Abstract
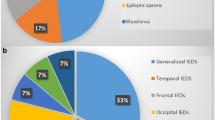
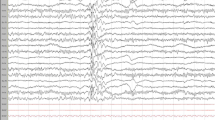
This study examined the nature and frequency of neurological and EEG abnormalities in 60 young children (ages 2–6 years) with pervasive developmental disorders. A number of standard neurological functions could not be adequately assessed due to the young age of the children and/or limited comprehension and cooperation. The most common neurological deficits were hyporeflexia, stereotypies, and hypotonia. EEG abnormalities were identified in 32% of the children while only two children were known to have clinical seizures. The frequency of cases with hypotonia or hyporeflexia was more common than in older children with this diagnosis. Results also indicate that EEG abnormalities are common in this young population but clinical seizures are rare, confirming other studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrien, J. L., Lenoir, P., Martineau, J., Perrot, A., Hameury, L., Larmande, C., et al. (1993). Blind ratings of early symptoms of autism based upon family home movies. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 32(3), 617–626.
Akshoomoff, N., Lord, C., Lincoln, A. J., Courchesne, R. Y., Carper, R. A., Townsend, J., et al. (2004). Outcome classification of preschoolers with autism spectrum disorders using MRI brain measures. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 43, 349–357.
American Psychiatric Association. (1994). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th ed.). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.
Arthur, G. (1980). Arthur adaptation of the leiter international performance scale. Wood Dale, IL: Stoelting.
Baird, G., Charman, T., Cox, A., Baron-Cohen, S., Swettenham, J., Wheelwright, S., et al. (2001). Screening and surveillence for autism and pervasive developmental disorders. Archives of Diseases in Childhood, 84, 468–475.
Ballaban-Gil, K., & Tuchman, R. (2000). Epilepsy and epileptiform EEG: Association with autism and language disorders. Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities Research Reviews, 6, 300–308.
Baranek, G. T. (2002). Efficacy of sensory and motor interventions for children with autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 32(5), 397–422.
Bauman, M. L. (1992). Motor dysfunction in autism. In A. B. Joseph, & R. R. Young, (Eds.), Movement disorders in neurology and psychiatry (pp. 660–663). Boston: Blackwell.
Carper, R. A., & Courchesne, E. (2005). Localized enlargement of the frontal cortex in early autism. Biological Psychiatry, 57(2), 126–133.
Charman, T., & Baird, G. (2002). Practitioner review: Diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder in 2- and 3-year-old children. Journal of Child Psychology & Psychiatry, 43(3), 289–305.
Courchesne, E., Karns, C., Davis, H. R., Ziccardi, R., Carper, R., Tigue, Z., et al. (2001). Unusual Brain Growth Patterns in Early Life in Patients with Autistic Disorder: An MRI Study. Neurology, 57, 245–254.
DiLavore, P. C., Lord, C., & Rutter, M. (1995). The pre-linguistic autism diagnostic observation schedule. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 25(4), 355–379.
Dunn, L. M., & Dunn, L. (1981). Manual for the Peabody Picture Vocabulary Test-Revised (PPVT-R). Circle Pines, MN: American Guidance Service.
Filipek, P. A., Accardo, P. J., Ashwal, S., Baranek, G. T., Cook, E. H. Jr., Dawson, G., et al. (2000). Practice parameter: screening and diagnosis of autism: report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the Child Neurology Society. Neurology, 55(4), 468–479.
Filipek, P. A., Accardo, P. J., Baranek, G. T., Cook, E. H. Jr., Dawson, G., Gordon, B., et al. (1999). The screening and diagnosis of autistic spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 29(6), 439–484.
Giovanardi Rossi, P., Parmeggiani, A., Bach, V., Santucci, M., & Visconti, P. (1995). EEG features and epilepsy in patients with autism. Brain and Development, 17, 169–174.
Giovanardi Rossi, P., Posar, A., & Parmeggiani, A. (2000). Epilepsy in adolescents and young adults with autistic disorder. Brain and Development, 22, 102–106.
Haas, R. H., Townsend, J., Courchesne, E., Lincoln, A. J., Schreibman, L., & Yeung-Courchesne, R. (1996). Neurologic abnormalities in infantile autism. Journal of Child Neurology, 11(2), 84–92.
Hardan, A. Y., Kilpatrick, M., Keshavan, M. S., & Minshew, N. J. (2003). Motor performance and anatomic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the basal ganglia in autism. Journal of Child Neurology, 18(5), 317–324.
Kim, S. J., Cox, N., Courchesne, R., Lord, C., Corsello, C., Akshoomoff, N., et al. (2002). Transmission disequilibrium mapping at the serotonin transporter gene (SLC6A4) region in autistic disorder. Molecular Psychiatry, 7, 278–288.
