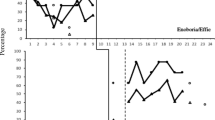
Abstract
We taught three typically developing siblings to occasion speech by implementing the Natural Language Paradigm (NLP) with their brothers with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). A non-concurrent multiple baseline design across children with ASD and sibling dyads was used. Ancillary behaviors of happiness, play, and joint attention for the children with ASD were recorded. Generalization of speech for the children with ASD across setting and peers was also measured. During baseline, the children with ASD displayed few target speech behaviors and the siblings inconsistently occasioned speech from their brothers. After sibling training, however, they successfully delivered NLP, and in turn, for two of the brothers with ASD, speech reached criterion. Implications of this research suggest the inclusion of siblings in interventions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. (5th edn.). Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Publishing.
Banda, D. R. (2015). Review of sibling interventions with children with autism. Education And Training in Autism and Developmental Disabilities, 50(3), 303–315.
Bass, J. D., & Mulick, J. A. (2007). Social play skill enhancement of children with autism using peers and siblings as therapists. Psychology in the Schools, 44(7), 727–735.
Celiberti, D. A., & Harris, S. L. (1993). Behavioral intervention for siblings of children with ASD: A focus on skills to enhance play. Behavior Therapy, 24(4), 573–599. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0005-7894(05)80319-3.
Chan, J. M., Lang, R., Rispoli, M., O’Reilly, M., Sigafoos, J., & Cole, H. (2009). Use of peer-mediated interventions in the treatment of autism spectrum disorders: A systematic review. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 3(4), 876–889.
Colletti, G., & Harris, S. L. (1977). Behavior modification in the home: Siblings as behavior modifiers, parents as observers. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 5(1), 21–30.
Coolican, J., Smith, I. M., & Bryson, S. E. (2010). Brief parent training in pivotal response treatment for preschoolers with ASD. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 51(12), 1321–1330.
Cooper, J. O., Heron, T. E., & Heward, W. L. (2007). Applied behavior analysis (2nd edn.). New York: Pearson Publishers.
Dunn, L. M., & Dunn, D. M. (2007). The peabody picture vocabulary test (4th edn.). Bloomington, MN: NCS Pearson, Inc.
Ekman, P., Freisen, W. V., & Ancoli, S. (1980). Facial signs of emotional experience. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 39(6), 1125.
Ferraioli, S. J., Hansford, A., & Harris, S. L. (2012). Benefits of including siblings in the treatment of ASD spectrum disorders. Cognitive And Behavioral Practice, 19(3), 413–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpra.2010.05.005.
Ferraioli, S. J., & Harris, S. L. (2011). Teaching joint attention to children with ASD through a sibling-mediated behavioral intervention. Behavioral Interventions, 26(4), 261–281. https://doi.org/10.1002/bin.336.
Gianoumis, S., Seiverling, L., & Sturmey, P. (2012). The effects of behavior skills training on correct teacher implementation of natural language paradigm teaching skills and child behavior. Behavioral Interventions, 27(2), 57–74.
Gillett, J. N., & LeBlanc, L. A. (2007). Parent-implemented natural language paradigm to increase language and play in children with ASD. Research In ASD Spectrum Disorders, 1(3), 247–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rasd.2006.09.003.
Green, C. W., & Reid, D. H. (1996). Defining, validating, and increasing indices of happiness among people with profound multiple disabilities. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 29(1), 67–78.
Harris, S. L. (1986). Parents as teachers: A four to seven year follow up of parents of children with ASD. Child & Family Behavior Therapy, 8(4), 39–47. https://doi.org/10.1300/J019v08n04_03.
Ihrig, K., & Wolchik, S. A. (1988). Peer versus adult models and autistic children’s learning: Acquisition, generalization, and maintenance. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 18(1), 67–79. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02211819.
Ingersoll, B., & Gergans, S. (2007). The effect of a parent-implemented imitation intervention on spontaneous imitation skills in young children with autism. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 28(2), 163–175.
Kasari, C., Paparella, T., Freeman, S., & Jahromi, L. B. (2008). Language outcome in autism: Randomized comparison of joint attention and play interventions. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 76(1), 125–137. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-006X.76.1.125.
Kassardjian, A., Taubman, M., Leaf, J., Edwards, A., McEachin, J., Leaf, R., & … Schulze, K. (2013). Utilizing Teaching Interactions to Facilitate Social Skills in the Natural Environment. Education & Training in Autism & Developmental Disabilities, 48(2), 245–257.
Koegel, R. L., O’Dell, M. C., & Koegel, L. K. (1987). A natural language teaching paradigm for nonverbal autistic children. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 17(2), 187–200. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01495055.
Laski, K. E., Charlop, M. H., & Schreibman, L. (1988). Training parents to use the Natural Language Paradigm to increase their autistic children’s speech. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 21(4), 391–400. https://doi.org/10.1901/jaba.1988.21-391.
LeBlanc, L. A., Geiger, K. B., Sautter, R. A., & Sidener, T. M. (2007). Using the Natural Language Paradigm (NLP) to increase vocalizations of older adults with cognitive impairments. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 28(4), 437–444.
Lovaas, O., Koegel, R., Simmons, J. Q., & Long, J. S. (1973). Some generalization and follow-up measures on autistic children in behavior therapy. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 6(1), 131–166. https://doi.org/10.1901/jaba.1973.6-131.
Luthar, S. S., & Cicchetti, D. (2000). The construct of resilience: Implications for interventions and social policies. Development and Psychopathology, 12, 857–885.
McCoy, K., & Hermansen, E. (2007). Video modeling for individuals with autism: A review of model types and effects. Education & Treatment Of Children, 30(4), 183–213. https://doi.org/10.1353/etc.2007.0029.
