Abstract
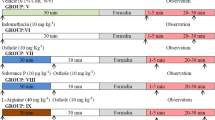
In continuation with our previous studies on osthole, bergapten, a closely related furanocoumarin was investigated for its ameliorative effect on chemically induced neurogenic and inflammatory hyperalgesia and inflammation in mice. Chemical hyperalgesia and inflammation was induced by administration of formalin (intraplantar), acetic acid (intraperitoneal) and carrageenan (intraplantar) to different groups of animals. Pain responses were quantified and median effective dose (ED50) of bergapten was calculated. Lipopolysaccharide challenge was administered to study inflammatory cytokines which were analyzed in plasma using ELISA. The expression of poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP), cyclooxygenase (COX-2) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) was quantified by immnofluorescence staining. Bergapten was found to ameliorate both neurogenic and inflammatory hyperalgesia precipitated by formalin, acetic acid induced writhing and carrageenan induced paw inflammation with ED50 dose of 2.96 mg/kg. Bergapten also significantly decreased the levels of TNF-α and IL-6 and the expression of PARP, COX-2 and iNOS in the spine. It is concluded that bergapten is an interesting molecule with significant analgesic and anti-inflammatory activity emanating through the modulation of multiple pain mediating pathways.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad SF, Attia SM, Zoheir KMA, Ashour AE, Bakheet SA (2014) Attenuation of the progression of adjuvant-induced arthritis by 3-aminobenzamide treatment. Int Immunopharmacol 19:52–59
Al-Asmari AK, Athar MT, Kadasah SG (2017) An updated phytopharmacological review on medicinal plant of Arab region: apium graveolens linn. Pharmacogn Rev 11(21):13–18
Asif M (2015) Pharmacological activities and phytochemistry of various plant containing coumarin derivatives. Curr Sci Perspect 1(3):77–90
Bai P, Virag L (2012) Role of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases in the regulation of inflammatory processes. FEBS Lett 64:327–337
Bose SK, Dewanjee S, Sahu R, Dey SP (2011) Effect of bergapten from Heracleum nepalense root on production of proinflammatory cytokines. Nat Prod Res 25(15):1444–1449
Choudhari SK, Chaudhary M, Bagde S, Gadbail AR, Joshi V (2013) Nitric oxide and cancer: a review. World J Surg Oncol 11(1):1–11
Cury Y, Picolo G, Gutierrez VP, Ferreira SH (2011) Pain and analgesia: the dual effect of nitric oxide in the nociceptive system. Nitric Oxide 25(3):243–254
Fan W, Huang F, Wu Z, Zhu X, Li D, He H (2012) The role of nitric oxide in orofacial pain. Nitric Oxide 26(1):32–37
Fischer M, Carli G, Raboisson P, Reeh P (2014) The interphase of the formalin test. Pain 155(3):511–521
Forstermann U, Sessa WC (2012) Nitric oxide synthases: regulation and function. Eur Heart J 33(7):829–837
Freire MAM, Guimaraes JS, Gomes-Leal W, Pereira A (2009) Pain modulation by nitric oxide in the spinal cord. Front Neurosci 3(2):175–181
Gallicchio M, Rosa AC, Benetti E, Collino M, Dianzani C, Fantozzi R (2006) Substance-P-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Br J Pharmacol 147(6):681–689
Hajhashemi V, Zolfaghari B, Yousefi A (2012) Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of Satureja hortensis seed essential oil, hydroalcoholic and polyphenolic extracts in animal models. Med Princ Pract 21(2):178–182
Hung WL, Suh JH, Wang Y (2017) Chemistry and health effects of furanocoumarins in grapefruit. J Food Drug Anal 25(1):71–83
Hwang HT, Wecksler A, Wagner KD, Hammock B (2013) Rationally designed multitarget agents against inflammation and pain. Curr Med Chem 20(13):1783–1799
