H., Dinov, I. D., Chang, C., Henry, M. L., Johnson, R. F., Thompson, P. M., Toga, A. W., Glover, G. H., Van Horn, J. D., & Gotlib, I. H. (2011). Resting-state fMRI can reliably map neural networks in children. NeuroImage, 55(1), 165–175.
Thompson, A., & Steinbeis, N. (2020). Sensitive periods in executive function development. Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences, 36, 98–105.
Tobin, M. C., Drager, K. D. R., & Richardson, L. F. (2014). A systematic review of social participation for adults with autism spectrum disorders: Support, social functioning, and quality. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 8(3), 214–229.
Torske, T., Nærland, T., Øie, M. G., Stenberg, N., & Andreassen, O. A. (2018). Metacognitive aspects of executive function are highly associated with social functioning on parent-rated measures in children with autism spectrum disorder. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, 11, 258.
Tournier, J. D., Mori, S., & Leemans, A. (2011). Diffusion tensor imaging and beyond. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 65(6), 1532–1556.
Toyomaki, A., & Murohashi, H. (2013). “Salience network” dysfunction hypothesis in autism spectrum disorders. Japanese Psychological Research, 55(2), 175–185.
Travers, B. G., Adluru, N., Ennis, C., Tromp, D. P. M., Destische, D., Doran, S., Bigler, E. D., Lange, N., Lainhart, J. E., & Alexander, A. L. (2012). Diffusion tensor imaging in autism spectrum disorder: A review. Autism Research, 5(5), 289–313.
Tunç, B., Yankowitz, L. D., Parker, D., Alappatt, J. A., Pandey, J., Schultz, R. T., & Verma, R. (2019). Deviation from normative brain development is associated with symptom severity in autism spectrum disorder. Molecular Autism, 10, 46.
Turner, G. R., & Spreng, R. N. (2015). Prefrontal engagement and reduced default network suppression co-occur and are dynamically coupled in older adults: The default-executive coupling hypothesis of aging. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 27(12), 2462–2476.
Uddin, L. Q. (2015). Salience processing and insular cortical function and dysfunction. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 16(1), 55–61.
Uddin, L. Q., Supekar, K. S., & Menon, V. (2019). Reconceptualizing functional brain connectivity in autism from a developmental perspective. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 7, 458.
Uddin, L. Q., Supekar, K. S., Rryali, S., & Menon, V. (2011). Dynamic reconfiguration of structural and functional connectivity across core neurocognitive brain networks with development. Journal of Neuroscience, 31(5), 18578–18589.
Vincent, J. L., Snyder, A. Z., Fox, M. D., Shannon, B. J., Andrews, J. R., Raichle, M. E., & Buckner, R. L. (2006). Coherent spontaneous activity identifies a hippocampal -parietal memory network. Journal of Neurophysiology, 96(6), 3517–3531.
Vogan, V. M., Leung, R. C., Safar, K., Martinussen, R., Smith, M. L., & Taylor, M. J. (2019). Longitudinal examination of everyday executive functioning in children with ASD: Relations with social, emotional, and behavioral functioning over time. Frontiers Iin Psychology, 9, 1774. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2018.01774
Wallace, G. L., Kenworthy, L., Pugliese, C. E., Popal, H. S., White, E. I., Brodsky, E., & Martin, A. (2016). Real-world executive functions in adults with autism spectrum disorder: Profiles of impairment and associations with adaptive functioning and co-morbid anxiety and depression. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 46(3), 1071–1083.
Walsh, M. J. M., Baxter, L. C., Smith, C. J., & Braden, B. B. (2019). Age group differences in executive network functional connectivity and relationships with social behavior in men with autism spectrum disorder. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 63, 63–77.
Wang, K., Li, K., & Niu, X. (2021). Altered functional connectivity in a triple-network model in autism with co-occurring attention deficit hyperactivity. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 12, 736755.
Washington, S. D., Gordon, E. M., Brar, J., Warburton, S., Sawyer, A. T., Wolfe, A., Mease-Ference, E. R., Girton, L., Hailu, A., Mbwana, J., Gaillard, W. D., Kalbfleisch, M. L., & Van Meter, J. W. (2014). Dysmaturation of the default mode network in autism. Human Brain Mapping, 35(4), 1284–1296.
Weiss, M. J., & Harris, S. L. (2001). Teaching social skills to people with autism. Behavior Modification, 25(5), 785–802.
Williams, B. R., Ponesse, J. S., Schachar, R. J., Logan, G. D., & Tannock, R. (1999). Development of inhibitory control across the life span. Developmental Psychology, 35(1), 205–213.
Willoughby, M. T., Wylie, A. C., & Little, M. H. (2019). Testing longitudinal associations between executive function and academic achievement. Developmental Psychology, 55(4), 767–779.
Woolrich, M. W., Jbabdi, S., Patenaude, B., Chappell, M., Makni, S., Behrens, T., Beckmann, C., Jenkinson, M., & Smith, S. M. (2009). Bayesian analysis of neuroimaging data in FSL. NeuroImage, 45(1), S173-186.
Yang, L., Chen, X., Shen, Y. Q., Wang, H., Liu, J. R., Mei, T., Ji, Z. Z., Guo, Y. Q., Wang, F. F., Xu, L. Z., Tang, X. Z., Ma, Z. H., Wang, L. Q., Liu, J., Cao, Q. J., & Yan, C. G. (2018). Altered developmental trajectories in intrinsic function between default, salience, and executive networks in high-functioning autism. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/252320
Yerys, B. E., Gordon, E. M., Abrams, D. N., Satterthwaite, T. D., Weinblatt, R., Jankowski, J. F., Strang, J., Kenworthy, L., Gaillard, W. D., & Vaidya, C. J. (2015). Default mode network segregation and social deficits in autism spectrum disorder: Evidence from non-mediated children DMN in children with ASD. NeuroImage Clinical, 9, 223–232.
Yuan, K. H., Chan, W., Marcouilides, G. A., & Bentler, P. M. (2016). Assessing structural equation models by equivalence testing with adjusted fit indexes. Structural Equation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal, 23(3), 1–12.
Zhu, J., & Qiu, A. (2022). Interindividual variability in functional connectivity discovers differential development of cognition and transdiagnostic dimensions of psychopathology in youth. NeuroImage, 260, 119482.
Acknowledgments
The current study utilized data from the Autism Brain Imaging Database Exchange (ABIDE) II, which is supported by NIMH grant R21MH107045. The authors did not receive any funding for the current study, and the authors do not have any ties to the grant funding this ABIDE II data aggregation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study design and development. Preparation of behavioral data was completed by JB, and preparation of neuroimaging data was completed by SD and CK. Model analysis was led by JB, and interpretation of models was a collaboration of all authors. Manuscript writing was led by JB. All authors contributed to the manuscript writing, revisions, and approval of the final manuscript submitted.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors do not have conflicts of interest to report.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blume, J., Dhanasekara, C.S., Kahathuduwa, C.N. et al. Central Executive and Default Mode Networks: An Appraisal of Executive Function and Social Skill Brain-Behavior Correlates in Youth with Autism Spectrum Disorder. J Autism Dev Disord (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-023-05961-4
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-023-05961-4