Abstract
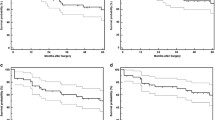
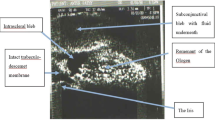
The aim was to report the results of deep sclerectomy (DS) with supraciliary hema implant and the influence of the surgical complications on intraocular pressure (IOP). Forty-eight eyes of 41 patients with open angle glaucoma (OAG), who underwent DS with supraciliary hema implant (Esnoper® V-2000), were included in this study. A significant IOP reduction was observed, changing from a preoperative mean of 24.6 ± 6.33 mmHg to 16.5 ± 4.4 mmHg (p < 0.001) at 12 months and 16.1 ± 3.4 mmHg (p < 0.001), at 24 months. Similarly, a significant reduction in the number of glaucoma drugs needed was observed, varying from 2.71 to 0.22 (p < 0.001) and 0.4 (p < 0.001), 1 and 2 years after surgery. Goniopuncture with the Nd:Yag Laser was performed in 30 eyes (62.5 %) with a mean time between the surgery and the procedure of 150 days, producing a mean IOP reduction of 4.0 mmHg (p < 0.001). The main intraoperative complications were microperforation of the trabeculodescemetic membrane (TDM) in 1 eye (2.08 %) The main early postoperative complications were seidel at 24 h in 11 eyes (22.91 %), hyphema in 7 eyes (14.58 %), choroidal detachment in 3 eyes (6.25 %) with macular folds in 2 (4.16 %) and need for additional mitomycin injections in 2 eyes (4.16 %). All these complications were spontaneously resolved. No correlation between these complications and final IOP was found, but a significant correlation between the presence of hyphema and higher IOP 24 months postoperatively (p = 0.048) was observed. DS with supraciliary hema implant is a safe and effective technique for the management of OAG. The presence of hyphema during the first week after the surgery could be considered as a negative prognostic factor in DS with supraciliary implantation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Muñoz G (2009) Nonstitch suprachoroidal technique for T-flux implantation in deep sclerectomy. J Glaucoma 18:262–264
Bonilla R, Loscos J, Valldeperas X, Parera MA, Sabala A (2012) Supraciliary hema implant in combined deep sclerectomy and phacoemulsification: one year results. Open Ophthalmol J 6:59–62
Mermoud A, Shaarawy T (2001) Non penetrating glaucoma surgery. Martin Dunitz, London, p 97
Development Core Team (2011) A language and environment for statistical computing. R foundation for statistical computing, Vienna, Austria. http://www.R-project.org/. Accessed May 2012
Cheng JW, Ma XY, Wei RL (2004) Efficacy of non-penetrating trabecular surgery for open angle glaucoma: a meta-analysis. Chin Med J. (Engl) 117:1006–1010
Lachkar Y, Neverauskiene J, Jeanteur-Lunel MN et al (2004) Nonpenetrating deep sclerectomy: a 6-year retrospective study. Eur J Ophthalmol 14:26–36
Ravinet E, Bovey E, Mermoud A (2004) T-Flux implant versus Healon GV in deep sclerectomy. J Glaucoma 13:46–50
Leszczyński R, Formińska-Kapuścik M, Bubała-Stachowicz B, Mrukwa-Kominek E, Filipek E, Pawlicki K (2012) Nonpenetrating very deep sclerectomy with hyaluronic acid implant vs trabeculectomy—a 2-year follow-up. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 250:1835–1841
Grieshaber MC, Schoetzau A, Flammer J, Orgül S (2013) Postoperative microhyphema as a positive prognostic indicator in canaloplasty. Acta Ophthalmol 91(2):151–156
Koch JM, Heiligenhaus A, Heinz C (2011) Canaloplasty and transient anterior chamber haemorrhage. A prognostic factor? Klin Monbl Augenheilkd 228:465–467
Hamel M, Shaarawy T, Mermoud A (2001) Deep sclerectomy with collagen implant in patients with glaucoma and high myopia. J Cataract Refract Surg 27:1410–1417
Konstas AG, Jay JL (1992) Modification of trabeculectomy to avoid postoperative hyphaema. The ‘guarded anteriorfistula’ operation. Br J Ophthalmol 76:353–357
Coob CJ, Chakrabarti S, Chadha V, Sanders R (2007) The effect of aspirin and warfarin therapy in trabeculectomy. Eye 21:598–603
Figus M, Bartolomei MP, Lazzeri S, Nardi M (2011) Very deep sclerectomy. J Glaucoma 20:67
Conflict of interest
None of the authors has conflict of interest
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Loscos, J., Valldeperas, X., Langhor, K. et al. Deep sclerectomy with supraciliary hema implant (Esnoper® V-2000): results and complications. Int Ophthalmol 35, 693–699 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-015-0037-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-015-0037-y