Abstract
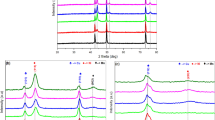
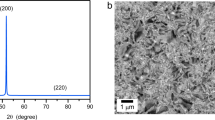
Grain size and texture of Ni electrodeposited from sulfamate baths depend greatly on current density. Increasing grain size is observed with increasing current density and the deposit texture changes from 〈110〉 at current densities lower than 5 mA cm−2 to 〈100〉 for higher current densities. Co-deposition of Mn modifies the deposit structure by favoring the growth of the 〈110〉 texture and decreasing the average grain size even as the current density increases. While the average Mn film content increases with increasing current density, local Mn concentrations are a more complex function of deposition parameters, as indicated by atom probe tomography measurements. In both direct-current plated and pulse plated films, large variations on a nanometer scale in local Mn concentration are observed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weil R., Sumka H.J. and Greene G.W. (1967). J. Electrochem. Soc. 114:449
Kelly J.J., Goods S.H. and Yang N.Y.C. (2003). Electrochem. Solid State Lett. 6:C88–91
Buchheit T.E., LaVan D.A., Michael J.R., Christenson T.R. and Leith S.D. (2002). Metall. Mater. Trans. A 33:539–554
Goods S.H., Kelly J.J. and Yang N.Y.C. (2004). Microsyst. Technol. 10:498–505
Mandich N.V. and Baudrand D.W. (2002). Plat. Surf. Finish. 89:68–76
Atanassov N. and Mitreva V. (1996). Surf. Coat. Technol. 78:144–149
Dini J.W. (1993). Electrodeposition: The Materials Science of Coatings and Substrates. Noyes Publications, Westwood
Malone G.A. (1987). Plat Surf Finish 74:50–56
A.A. Talin, E.A. Marquis, S.H. Goods and J.J. Kelly, Acta Mater. (in press)
Kocks U.F., Tome C.N. and Wenk H.R. (1998). Texture and Anisotropy, Preferred Orientatoin in Polyscyrtals and their Effect on Materials Properties. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Information on the BEARTEX package is available via the following web site: http://www.eps.berkeley.edu/∼Wenk/TexturePage/beartex.html
Goldstein J.I. et al. (2003). Scanning Electron Microscopy and X-ray Microanalysis. Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishing, New York
Miller M.K. and Smith G.D.W. (1989). Atom Probe Microanalysis: Principles and Applications to Materials Problems. MSR, Pittsburg
Atanassov N. and Schils H.W. (1999). J. Appl. Electrochem. 29:51
Thuvander M., Abraham M., Cerezo A. and Smith G.D.W. (2001). Mater. Sci. Technol. 17:961–970
Acknowledgements
Joshua Funamura, Andy Gardea, and Michael Rye are thanked for support in sample preparation and characterization. EAM specially thanks the staff at Imago Scientific Instruments Co., and the Northwestern University Center for Atom Probe Tomography. Sandia is a multiprogram laboratory operated by Sandia Corporation, a Lockheed-Martin Company, for the United States Department of Energy National Nuclear Security Administration under contract DE-AC04-94AL85000.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marquis, E.A., Talin, A.A., Kelly, J.J. et al. Effects of current density on the structure of Ni and Ni–Mn electrodeposits. J Appl Electrochem 36, 669–676 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-006-9119-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-006-9119-x