Jean YH, Chen WF, Duh CY, Huang SY, Hsu CH, Lin CS, Sung CS, Chen IM, Wen ZH (2008) Inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 participate in anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of the natural marine compound lemnalol from Formosan soft coral Lemnalia cervicorni. Eur J Pharmacol 578(2–3):323–331
Khan S, Choi RJ, Lee J, Kim YS (2016) Attenuation of neuropathic pain and neuroinflammatory responses by a pyranocoumarin derivative, anomalin in animal and cellular models. Euro J Pharmcol 774:95–104
Koch A, Zacharowski K, Boehm O, Stevens M, Lipfert P, Von Giesen HJ, Wolf A, Freynhagen R (2007) Nitric oxide and pro-inflammatory cytokines correlate with pain intensity in chronic pain patients. Inflamm Res 56(1):32–37
Le Page C, Sanceau J, Drapier JC, Wietzerbin J (1998) Inhibitors of ADP ribosylation impair in-ducible nitric oxide synthase gene transcription through inhibition of NFκB activation. Bio-chem Biophys Res Commun 243:451–457
Li XJ, Zhu Z, Han SL, Zhang ZL (2016) Bergapten exerts inhibitory effects on diabetes-related osteoporosis via the regulation of the PI3K/AKT, JNK/MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways in osteoprotegerin knockout mice. Int J Mol Med 38(6):1661–1672
Liao M, Song G, Cheng X, Diao X, Sun Y, Zhang L (2018) Simultaneous determination of six coumarins in rat plasma and metabolites identification of bergapten in vitro and in vivo. J Agri Food Chem 66(18):4602–4613
Luszczki JJ, Andres-Mach M, Glensk M, Skalicka-Wozniak K (2010) Anticonvulsant effects of four linear furanocoumarins, bergapten, imperatorin, oxypeucedanin, and xanthotoxin, in the mouse maximal electroshock-induced seizure model: a comparative study. Pharmacol Rep 62(6):1231–1236
McNamara CR, Mandel-Brehm J, Bautista DM, Siemens J, Deranian KL, Zhao M, Hayward NJ, Chong JA, Julius D, Moran MM, Fanger CM (2007) TRPA1 mediates formalin-induced pain. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104(33):13525–13530
Meena S, Kumar A, Chauhan S (2011) Possible involvement of nitric oxide mechanism in the protective effect of Melatonin against sciatic nerve ligation induced behavioral and biochemical alterations in rats. Int J Drug Dev Res 3:224–233
Mira A, Alkhiary W, Shimizu K (2017) Antiplatelet and anticoagulant activities of angelica shikokiana extract and its isolated compounds. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost 23(1):91–99
Navarra M, Ferlazzo N, Cirmi S, Trapasso E, Bramanti P, Lombardo GE, Gangemi S (2015) Effects of bergamot essential oil and its extractive fractions on SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cell growth. J Pharm Pharmacol 67(8):1042–1053
Nogueira CW, Quinhones EB, Jung EA, Zeni G, Rocha JB (2003) Anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive activity of d iphenyl diselenide. Inflamm Res 52(2):56–63
Ohtsu N, Takaoka K, Segawa E, Hashitani S, Noguchi K, Kishimoto H, Urade M (2010) Antitumor effects of inhibitors of nitric oxide synthase or cyclooxygenase-2 on human KB carcinoma cells overexpressing COX-2. Oncol Rep 24(1):31–36
Patcher P, Szabo C (2007) Role of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP-1) in cardiovascular diseases: the therapeutic potential of PARP inhibitors. Cardiovasc Drug Rev 25:235–260
Pinho-Ribeiro FA, Hohmann MS, Borghi SM, Zarpelon AC, Guazelli CF, Manchope MF, Casagrande R, Verri WA Jr (2003) Protective effects of the flavonoid hesperidin methyl chalcone in inflammation and pain in mice: role of TRPV1, oxidative stress, cytokines and NF-κB. Chem Biol Interact 228:88–99
Pitcher MH (2018) The impact of exercise in rodent models of chronic pain. Curr Osteoporos Rep 16(4):1–16
Pitcher MH, Gonzalez-Cano R, Vincent K, Lehmann M, Cobos EJ, Coderre TJ, Baeyens JM, Cervero F (2017) Mild social stress in mice produces opioid-mediated analgesia in visceral but not somatic pain states. J Pain 18(6):716–725
