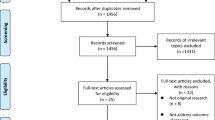
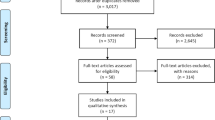
Abstract
As the link between maternal obesity and risk of autism among offspring is unclear, the present study assessed this association. A systematic search of an electronic database was performed to identify observational studies that examined the association between maternal obesity and autism. The outcome measures were odds ratios comparing offspring autism risk between obese and normal-weight mothers. Five observational studies were included in the meta-analysis. A fixed-effects model was used since low heterogeneity was observed between studies. The pooled adjusted odds ratio was 1.47 (95 % CI 1.24–1.74). The meta-analysis results support an increased risk of autism spectrum disorder in children of women who were obese during pregnancy. However, further study is warranted to confirm these results.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.
Atladóttir, H. Ó., Thorsen, P., Østergaard, L., Schendel, D. E., Lemcke, S., Abdallah, M., & Parner, E. T. (2010). Maternal infection requiring hospitalization during pregnancy and autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 40(12), 1423–1430.
Baird, G., Simonoff, E., Pickles, A., Chandler, S., Loucas, T., Meldrum, D., & Charman, T. (2006). Prevalence of disorders of the autism spectrum in a population cohort of children in South Thames: The special needs and autism project (SNAP). Lancet, 368(9531), 210–215.
Baron-Cohen, S., Scott, F. J., Allison, C., Williams, J., Bolton, P., Matthews, F. E., & Brayne, C. (2009). Prevalence of autism-spectrum conditions: UK school-based population study. British Journal of Psychiatry, 194(6), 500–509.
Bilder, D. A., Bakian, A. V., Viskochil, J., Clark, E. A., Botts, E. L., Smith, K. R., et al. (2013). Maternal prenatal weight gain and autism spectrum disorders. Pediatrics, 132(5), e1276–e1283.
Bolton, P., Pickles, A., Murphy, M., & Rutter, M. (1998). Autism, affective and other psychiatric disorders: patterns of familial aggregation. Psychological Medicine, 28(02), 385–395.
Buescher, A. V., Cidav, Z., Knapp, M., & Mandell, D. S. (2014). Costs of autism spectrum disorders in the United Kingdom and the United States. JAMA Pediatrics, 168(8), 721–728.
Catalano, P. M., Kirwan, J. P., Haugel-de Mouzon, S., & King, J. (2003). Gestational diabetes and insulin resistance: role in short-and long-term implications for mother and fetus. Journal of Nutrition, 133(5), 1674S–1683S.
CDC. (2014). Prevalence of autism spectrum disorders among children aged 8 years: Autism and developmental disabilities monitoring network, 11 sites, United States, 2010. MMWR Surveillance Summaries, 63(2), 1–22.
Chen, X., & Scholl, T. O. (2005). Oxidative stress: changes in pregnancy and with gestational diabetes mellitus. Current Diabetes Reports, 5(4), 282–288.
Das, U. (2001). Is obesity an inflammatory condition? Nutrition, 17(11), 953–966.
Dodds, L., Fell, D. B., Shea, S., Armson, B. A., Allen, A. C., & Bryson, S. (2011). The role of prenatal, obstetric and neonatal factors in the development of autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 41(7), 891–902.
Eidelman, A. I., & Samueloff, A. (2002) The pathophysiology of the fetus of the diabetic mother. Seminars in perinatology. Elsevier (pp 232–236).
Ervin, R. B. (2009). Prevalence of metabolic syndrome among adults 20 years of age and over, by sex, age, race and ethnicity, and body mass index: United States. National Health Statistics Reports, 13, 1–8.
Flegal, K. M., Carroll, M. D., Ogden, C. L., & Curtin, L. R. (2010). Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999–2008. JAMA, 303(3), 235–241.
Gardener, H., Spiegelman, D., & Buka, S. L. (2009). Prenatal risk factors for autism: Comprehensive meta-analysis. British Journal of Psychiatry, 195(1), 7–14.
Georgieff, M. K. (2006). The effect of maternal diabetes during pregnancy on the neurodevelopment of offspring. Minnesota Medicine, 89(3), 44–47.
Georgieff, M. K. (2008). The role of iron in neurodevelopment: Fetal iron deficiency and the developing hippocampus. Biochemical Society Transactions, 36(Pt 6), 1267.
Greenland, S. (1987). Quantitative methods in the review of epidemiologic literature. Epidemiologic Reviews, 9(1), 1–30.
Higgins, J. P., Thompson, S. G., Deeks, J. J., & Altman, D. G. (2003). Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. British Medical Journal, 327(7414), 557.