Moore, T., & Carey, L. (2005). Friendship formation in adults with learning disabilities: Peer-mediated approaches to social skills development. British Journal of Learning Disabilities, 33(1), 23–26. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-3156.2004.00292.x.
National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities. (2014). Prevalence of Autism Spectrum Disorder Among Children Aged 8 Years—Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 11 Sites, United States, 2010. Retrieved from http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/ss6302a1.htm?s_cid=ss6302a1_w.
Parsons, M. B., Reid, D. H., Bentley, E., Inman, A., & Lattimore, L. P. (2012). Identifying indices of happiness and unhappiness among adults with autism: Potential targets for behavioral assessment and intervention. Behavior Analysis in Practice, 5(1), 15–25.
Pellecchia, M., & Hineline, P. N. (2007). Generalization of mands in children with autism from adults to peers. The Behavior Analyst Today, 8(4), 483–491.
Pierce, K., & Schreibman, L. (1995). Increasing complex social behaviors in children with ASD: Effects of peer-implemented pivotal response training. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 28(3), 285–295. https://doi.org/10.1901/jaba.1995.28-285.
Rogers, S. J. (2006). Evidence-based interventions for language development in young children with autism. In T. Charman, W. Stone, T. Charman & W. Stone (Eds.), Social & communication development in autism spectrum disorders: Early identification, diagnosis, & intervention (pp. 143–179). New York: Guilford Press.
Schertz, H. H., & Odom, S. L. (2007). Promoting joint attention in toddlers with autism: A parent-mediated developmental model. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 37(8), 1562–1575.
Schertz, H. H., Odom, S. L., Baggett, K. M., & Sideris, J. H. (2013). Effects of Joint Attention Mediated Learning for toddlers with autism spectrum disorders: An initial randomized controlled study. Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 28(2), 249–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecresq.2012.06.006.
Schreibman, L., & Anderson, A. (2001). Focus on integration: The future of the behavioral treatment of ASD. Behavior Therapy, 32(4), 619–632. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0005-7894(01)80012-5.
Schreibman, L., O’Neill, R. E., & Koegel, R. L. (1983). Behavioral training for siblings of autistic children. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 16(2), 129–138. https://doi.org/10.1901/jaba.1983.16-129.
Seiverling, L., Pantelides, M., Ruiz, H. H., & Sturmey, P. (2010). The effect of behavioral skills training with general-case training on staff chaining of child vocalizations within natural language paradigm. Behavioral Interventions, 25(1), 53–75.
Shire, S., Goods, K., Shih, W., Distefano, C., Kaiser, A., Wright, C., & … Kasari, C. (2015). Parents’ adoption of social communication intervention strategies: Families including children with autism spectrum disorder who are minimally verbal. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 45(6), 1712–1724. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-014-2329-x.
Shivers, C. M., & Plavnick, J. B. (2015). Sibling involvement in interventions for individuals with autism spectrum disorders: A systematic review. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 45(3), 685–696. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-014-2222-7.
Smith, A. J., Bihm, E. M., Tavkar, P., & Sturmey, P. (2005). Approach-avoidance and happiness indicators in natural environments: A preliminary analysis of the Stimulus Preference Coding System. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 26(3), 297–313.
Sparrow, S. S., Cicchetti, D. V., & Balla, D. A. (2005). Vineland-II adaptive behavior scales: Survey forms manual. Circle Pines, MN: AGS Publishing.
Stadnick, N., Stahmer, A., & Brookman-Frazee, L. (2015). Preliminary effectiveness of project imPACT: A parent-mediated intervention for children with autism spectrum disorder delivered in a community program. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 45(7), 2092–2104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-015-2376-y.
Stahmer, A. C., & Schreibman, L. (1992). Teaching children with autism appropriate play in unsupervised environments using a self-management treatment package. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 25(2), 447–459. https://doi.org/10.1901/jaba.1992.25-447.
Stokes, T. F., & Baer, D. M. (1977). An implicit technology of generalization. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 10(2), 349–367. https://doi.org/10.1901/jaba.1977.10-349.
Tomasello, M., & Farrar, M. J. (1986). Joint attention and early language. Child Development, 57, 1454–1463.
Toth, K., Munson, J., Meltzoff, A. N., & Dawson, G. (2006). Early predictors of communication development in young children with autism spectrum disorder: Joint attention, imitation, and toy play. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 36(8), 993–1005.
Tsao, L., & Odom, S. L. (2006). Sibling-mediated social interaction intervention for young children With ASD. Topics In Early Childhood Special Education, 26(2), 106–123. https://doi.org/10.1177/02711214060260020101.
Walton, K. M., & Ingersoll, B. R. (2012). Evaluation of a sibling-mediated imitation intervention for young children with ASD. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 14(4), 241–253. https://doi.org/10.1177/1098300712437044.
Williams, K. T. (2007). Expressive vocabulary test. (2nd edn). Circle Pines, MN: AGS Publishing.
Zhang, J., & Wheeler, J. J. (2011). A meta-analysis of peer-mediated interventions for young children with autism spectrum disorders. Education And Training In Autism And Developmental Disabilities, 46(1), 62–77.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
VS conceived of the study, participated in its design and coordination, performed the measurement, helped in the interpretation of the data, and drafted the manuscript; MHC conceived of the study, participated in its design, coordination, and interpretation of the data, and helped to draft the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spector, V., Charlop, M.H. A Sibling-Mediated Intervention for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: Using the Natural Language Paradigm (NLP). J Autism Dev Disord 48, 1508–1522 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-017-3404-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-017-3404-x