Abstract
This paper presents the results of a numerical study of the kinetics of electrochemical oxidation of different organic substances at boron doped diamond (BDD).
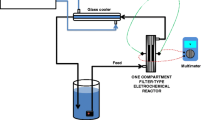
It is well established that oxidation of organics at BDD anodes takes place in the potential region of oxygen evolution, through reaction steps in which OH radicals are involved: these radicals can react with organic compounds to give more oxidised substances, or with water to give oxygen. Because of the high reactivity of OH radicals these reactions are confined to a thin film adjacent to the electrode surface. A mathematical model was implemented, which accounts for chemical and electrochemical reactions, as well as for the transport phenomena involved in the process: the parameters of the model were derived from experimental data. The model allowed calculation of the trend with time of reactant concentration, reaction intermediates and oxidisable agents: their space profiles in the reactor were also obtained. The numerical predictions of the model were compared with experimental results obtained from galvanostatic electrolyses of different organic compounds: (a) 2,4,6-trihydroxy-1,3,5 triazine also known as cyanuric acid (CA), which is well known to be refractory to oxidation with OH; (b) atrazine (ATR) the most oxidisable precursor of CA, and (c) phenol which is considered as an OH scavenger because of its high reactivity. The agreement between experimental and model predicted data was good in all the examined conditions.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a :
-
Specific electrode area \(a=\frac{A}{V}\) (m−1)
- A :
-
Electrode area (m2)
- C i :
-
Concentration of the ith compound (mol m−3)
- d :
-
Nozzle diameter (m)
- D i :
-
Diffusivity of the ith compound (m2 s−1)
- F :
-
Faraday number (C mol−1)
- i :
-
Current density (A m−2)
- i lim :
-
Limiting current density (A m−2)
- k i :
-
OH-organic specific reaction rate (dm3 mol−1 s−1)
- k m :
-
Mass transfer coefficient (m s−1)
- k OH :
-
OH deactivation specific reaction rate (s−1)
- Re :
-
Reynolds number \(Re=\frac{v d \rho}{\mu}\)
- Sc :
-
Schmidt number \(Sc=\frac{\mu }{\rho D_i}\)
- Sh :
-
Sherwood number \(Sh=\frac{k_{\rm m} d}{D_i}\)
- V :
-
Volume of solution (m3)
- δ:
-
Diffusion layer thickness \(\delta =\frac{D_i}{k_{\rm m}}\) (m)
- μ:
-
Viscosity of electrolyte (kg m−1 s−1)
- ν:
-
Linear velocity in the nozzle (m s−1)
- ρ:
-
Density of electrolyte (kg m3)
References
Simond O., Schaller V., Comninellis C. (1997). Electrochim. Acta 13–14:2009
Panizza M., Michaud P., Cerisola G., Comninellis C. (2001). Binny. Electrochem. Comm. 3:336
Gherardini L., Michaud P., Panizza M., Cerisola G., Comninellis C. (2001). J. Electrochem Soc. D78:148
Iniesta J., Michaud P., Panizza M., Cerisola G., Aldaz A., Comninellis C. (2001). Electrochim. Acta 46:3573
Polcaro A.M., Mascia M., Palmas S., Vacca A. (2005). Electrochim. Acta 50:1841
Rodrigo M.A., Michaud P., Duo I., Panizza M., Cerisola G., Comninellis C. (2001). J. Electrochem. Soc. 148:D60
Polcaro A.M., Mascia M., Palmas S., Vacca A. (2003). J. Appl. Electrochem. 33:885
Polcaro A.M., Mascia M., Palmas S., Vacca A. (2004). Electrochim. Acta 49:649
Canizares P., Garcia-Gomez J., Lobato J., Rodrigo M.A. (2004). Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 43:1915
Cañizares P., Sáez C., Lobato J., Rodrigo M.A. (2004). Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 43:6629
Cañizares P., Sáez C., Lobato J., Rodrigo M.A. (2004). Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 43:1944
Cañizares P., Lobato J., Paz R., Rodrigo M.A., Sáez C. (2005). Wat. Res. 39:2687
Nasr B., Abdellatif G., Cañizares P., Sáez C., Lobato J., Rodrigo M.A. (2005). Environ. Sci. Technol. 39:7234
Pelizzetti E., Maurino V., Minero C., Carlin V., Tosato M.L., Pramauro E., Zerbinati O. (1990). Environ. Sci. Technol. 24:1559
Bozzi A., Dhananjeyan M., Guasaquillo I., Parra S., Pulgarin C., Weins C., Kiwi J. (2004). J. Photochem. Photobiol. A: Chem. 162:179
Minero C., Pelizzetti E., Malato S., Blanco J. (1996). Solar Energy 56:411
Young-Chul Oh, Jenks W.S. (2004). J. Photochem. Photobiol. A: Chem. 162:323
Perry R.H., Green D.W. (1997). Perry’s Chemical Engineers’ Handbook 7th edn. Mc Graw Hill, New York
Kicuchi Y., Sunada K., Iyoda T., Hashimoto K., Fujishima A. (1997). J. Photochem. Photobiol. A: Chem. 106:51
Ross F., Ross A.B. (1977). Selected Specific Rates of Reactions of Transient from Water in Aqueous Solution III Hydroxyl Radical and Perhydroxyl Radical and their Radical Ions. US Dept. of Commerce, Washington
Hoffmann R., Martin S.T., Choi W., Bahnemann D. (1995). Chem. Rev. 95:69
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mascia, M., Vacca, A., Palmas, S. et al. Kinetics of the electrochemical oxidation of organic compounds at BDD anodes: modelling of surface reactions. J Appl Electrochem 37, 71–76 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-006-9217-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-006-9217-9