Abstract
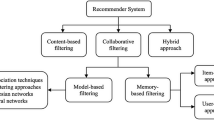
Nowadays people manage their social circles via a variety of online social media which employ social recommendation as an important component. Among social recommendation methods, global methods take an emphasis on common tastes between people while local methods assume that new relations are established mainly through people’s common friends. However, in a real social network, both local and global relations exist, which motivate us to integrate them to improve recommendation performance. To achieve the goal, we proposed a novel hybrid method GLORY to combine global associations with local correlations for social recommendation. GLORY consists of two components: GLOBE and LORY. The former is a globalised regression model to explore the concordance between people’s preference with the relatedness of their friends. The latter is an integration method to fuse global and local correlations via a rigorous statistical model to calibrate the statistical significance of these correlations. Furthermore, we demonstrated the effectiveness of our methods via 10-fold large-scale cross-validation on three real social network datasets (Facebook, Last.fm and Epinions). Results show that GLORY significantly outperform the state-of-the-art methods while LORY is effective across various global and local methods, indicating their promising future for social recommendations.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adomavicius, G., & Tuzhilin, A. (2005). Toward the next generation of recommender systems: A survey of the state-of-the-art and possible extensions. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 17, 734–749.
AlFalahi, K., Atif, Y., & Abraham, A. (2016). Folksonomy-Based Recommender Systems: A State-of-the-Art Review. International Journal of Intelligent Systems, 31, 314–346.
Alon, U. (2007). Network motifs: theory and experimental approaches. Nature Reviews Genetics, 8(6), 450–461.
Anagnostopoulos, A., Kumar, R., & Mahdian, M. (2008). Influence and correlation in social networks. In The 14th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, 5, 7–15. ACM.
Backstrom, L., & Leskovec, J. (2011) Supervised random walks: predicting and recommending links in social networks. In The 4th ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining (pp. 635–644).
Bhattacharya, D., & Ram, S. (2015). RT @News: An Analysis of News Agency Ego Networks in a Microblogging Environment. ACM Transactions Management Information Systems, 6(3), 11:1–11:25.
Bouadjenek, M. R., Hacid, H., & Bouzeghoub, M. (2016). Social networks and information retrieval, how are they converging? A survey, a taxonomy and an analysis of social information retrieval approaches and platforms. Information Systems, 56, 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.is.2015.07.008.
Cacheda, F., Carneiro, V., Fernandez, D., & Formoso, V. (2011). Comparison of collaborative filtering algorithms: limitations of current techniques and proposals for scalable, high-performance recommender systems. ACM Transactions on the Web, 5, 2:1–2:33.
Cannistraci, C. C. V., & Alanis-Lobato, G. (2013). Ravasi, T. From link-prediction in brain connectomes and protein interactomes to the local-community-paradigm in complex networks. Scientific Reports, 3, 1–13.
Easley, D., & Kleinberg, J. (2010). Networks, crowds, and markets: reasoning about a highly connected world. Science, 81(80), 744.
Eom, Y. H., & Jo, H. H. (2014). Generalized friendship paradox in complex networks: the case of scientific collaboration. Scientific Reports, 4, 4603.
Gan, M. (2014). Walking on a User Similarity network towards personalized recommendations. PloS One, 9, e114662.
Gan, M. (2016a). COUSIN: a network-based regression model for personalized recommendations. Decision Support Systems, 82, 58–68.
Gan, M. (2016b). Taffy: incorporating tag information into a diffusion process for personalized recommendations. World Wide Web-internet & Web Information Systems, 19, 933–955.
Gan, M., & Jiang, R. (2013a). Constructing a user similarity network to remove adverse influence of popular objects for personalized recommendation. Expert Systems with Applications, 40, 4044–4053.
Gan, M., & Jiang, R. (2013b). Improving accuracy and diversity of personalized recommendation through power law adjustments of user similarities. Decision Support Systems, 55(3), 811–821.
Georgiou, O., & Tsapatsoulis, N. (2010) The importance of similarity metrics for representative users identification in recommender systems. In Artificial Intelligence Applications and Innovations. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Herlocker, J. L., Konstan, J. A., Terveen, K., & Riedl, J. T. (2004). Evaluating collaborative filtering recommender systems. ACM Transactions on Information Systems, 22, 5–53.
Ho, Q., Yin, J., & Xing, E. P. (2012). On triangular versus edge representations - towards scalable modelling of networks. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 25, 1–9.
Huang, Z., Chen, H., & Zeng, D. (2004). Applying associative retrieval techniques to alleviate the sparsity problem in collaborative filtering. ACM Transactions on Information Systems, 22, 116–142.
Jaccard, P. (1901). Distribution de la flore alpine dans le bassin des Dranses et dans quelques régions voisines. Bull la Société Vaudoise des Sci Nat, 37, 241–272.
Jamali, M., & Ester, M. (2010) A matrix factorization technique with trust propagation for recommendation in social networks. In the 4th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, 45, 135–142. ACM.
Kardara, M., Papadakis, G., Papaoikonomou, A., Tserpes, K., & Varvarigou, T. (2015). Large-scale evaluation framework for local influence theories in Twitter. Information Processing & Management, 51(1), 226–252.
Katz, L. (1953). A new status index derived from sociometric analysis. Psychometrika, 18, 39–43.
Koren, Y., Bell, R., & Volinsky, C. (2009) Matrix factorization techniques for recommender systems. Computer, 42(8), 30–37.
