Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the effectiveness of combined photodynamic therapy with verteporfin and intrastromal injection of bevacizumab for the treatment of corneal neovascularization in patients with Stevens–Johnson syndrome (SJS).
Methods
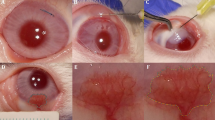
Eight eyes of eight patients with SJS having corneal neovascularization who were refractory to 1% prednisolone instillation received photodynamic therapy with verteporfin (6 mg/m2) combined with intrastromal bevacizumab injection (2.5 mg/0.1 mL). Best-corrected visual acuity and intraocular pressure were assessed, and slit-lamp biomicroscopic examination was performed before treatment and at 1 week and every month. A chronic ocular manifestation score was assigned based on the involvement area or the severity before treatment. The cumulative length of corneal blood vessels and area of corneal neovascularization were measured by anterior segment photographs before and after treatment.
Results
At 3 and 6 months after treatment, all eyes showed regression of corneal neovascularization. Complete regression was achieved in five eyes (62.5%) and partial regression in three eyes (37.5%). Among five patients who were followed up for more than 1 year, two eyes maintained complete regression and one eye maintained partial regression at 1 year. However, two eyes with severe chronic ocular manifestation showed revascularization.
Conclusions
Combined photodynamic therapy with intrastromal bevacizumab injection can effectively inhibit corneal neovascularization in patients with SJS. However, patients with severe chronic ocular manifestation may exhibit revascularization.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saeed HN, Kohanim S, Le HG et al (2016) Stevens–Johnson syndrome and corneal ectasia: management and a case for association. Am J Ophthalmol 169:276–281
Kohanim S, Palioura S, Saeed HN et al (2016) Stevens–Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis—a comprehensive review and guide to therapy. I. Systemic disease. Ocul Surf 14(1):2–19
Gregory DG (2016) New grading system and treatment guidelines for the acute ocular manifestations of Stevens–Johnson syndrome. Ophthalmology 123(8):1653–1658
John T, Foulks GN, John ME et al (2002) Amniotic membrane in the surgical management of acute toxic epidermal necrolysis. Ophthalmology 109(2):351–360
Chang YS, Huang FC, Tseng SH et al (2007) Erythema multiforme, Stevens–Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis: acute ocular manifestations, causes, and management. Cornea 26(2):123–129
Jongkhajornpong P, Lekhanont K, Siriyotha S et al (2017) Factors contributing to long-term severe visual impairment in Stevens–Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Ophthalmol 2017:2087578
Uy HS, Chan PS, Ang RE (2008) The topical bevacizumab and ocular surface neovascularization in patients with Stevens–Johnson syndrome. Cornea 27(1):70–73
Di Pascuale MA, Espana EM, Liu DT et al (2005) Correlation of corneal complications with eyelid cicatricial pathologies in patients with Stevens–Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis syndrome. Ophthalmology 112(5):904–912
Cursiefen C, Masli S, Ng TF et al (2004) Roles of thrombospondin-1 and -2 in regulating corneal and iris angiogenesis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45(4):1117–1124
Phillips K, Arffa R, Cintron C et al (1983) Effect of prednisolone and medroxyprogesterone on corneal wound healing, ulceration, and neovascularization. Arch Ophthalmol 101(4):640–643
Ambati BK, Joussen AM, Ambati J et al (2002) Angiostatin inhibits and regresses corneal neovascularization. Arch Ophthalmol 120(8):1063–1068
Corrent G, Roussel TJ, Tseng SCG et al (1989) Promation of graft survival by photothrombotic occlusion of corneal neovascularization. Arch Ophthalmol 107(10):1501–1506
Pillai CT, Dua HS, Hossain P (2000) Fine needle diathermy occlusion of corneal vessels. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 41(8):2148–2153
