Abstract
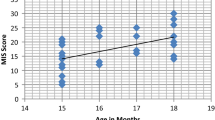
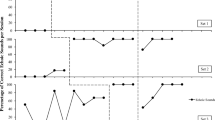
The Motor and Vocal Imitation Assessment (MVIA) was developed to evaluate a proposed hierarchy of imitation skills that could be used to formulate an experimentally-validated instructional guide for intervention. Imitation performance was assessed via the MVIA in 30 typically developing (TD) children and 30 children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). Children with ASD and TD demonstrated similar patterns of imitation. Children had higher performance scores in object imitation, followed by body, then vocal, and lastly facial imitation. The results revealed a pattern of imitation performance that provides the basis for an experimentally-validated instructional guide for intervention.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abravanel, E., Levan-Goldschmidt, E., & Stevenson, M. B. (1976). Action imitation: The early phase of infancy. Child Development, 47(4), 1032–1044.
Baer, D. M., Peterson, R. F., & Sherman, J. A. (1967). The development of imitation by reinforcing behavioral similarity to a model. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 10(5), 405–416.
Bandura, A. (1977). Social learning theory. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Beadle-Brown, J. (2004). Elicited imitation in children and adults with autism: The effect of different types of actions. Journal of Applied Research in Intellectual Disabilities, 17(1), 37–48.
Cardon, T. A. (2012). Teaching caregivers to implement video modeling imitation training via iPad for their children with autism. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 6(4), 1389–1400.
Cardon, T. A., & Wilcox, M. J. (2011). Promoting imitation in young children with autism: A comparison of reciprocal imitation training and video modeling. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 41(5), 654–666.
Charman, T., Baron-Cohen, S., Swettenham, J., Baird, G., Drew, A., & Cox, A. (2003). Predicting language outcome in infants with autism and pervasive developmental disorder. International Journal of Language & Communication Disorders, 38(3), 265–285.
Charman, T., Swettenham, J., Baron-Cohen, S., Cox, A., Baird, G., & Drew, A. (1997). Infants with autism: An investigation of empathy, pretend play, joint attention, and imitation. Developmental Psychology, 33(5), 781.
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (2nd ed.). Hillsdale, NJ: Eribaum.
Constantino, J. N. (2002). Social responsiveness scale-adult version (SRS). Los Angeles, CA: Western Psychological Services.
Dawson, G., & Adams, A. (1984). Imitation and social responsiveness in autistic children. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 12(2), 209–226.
Dawson, G., Rogers, S., Munson, J., Smith, M., Winter, J., Greenson, J., et al. (2010). Randomized, controlled trial of an intervention for toddlers with autism: the Early Start Denver Model. Pediatrics, 125(1), e17–e23.
Delano, M. E. (2007). Video modeling interventions for individuals with autism. Remedial and Special Education, 28(1), 33–42.
DeMyer, M. K., Alpern, G. D., Barton, S., DeMyer, W. E., Churchill, D. W., Hingtgen, J. N., et al. (1972). Imitation in autistic, early schizophrenic, and non-psychotic subnormal children. Journal of Autism and Childhood Schizophrenia, 2(3), 264–287.
Elsner, B. (2007). Infants’ imitation of goal-directed actions: The role of movements and action effects. Acta Psychologica, 124(1), 44–59.
Field, T. M., Woodson, R., Cohen, D., Greenberg, R., Garcia, R., & Collins, K. (1983). Discrimination and imitation of facial expressions by term and preterm neonates. Infant Behavior & Development.
Fenson, L., Dale, P. S., Reznick, J. S., Thal, D., Bates, E., Hartung, J. P., et al. (1993). The MacArthur communicative development inventories: User’s guide and technical manual. San Diego, CA: Singular Publishing Group.
Fitch, W. T. (2000). The evolution of speech: A comparative review. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 4(7), 258–267.
Fleiss, J. L., & Cohen, J. (1973). The equivalence of weighted kappa and the intraclass correlation coefficient as measures of reliability. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 33, 613–619.