Lee, J., Agrawal, M., & Rao, H. R. (2015). Message diffusion through social network service: The case of rumor and non-rumor related tweets during Boston bombing 2013. Information Systems Frontiers, 17(5), 997–1005.
Leskovec, J., Backstrom, L., Kumar, R., & Tomkins, A. (2008) Microscopic evolution of social networks. ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (pp. 462–470). ACM.
Leskovec, J., Huttenlocher, D., & Kleinberg, J. (2010) Signed networks in social media. Sigchi Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (pp. 1361–1370). ACM.
Li, M., Zou, H., Guan, S., Gong, X., Li, K., et al. (2013a). A coevolving model based on preferential triadic closure for social media networks. Scientific Reports, 3, 2512.
Li, Y. M., Hsiao, H. W., & Lee, Y. L. (2013b). Recommending social network applications via social filtering mechanisms. Information Sciences, 239, 18–30.
Li, Y., Lin, L., & Lin, Y. (2014). A recommender mechanism for social knowledge navigation in an online encyclopedia. Information Processing & Management, 50(5), 634–652.
Liao, H., & Zeng, A. (2015). Reconstructing propagation networks with temporal similarity. Scientific Reports, 5, 11404.
Liu, L., Xu, J., Liao, S. S., & Chen, H. (2014). A real-time personalized route recommendation system for self-drive tourists based on vehicle to vehicle communication. Expert Systems with Applications, 41(7), 3409–3417.
McKerlich, R., Ives, C., & McGreal, R. (2013). Measuring use and creation of open educational resources in higher education. International Review of Research in Open and Distance Learning, 14(4), 90–103.
Menon, A., & Elkan, C. (2011). Link prediction via matrix factorization. Mach Learn Knowledge Discovery Databases, 6912, 437–452.
Milo, R., Shen-Orr, S., Itzkovitz, S., Kashtan, N., Chklovskii, D., & Alon, U. (2002). Network motifs: simple building blocks of complex networks. Science, 298(5594), 824–827.
Newman, M. E., & Park, J. (2003). Why social networks are different from other types of networks. Physical Review E, 68(3), 036122.
Paterek, A. (2007) Improving regularized singular value decomposition for collaborative filtering. In KDD Cup and Workshop.
Rapoport, A. (1953). Spread of information through a population with socio-structural bias: I. Assumption of transitivity. The Bulletin of Mathematical Biophysics, 15(4), 523–533.
Rong, W., Peng, B., Ouyang, Y., Liu, K., & Xiong, Z. (2015). Collaborative personal profiling for web service ranking and recommendation. Information Systems Frontiers, 17(6), 1265–1282.
Shervashidze, N., Vishwanathan, S. V. N., Petri, T. H., Mehlhorn, K., & Borgwardt, K. M. (2009) Efficient graphlet kernels for large graph comparison. Aistats, 488–495.
Tang, J., Gao, H., Hu, X., & Liu, H. (2013) Exploiting homophily effect for trust prediction. ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining (pp. 53–62). ACM.
Tsai, C. W., Lai, C. F., Chao, H. C., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2015). Big data analytics: a survey. Journal of Big Data, 2(1), 1–32.
Tsourakakis, C. E. (2008) Fast counting of triangles in large real networks without counting: Algorithms and laws. Eighth IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (pp. 608–617). IEEE Computer Society.
Viswanath, B., Mislove, A., Cha, M., & Gummadi, K. P. (2009) On the evolution of user interaction in Facebook. In The 2nd ACM Workshop on Online Social Networks, 39, 37–42. ACM.
Watts, D. J., & Strogatz, S. H. (1998). Collective dynamics of “small-world” networks. Nature, 393, 440–442.
Xie, H., Li, X., Wang, T., Raymond, Y. K., Lau, T. L., Wong, L. C., Fu, L., & Wang, Q. L. (2016). Incorporating sentiment into tag-based user profiles and resource profiles for personalized search in folksonomy. Information Processing & Management, 52(1), 61–72.
Yang, S. H., Long, B., Smola, A., Sadagopan, N., Zheng, Z., & Zha, H. (2011) Like like alike: joint friendship and interest propagation in social networks. In The 20th International Conference on World Wide Web (pp. 537–546).
Yu, Z., Wang, C., Bu, J., Wang, X., Wu, Y., & Chen, C. (2015). Friend recommendation with content spread enhancement in social networks. Information Sciences, 309, 102–118.
Zhang, J., Wang, Y., & Vassileva, J. (2013a). SocConnect: A personalized social network aggregator and recommender. Information Processing & Management, 49(3), 721–737.
Zhang, Z., Zeng, D. D., Abbasi, A., Peng, J., & Zheng, X. (2013b) A random walk model for item recommendation in social tagging systems. ACM Transactions on Management Information Systems, 4(2), 8.
Zhou, T., Ren, J., Medo, M., & Zhang, Y. C. (2007). Bipartite network projection and personal recommendation. Physical Review E, 76, 46115.
Acknowledgements
This work was partly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants No. 71471016 and No. 71101010, and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities under Grants No. FRF-BR-16-002B.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gan, M., Sun, L. & Jiang, R. GLORY: Exploration and integration of global and local correlations to improve personalized online social recommendations. Inf Syst Front 21, 925–939 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-017-9797-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-017-9797-4