Kim, Y. S., Fombonne, E., Koh, Y. J., Kim, S. J., Cheon, K. A., & Leventhal, B. L. (2014). A comparison of DSM-IV pervasive developmental disorder and DSM-5 autism spectrum disorder prevalence in an epidemiologic sample. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 53(5), 500–508.
Krakowiak, P., Walker, C. K., Bremer, A. A., Baker, A. S., Ozonoff, S., Hansen, R. L., & Hertz-Picciotto, I. (2012). Maternal metabolic conditions and risk for autism and other neurodevelopmental disorders. Pediatrics, 129(5), e1121–e1128.
Kyrou, I., & Tsigos, C. (2009). Stress hormones: Physiological stress and regulation of metabolism. Current Opinion in Pharmacology, 9(6), 787–793.
Man, K. K., Tong, H. H., Wong, L. Y., Chan, E. W., Simonoff, E., & Wong, I. C. (2015). Exposure to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors during pregnancy and risk of autism spectrum disorder in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 49C, 82–89.
Miles, J. H. (2011). Autism spectrum disorders—a genetics review. Genetics in Medicine, 13(4), 278–294.
Moss, B. G., & Chugani, D. C. (2014). Increased risk of very low birth weight, rapid postnatal growth, and autism in underweight and obese mothers. American Journal of Health Promotion, 28(3), 181–188.
Newschaffer, C. J., Croen, L. A., Daniels, J., Giarelli, E., Grether, J. K., Levy, S. E., et al. (2007). The epidemiology of autism spectrum disorders. Annual Reviews in Public Health, 28, 235–258.
Olefsky, J. M., & Glass, C. K. (2010). Macrophages, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Annual Review of Physiology, 72, 219–246.
Pardo, C. A., Vargas, D. L., & Zimmerman, A. W. (2005). Immunity, neuroglia and neuroinflammation in autism. International Review of Psychiatry, 17(6), 485–495.
Ramsay, J. E., Ferrell, W. R., Crawford, L., Wallace, A. M., Greer, I. A., & Sattar, N. (2002). Maternal obesity is associated with dysregulation of metabolic, vascular, and inflammatory pathways. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 87(9), 4231–4237.
Reynolds, L. C., Inder, T. E., Neil, J. J., Pineda, R. G., & Rogers, C. E. (2014). Maternal obesity and increased risk for autism and developmental delay among very preterm infants. Journal of Perinatology, 34(9), 688–692.
Rosen, B. N., Lee, B. K., Lee, N. L., Yang, Y., & Burstyn, I. (2014). Maternal smoking and autism spectrum disorder: A meta-analysis. Journal of autism and developmental disorders, 45(6), 1689–1698.
Sandin, S., Lichtenstein, P., Kuja-Halkola, R., Larsson, H., Hultman, C. M., & Reichenberg, A. (2014). The familial risk of autism. JAMA, 311(17), 1770–1777.
Simonoff, E., Pickles, A., Charman, T., Chandler, S., Loucas, T., & Baird, G. (2008). Psychiatric disorders in children with autism spectrum disorders: prevalence, comorbidity, and associated factors in a population-derived sample. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 47(8), 921–929.
Suren, P., Gunnes, N., Roth, C., Bresnahan, M., Hornig, M., Hirtz, D., et al. (2014). Parental obesity and risk of autism spectrum disorder. Pediatrics, 133(5), e1128–e1138.
Wells, G., Shea, B., O’Connell, D., Peterson, J., Welch, V., & Losos, M. (2013) The Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality if nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses 2009.
Xu, G., Jing, J., Bowers, K., Liu, B., & Bao, W. (2014). Maternal diabetes and the risk of autism spectrum disorders in the offspring: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 44(4), 766–775.
Zavalza-Gómez, A. B., Anaya-Prado, R., Rincón-Sánchez, A. R., & Mora-Martínez, J. M. (2008). Adipokines and insulin resistance during pregnancy. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, 80(1), 8–15.
Zumoff, B., & Strain, G. W. (1994). A perspective on the hormonal abnormalities of obesity: Are they cause or effect? Obesity Research, 2(1), 56–67.
Author Contributions
Ya-Min Li and Si-Yuan Tang conceived and designed the experiments. Jian-Jun Ou, Li Liu and Dan Zhang performed the experiments. Ya-Min Li, Jing-Ping Zhao and Si-Yuan Tang analyzed the data. Ya-Min Li and Jian-Jun Ou contributed software, hardware and analysis tools. Ya-Min Li, Jing-Ping Zhao and Si-Yuan Tang wrote the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Research Involving Human Participants and/or Animals
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, YM., Ou, JJ., Liu, L. et al. Association Between Maternal Obesity and Autism Spectrum Disorder in Offspring: A Meta-analysis. J Autism Dev Disord 46, 95–102 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-015-2549-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-015-2549-8