Garfinkle, A. N., & Schwartz, I. S. (2002). Peer imitation increasing social interactions in children with autism and other developmental disabilities in inclusive preschool classrooms. Topics in Early Childhood Special Education, 22(1), 26–38.
Green, G., Brennan, L. C., & Fein, D. (2002). Intensive behavioral treatment for a toddler at high risk for autism. Behavior Modification, 26(1), 69–102.
Guillaume, P. (1971). Imitation in children. Trans. EP Halperin.
Heyes, C. (2010). Mesmerising mirror neurons. Neuroimage, 51(2), 789–791.
Hwang, B., & Hughes, C. (2000). The effects of social interactive training on early social communicative skills of children with autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 30(4), 331–343.
Ingersoll, B. (2008). The social role of imitation in autism: Implications for the treatment of imitation deficits. Infants & Young Children, 21(2), 107–119.
Ingersoll, B. (2012). Brief report: Effect of a focused imitation intervention on social functioning in children with autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 42(8), 1768–1773.
Jones, S. S. (2007). Imitation in infancy the development of mimicry. Psychological Science, 18(7), 593–599.
Kasari, C., Freeman, S., & Paparella, T. (2006). Joint attention and symbolic play in young children with autism: A randomized controlled intervention study. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 47(6), 611–620.
Kasari, C., Paparella, T., Freeman, S., & Jahromi, L. B. (2008). Language outcome in autism: Randomized comparison of joint attention and play interventions. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 76(1), 125.
Kleeberger, V., & Mirenda, P. (2010). Teaching generalized imitation skills to a preschooler with autism using video modeling. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 12(2), 116–127.
Leaf, R., & McEachin, J. (1999). A work in progress: Behavior management strategies and a curriculum for intensive behavioral treatment of autism. New York: DRL Books.
Ledford, J. R., & Wolery, M. (2011). Teaching imitation to young children with disabilities: A review of the literature. Topics in Early Childhood Special Education, 30(4), 245–255.
Lord, C., Rutter, M., DiLavore, P. C., & Risi, S. (1999). Autism diagnostic observation schedule-WPS (ADOS-WPS). Los Angeles, CA: Western Psychological Services.
Lovaas, O. I. (1987). Behavioral treatment and normal educational and intellectual functioning in young autistic children. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 55(1), 3.
Lovaas, O. I. (2003). Teaching individuals with developmental delays: Basic intervention techniques. Austin, TX: PRO-Ed.
Lovaas, O. I., Ackerman, A., Alexander, D., Firestone, P., Perkins, J., & Young, D. (1981). Teaching developmentally disabled children: The me book. Austin, TX: PRO-ed.
Lovaas, O. I., Freitas, L., Nelson, K., & Whalen, C. (1967). The establishment of imitation and its use for the development of complex behavior in schizophrenic children. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 5(3), 171–181.
Masur, E. F. (2008). Vocal and action imitation by infants and toddlers during dyadic interactions: Development, causes, and consequences. In S. J. Rogers & J. H. G. Williams (Eds.), Imitation and the social mind: Autism and typical development (pp. 27–47). New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Masur, E. F., & Ritz, E. G. (1984). Patterns of gestural, vocal, and verbal imitation performance in infancy. Merrill-Palmer Quarterly, 1982, 369–392.
McDowell, L. S., Gutierrez, A., Jr., & Bennett, K. D. (2015). Analysis of live modeling plus prompting and video modeling for teaching imitation to children with autism. Behavioral Interventions, 30(4), 333–351.
McDuffie, A., Turner, L., Stone, W., Yoder, P., Wolery, M., & Ulman, T. (2007). Developmental correlates of different types of motor imitation in young children with autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 37(3), 401–412.
McEwen, F., Happe, F., Bolton, P., Rijsdijk, F., Ronald, A., & Dworzynski, K. (2007). Origins of individual difference in imitation: Links with language, pretend play, and socially insightful behavior in 2-year-old twins. Child Development, 78(2), 474–492.
Meindl, J. N., & Cannella-Malone, H. I. (2011). Initiating and responding to joint attention bids in children with autism: A review of the literature. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 32(5), 1441–1454.