Qian CX, Bahar I, Levinger E et al (2008) Superficial keratectomy and subconjunctival bevacizumab injection for corneal neovascularization. Cornea 27(9):1090–1092
Brooks BJ, Ambati BK, Marcus DM et al (2004) Photodynamic therapy for corneal neovascularisation and lipid degeneration. Br J Ophthalmol 88(6):840
Yoon KC, You IC, Kang IS et al (2007) Photodynamic therapy with verteporfin for corneal neovascularization. Am J Ophthalmol 144(3):390–395
Chang JH, Garg NK, Lunde E et al (2012) Corneal neovascularization: an anti-VEGF therapy review. Surv Ophthalmol 57(5):415–429
Kim YC, Grossniklaus HE, Edelhauser HF et al (2014) Intrastromal delivery of bevacizumab using microneedles to treat corneal neovascularization. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 55(11):7376–7386
Tatar O, Adam A, Shinoda K et al (2006) Expression of VEGF and PEDF in choroidal neovascular membranes following verteporfin photodynamic therapy. Am J Ophthalmol 142(1):95–104
You IC, Kang IS, Lee SH, Yoon KC (2009) Therapeutic effect of subconjunctival injection of bevacizumab in the treatment of corneal neovascularization. Acta Ophthalmol 87(6):653–658
Bahar I, Kaiserman I, McAllum P et al (2008) Subconjunctival bevacizumab injection for corneal neovascularization. Cornea 27(2):142–147
You IC, Im SK, Lee SH, Yoon KC (2011) Photodynamic therapy with verteporfin combined with subconjunctival injection of bevacizumab for corneal neovascularization. Cornea 30(1):30–33
Sotozono C, Ang LP, Koizumi N et al (2007) New grading system for the evaluation of chronic ocular manifestations in patients with Stevens–Johnson syndrome. Ophthalmology 114(7):1294–1302
Kim DH, Yoon KC, Seo KY et al (2015) The role of systemic immunomodulatory treatment and prognostic factors on chronic ocular complications in Stevens–Johnson syndrome. Ophthalmology 122(2):254–264
Lee HS, Mayumi U, Yoon KC et al (2016) Analysis of ocular manifestation and genetic association of allopurinol-induced Stevens–Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in south Korea. Cornea 35(2):199–204
Koenig Y, Bock F, Horn F et al (2009) Short- and long-term safety profile and efficacy of topical bevacizumab (Avastin) eye drops against corneal neovascularization. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 247(10):1375–1382
Kesarwani S, Sahu SK, Basu S (2012) Bilateral response after unilateral subconjunctival bevacizumab injection in a child with Stevens–Johnson syndrome. J AAPOS 16(3):309–311
Uy HS, Yu EN, Sua AS (2011) Histologic findings of bevacizumab-treated human conjunctiva in Stevens–Johnson syndrome. Cornea 30(11):1273–1276
Erdurmus M, Totan Y (2007) Subconjunctival bevacizumab for corneal neovascularization. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 245(10):1577–1579
Kim SW, Ha BJ, Kim EK et al (2008) The effect of topical bevacizumab on corneal neovascularization. Ophthalmology 115(6):e33–e38
Veritti D, Vergallo S, Lanzetta P (2012) Triple therapy for corneal neovascularization: a case report. Eur J Ophthalmol 22(Suppl 7):S126–S128
Kim RY, Chung SK, Kim MS, Ra H (2016) Effects of combined photodynamic therapy and topical bevacizumab treatment on corneal neovascularization in rabbits. Cornea 35(12):1615–1620
Acknowledgements
This study was partially supported by the Chonnam National University Hospital Biomedical Research Institute (CRI 13906-22) and Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (2017R1A2B4003367).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that he/she has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoon, H.J., Kim, M.K., Seo, K.Y. et al. Effectiveness of photodynamic therapy with verteporfin combined with intrastromal bevacizumab for corneal neovascularization in Stevens–Johnson syndrome. Int Ophthalmol 39, 55–62 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-017-0786-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-017-0786-x