Klin, A., Sparrow, S. S., Marans, W. D., Carter, A., & Volkmar, F. R. (2000). Assessment issues in children, adolescents with Asperger syndrome. In A. Klin, F. R. Volkmar, & S. S. Sparrow, (Eds.), Asperger syndrome. New York: Guilford Press.
Le Couteur, A., Rutter, M., Lord, C., Rios, P., Robertson, S.,& Holdgrafer, M., et al. (1989). Autism diagnostic interview: a standardized investigator-based instrument. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 19(3), 363–387.
Lord, C., & Risi, S. (2000). Diagnosis of autism spectrum disorders in young children. In A. Wetherby, & B. Prizant, (Eds.), Autism spectrum disorders: A transactional developmental perspective (pp. 167–190). Baltimore: Paul H. Brookes Publishing Co.
Lord, C., Risi, S., Lambrecht, L., Cook E. H Jr, Leventhal, B. L.,& DiLavore, P. C., et al. (2000). The Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule—Generic: A standard measure of social and communication deficits associated with the spectrum of autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 30(3), 205–223.
Lord, C., Rutter, M., & Le Couteur, A. (1994). Autism Diagnostic Interview-Revised: a revised version of a diagnostic interview for caregivers of individuals with possible pervasive developmental disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 24(5), 659–685.
McVicar, K. A., & Shinnar, S. (2004). Landau-Kleffner Syndrome, Electrical Status Epilepticus in Slow Wave Sleep, and Language Regression in Children. Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities Research Reviews, 10, 144–149.
Minshew, N. J., Sung, K., Jones, B. L., & Furman, J. M. (2006). Underdevelopment of the postural control system in autism. Neurology, 63, 2056–2061.
Minshew, N. J., Sweeney, J. A., Bauman, M. L., & Webb, S. J. (2005). Neurologic aspects of autism. In F. R. Volkmar, R. Paul, A. Klin & D. Cohen (Eds.), Autism and pervasive developmental disorders (3rd ed., Vol. 1, pp. 473–514). Hoboken, N.J.: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Mullen, E. M. (1995). Mullen scales of early learning (AGS ed.). Circle Pines, MN: American Guidance Service Inc.
Muller, R. A., Kleinhans, N., Kemmotsu, N., Pierce, K., & Courchesne, E. (2003). Abnormal variability and distribution of functional maps in autism: an FMRI study of visuomotor learning. American Journal of Psychiatry, 160, 1847–1862.
Muller, R. A., Pierce, K., Ambrose, J. B., Allen, G., & Courchesne, E. (2001). Atypical patterns of cerebral motor activation in autism: a functional magnetic resonance study. Biological Psychiatry, 49(8), 665–676.
Rapin, I. (Ed.). (1996). Preschool children with inadequate communication: Developmental language disorder, autism, low IQ (Clinics in Developmental Medicine, Vol. 139). London: Mac Keith Press.
Rogers, S. (2001). Diagnosis of autism before the age of 3. International Review of Mental Retardation, 23, 1–31.
Schopler, E., Reichler, R. J., & Rochen Renner, B. (1988). The Childhood Autism Rating Scale: Western Psychological Services.
Shinnar, S., Rapin, I., Arnold, S., Tuchman, R. F., Shulman, L., Ballaban-Gil, K., et al. (2001). Language regression in childhood. Pediatric Neurology, 24, 183–189.
Sparrow, S., Balla, D., & Cicchetti, D. (1984). Vineland scales of adaptive behavior: Interview edition, survey form. Circle Pines, MN: American Guidance Service.
Teitelbaum, P., Teitelbaum, O., Nye, J., Fryman, J., & Maurer, R. G. (1998). Movement analysis in infancy may be useful for early diagnosis of autism. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 95(23), 13982–13987.
Thorndike, R. L., Hagen, E. P., & Sattler, J. M. (1986). The Stanford-Binet intelligence scale: Fourth Edition. Chicago: The Riverside Publishing Company.
Tuchman R., & Rapin, I. (2002). Epilepsy and autism. Lancet Neurology, 1, 352–358.
Tuchman, R. F., & Rapin, I. (1997). Regression in pervasive developmental disorders: Seizures and epileptiform electroencephalogram correlates. Pediatrics, 99, 560–566.
Wechsler, D. (1991). Wechsler intelligence scale for children, Third Edition. San Antonio: The Psychological Corporation.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the families who participated in this study. Catherine Lord, Ph.D., Senia Pizzo, Ph.D., and Alan Lincoln, Ph.D. provided diagnostic information, and Vera Grindell, B.S. assisted in data analyses. Mark Nespeca, M.D. assisted with EEG interpretation. Supported by NINDS grant R01NS19855.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akshoomoff, N., Farid, N., Courchesne, E. et al. Abnormalities on the Neurological Examination and EEG in Young Children with Pervasive Developmental Disorders. J Autism Dev Disord 37, 887–893 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-006-0216-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-006-0216-9