Meltzoff, A. N. (2005). Imitation and other minds: The “like me” hypothesis. Perspectives on Imitation: From Neuroscience to Social Science, 2, 55–77.
Meltzoff, A. N., & Moore, M. K. (1983). The origins of imitation in infancy: Paradigm, phenomena, and theories. Advances in Infancy Research.
Meltzoff, A. N., & Moore, M. K. (1997). Explaining facial imitation: A theoretical model. Early Development & Parenting, 6(3–4), 179.
Mercado, E., III, Mantell, J. T., & Pfordresher, P. Q. (2014). Imitating sounds: A cognitive approach to understanding vocal imitation. Comparative Cognition & Behavior Reviews. https://doi.org/10.3819/ccbr.2014.90002.
Metz, J. R. (1965). Conditioning generalized imitation in autistic children. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 2(4), 389–399.
Mody, M., Shui, A. M., Nowinski, L. A., Golas, S. B., Ferrone, C., O’Rourke, J. A., et al. (2017). Communication deficits and the motor system: exploring patterns of associations in autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 47(1), 155–162.
Mullen, E. M. (1995). Mullen: scales of early learning (AGS ed.). Circle Pines, MN: American Guideline Service Inc.
Mundy, P., Hogan, A., & Doehring, P. (1996). A manual for the abridged early social communication scales (ESCS). Miami: University of Miami.
Nadel, J., Guérini, C., Pezé, A., & Rivet, C. (1999). The evolving nature of imitation as a format for communication. In J. Nadel & G. Butterworth (Eds.), Cambridge studies in cognitive perceptual development Imitation in infancy (pp. 209–234). New York: Cambridge University Press.
Narum, S. R. (2006). Beyond Bonferroni: Less conservative analyses for conservation genetics. Conservation Genetics, 7(5), 783–787.
Over, H., & Carpenter, M. (2013). The social side of imitation. Child Development Perspectives, 7(1), 6–11.
Partington, J. W. (2008). The assessment of basic language and learning skills-revised (The ABLLS-R). Pleasant Hills, CA: Behavior Analysts.
Peck, C. A., Apolloni, T., Cooke, T. P., & Raver, S. A. (1978). Teaching retarded preschoolers to imitate the free-play behavior of nonretarded classmates: Trained and generalized effects. The Journal of Special Education, 12(2), 195–207.
Piaget, J. (1951). Play, dreams, and imitation in childhood. New York: Routledge.
Piasta, S. B., & Wagner, R. K. (2010). Developing early literacy skills: A meta-analysis of alphabet learning and instruction. Reading Research Quarterly, 45(1), 8–38.
Plavnick, J. B., Sam, A. M., Hume, K., & Odom, S. L. (2013). Effects of video-based group instruction for adolescents with autism spectrum disorder. Exceptional Children, 80(1), 67–83.
Poulson, C. L., Kyparissos, N., Andreatos, M., Kymissis, E., & Parnes, M. (2002). Generalized imitation within three response classes in typically developing infants. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 81(3), 341–357.
Raver, S. A., Cooke, T. P., & Apolloni, T. (1978). Developing nonretarded toddlers as verbal models for retarded classmates. Child Study Journal, 8, 1–8.
Rogers, S. J., Hepburn, S. L., Stackhouse, T., & Wehner, E. (2003). Imitation performance in toddlers with autism and those with other developmental disorders. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 44(5), 763–781.
Rogers, S. J., & Pennington, B. F. (1991). A theoretical approach to the deficits in infantile autism. Development and Psychopathology, 3(2), 137–162.
Rogers, S. J., Young, G. S., Cook, I., Giolzetti, A., & Ozonoff, S. (2010). Imitating actions on objects in early-onset and regressive autism: Effects and implications of task characteristics on performance. Development and Psychopathology, 22(1), 71–85.
Rosales-Ruiz, J., & Baer, D. M. (1997). Behavioral cusps: A developmental and pragmatic concept for behavior analysis. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 30(3), 533–544.
Schanding, G. T., Jr., Nowell, K. P., & Goin-Kochel, R. P. (2012). Utility of the social communication questionnaire-current and social responsiveness scale as teacher-report screening tools for autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 42(8), 1705–1716.