Satyanarayana PS, Jain NK, Singh A, Kulkarni SK (2004) Isobolographic analysis of interaction between cyclooxygenase inhibitors and tramadol in acetic acid-induced writhing in mice. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 28(4):641–649
Schmidtko A, Tegeder I, Geisslinger G (2009) No NO, no pain? The role of nitric oxide and cGMP in spinal pain processing. Trends Neurosci 32(6):339–346
Singh G, Bhatti R, Mannan R, Singh D, Kesavan A, Singh P (2018) Osthole ameliorates neurogenic and inflammatory hyperalgesia by modulation of iNOS, COX-2, and inflammatory cytokines in mice. Inflammopharmacology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-018-0486-9
Slater D, Kunnathil S, McBride J, Koppala R (2010) Pharmacology of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and opioids. Inflammopharmacology 27(4):400–411
Stubbs B, Koyanagi A, Thompson T, Veronese N, Carvalho AF, Solomi M, Mugisha J, Schofield P, Cosco T, Wilson N, Vancampfort D (2016) The epidemiology of back pain and its relationship with depression, psychosis, anxiety, sleep disturbances, and stress sensitivity: data from 43 low-and middle-income countries. Gen Hosp Psychiatry 43:63–70
Szabo G, Baahrle S, Stumpf N, Sonnenberg K, Szabo E, Pacher P, Csont T, Schulz R, Dengler TJ, Liaudet L, Jagtap PG (2002) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibition reduces reperfusion injury after heart transplantation. Circ Res 90(1):100–116
Tian Y, Shi R, Gao M, Wang H, Du Y, Zhang L, Zhang M (2017) Differentiation of furanocoumarin isomers with ratio of relative abundance of characteristic fragment ions and application in Angelicae dahuricae radix. Chromatographia 80(9):1401–1410
Venugopala KN, Rashmi V, Odhav B (2013) Review on natural coumarin lead compounds for their pharmacological activity. Biomed Res Int 2013:1–14
Wang WK, Angell AD, Craig C, Dawson J, Garvey E, Moncada S, Monkhouse J, Rees D, Russell LJ, Russell RJ, Schwartz S (2005) GW274150 and GW273629 are potent and highly selective inhibitors of inducible nitric oxide synthase in vitro and in vivo. Br J Pharmacol 145(3):301–312
Wang C, Chen H, Luo H, Zhu L, Zhao Y, Tian H, Wang R, Shang P, Zhao Y (2015) Microgravity activates p38 MAPK-C/EBPβ pathway to regulate the expression of arginase and inflammatory cytokines in macrophages. Inflamm Res 64(5):303–311
Yang Y, Zheng K, Mei W, Wang Y, Yu C, Yu B, Deng S, Hu J (2018) Anti-inflammatory and proresolution activities of bergapten isolated from the roots of Ficus hirta in an in vivo zebrafish model. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 496(2):763–769
Yi M, Zhang H, Lao L, Xing GG, Wan Y (2011) Anterior cingulate cortex is crucial for contra-but not ipsi-lateral electro-acupuncture in the formalin-induced inflammatory pain model of rats. Mol Pain 7(1):61–68
Acknowledgements
RB is thankful to Department of Science & Technology, Govt. of India for financial support (Grant No. EMR/2016/005878) under Extra Mural Research Project. GS and AK are thankful to the University Grants Commission (UGC) (Grant No. F1-17.1/2017-18/RGNF-2017-18-SC-PUN-35330), New Delhi for scholarship under NFSC and MANF scheme respectively. The authors also gratefully acknowledge the facilities provided by the UGC (Grant No. F1-17.1/2017-18/MANF-2017-18-PUN-84339) under university with potential for excellence (UPE) scheme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors do not have any conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, G., Kaur, A., Kaur, J. et al. Bergapten inhibits chemically induced nociceptive behavior and inflammation in mice by decreasing the expression of spinal PARP, iNOS, COX-2 and inflammatory cytokines. Inflammopharmacol 27, 749–760 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-019-00585-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-019-00585-6