Sigman, M., & Ungerer, J. A. (1984). Cognitive and language skills in autistic, mentally retarded, and normal children. Developmental Psychology, 20(2), 293.
Smith, I. M., & Bryson, S. E. (1994). Imitation and action in autism: A critical review. Psychological Bulletin, 116(2), 259.
Stark, R. E. (1980). Stages of speech development in the first year of life. In Child phonology (pp. 73–92).
Stern, D. N. (1985). The interpersonal world of the infant: A view from psychoanalysis and developmental psychology. London: Karnac Books.
Stone, W. L., Ousley, O. Y., & Littleford, C. D. (1997). Motor imitation in young children with autism: What’s the object? Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 25(6), 475–485.
Stone, W. L., & Yoder, P. J. (2001). Predicting spoken language level in children with autism spectrum disorders. Autism, 5(4), 341–361.
Sundberg, M. L. (2008). Verbal behavior milestones assessment and placement program: The VB-MAPP. Concord, CA: AVB Press.
Toth, K., Munson, J., Meltzoff, A. N., & Dawson, G. (2006). Early predictors of communication development in young children with autism spectrum disorder: Joint attention, imitation, and toy play. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 36(8), 993–1005.
Trevarthen, C., Kokkinaki, T., & Fiamenghi, G. A., Jr. (1999). What infants’ imitations communicate: With mothers, with fathers and with peers. In J. Nadel & G. Butterworth (Eds.), Imitation in infancy (pp. 127–185). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Uzgiris, I. (1981). Two functions of imitation during infancy. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 4(1), 1–12.
Uzgiris, I. (1999). Imitation as activity: Its developmental aspects. In Imitation in infancy (186–206).
Uzgiris, I. C., & Hunt, J. (1975). Assessment in infancy: Ordinal scales of psychological development. Illinois: University of Illinois.
Vanvuchelen, M., Roeyers, H., & De Weerdt, W. (2007). Nature of motor imitation problems in school-aged boys with autism: A motor or a cognitive problem? Autism, 11(3), 225–240.
Venn, M. L., Wolery, M., Werts, M. G., Morris, A., DeCesare, L. D., & Cuffs, M. S. (1993). Embedding instruction in art activities to teach preschoolers with disabilities to imitate their peers. Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 8(3), 277–294.
Vivanti, G., McCormick, C., Young, G. S., Abucayan, F., Hatt, N., Nadig, A., et al. (2011). Intact and impaired mechanisms of action understanding in autism. Developmental Psychology, 47(3), 841–844.
Vivanti, G., Nadig, A., Ozonoff, S., & Rogers, S. J. (2008). What do children with autism attend to during imitation tasks? Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 101(3), 186–205.
Vivanti, G., Trembath, D., & Dissanayake, C. (2014). Mechanisms of imitation impairment in autism spectrum disorder. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 42(8), 1395–1405.
Wainer, A. L., & Ingersoll, B. R. (2015). Increasing access to an ASD imitation intervention via a telehealth parent training program. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 45(12), 3877–3890.
Williams, J. H., Whiten, A., & Singh, T. (2004). A systematic review of action imitation in autistic spectrum disorder. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 34(3), 285–299.
National Research Council (US). (2001). Committee on grand challenges in environmental sciences. Grand challenges in environmental sciences. Washington, DC: National Academy Press.
Yando, R., Seitz, V., & Zigler, E. (1978). Imitation: A developmental perspective. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Young, G. S., Rogers, S. J., Hutman, T., Rozga, A., Sigman, M., & Ozonoff, S. (2011). Imitation from 12 to 24 months in autism and typical development: A longitudinal Rasch analysis. Developmental Psychology, 47(6), 1565–1578.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EEA conceptualized and designed this study, drafted the manuscript, and approves the final version being submitted. AG contributed to the design, has reviewed and contributed to the current manuscript, and approves of the final version being submitted.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Espanola Aguirre, E., Gutierrez, A. An Assessment and Instructional Guide for Motor and Vocal Imitation. J Autism Dev Disord 49, 2545–2558 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-019-04008-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-019-04008-x