Abstract
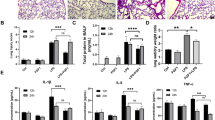
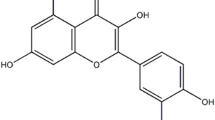
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a deadly disease and lacks effective treatments. Inflammation and oxidative stress play key roles in ARDS development. We aimed to evaluate the efficacy of pretreatment of silymarin, which has capacities of anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative stress, in ARDS. We used lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to generate an ARDS rat model, which was pretreated with silymarin. Lung wet/dry ratio and broncho-alveolar lavage fluid (BALF) analyses were performed. Histological changes of the lungs were evaluated using hematoxylin and eosin staining. Cells and proteins in BALF were determined. Protein levels in the lungs were assessed using immunoblotting. LPS administration significantly caused an increased lung wet/dry ratio, an elevated protein level in BALF, and an impaired pulmonary function in the rats. Silymarin mitigated these changes in a dose-dependent manner. Silymarin ameliorated LPS-induced histological changes of the lungs, and reduced infiltration of lymphocytes, macrophages, and neutrophils. Consistently, concentrations of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interferon-γ, interleukin (IL)-6, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α were increased, while that of anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 was decreased in BALF. Additionally, silymarin pretreatment partially inactivated multiple mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways in the lungs. Silymarin mitigated LPS-induced lung impairments by down-regulating inflammation in a rat model.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chambers CS, Holeckova V, Petraskova L, Biedermann D, Valentova K, Buchta M, Kren V (2017) The silymarin composition… and why does it matter? Food Res Int. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2017.07.017
Chow CW, Herrera Abreu MT, Suzuki T, Downey GP (2003) Oxidative stress and acute lung injury. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 29:427–431. doi:10.1165/rcmb.F278
Demir M, Amanvermez R, Kamali Polat A, Karabicak I, Cinar H, Kesicioglu T, Polat C (2014) The effect of silymarin on mesenteric ischemia-reperfusion injury. Med Princ Pract 23:140–144. doi:10.1159/000356860
El-Lakkany NM, Hammam OA, El-Maadawy WH, Badawy AA, Ain-Shoka AA, Ebeid FA (2012) Anti-inflammatory/anti-fibrotic effects of the hepatoprotective silymarin and the schistosomicide praziquantel against Schistosoma mansoni-induced liver fibrosis. Parasite Vectors 5:9. doi:10.1186/1756-3305-5-9
Espinosa-Diez C, Miguel V, Mennerich D, Kietzmann T, Sanchez-Perez P, Cadenas S, Lamas S (2015) Antioxidant responses and cellular adjustments to oxidative stress. Redox Biol 6:183–197. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2015.07.008
Han S, Mallampalli RK (2015) The acute respiratory distress syndrome: from mechanism to translation. J Immunol 194:855–860. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1402513
Huang Q, Wu LJ, Tashiro S, Onodera S, Li LH, Ikejima T (2005) Silymarin augments human cervical cancer HeLa cell apoptosis via P38/JNK MAPK pathways in serum-free medium. J Asian Nat Prod Res 7:701–709. doi:10.1080/1028602042000324862
Jia R, Cao L, Du J, Xu P, Jeney G, Yin G (2013) The protective effect of silymarin on the carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced liver injury in common carp (Cyprinus carpio). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 49:155–161. doi:10.1007/s11626-013-9587-3
Khilnani GC, Hadda V (2011) Corticosteroids and ARDS: a review of treatment and prevention evidence. Lung India 28:114–119. doi:10.4103/0970-2113.80324
Kim SH, Oh DS, Oh JY, Son TG, Yuk DY, Jung YS (2016) Silymarin prevents restraint stress-induced acute liver injury by ameliorating oxidative stress and reducing inflammatory response. Molecules 21:443. doi:10.3390/molecules21040443
Kvasnicka F, Biba B, Sevcik R, Voldrich M, Kratka J (2003) Analysis of the active components of silymarin. J Chromatogr A 990:239–245
Laffey JG, Talmor D (2013) Predicting the development of acute respiratory distress syndrome: searching for the “Troponin of ARDS”. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 187:671–672
Lang S, Li L, Wang X, Sun J, Xue X, Xiao Y, Zhang M, Ao T, Wang J (2017) CXCL10/IP-10 neutralization can ameliorate lipopolysaccharide-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome in rats. PLoS ONE 12:e0169100. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0169100
Li D, Hu J, Wang T, Zhang X, Liu L, Wang H, Wu Y, Xu D, Wen F (2016) Silymarin attenuates cigarette smoke extract-induced inflammation via simultaneous inhibition of autophagy and ERK/p38 MAPK pathway in human bronchial epithelial cells. Sci Rep 6:37751. doi:10.1038/srep37751
Lovelace ES, Wagoner J, MacDonald J, Bammler T, Bruckner J, Brownell J, Beyer RP, Zink EM, Kim YM, Kyle JE, Webb-Robertson BJ, Waters KM, Metz TO, Farin F, Oberlies NH, Polyak SJ (2015) Silymarin suppresses cellular inflammation by inducing reparative stress signaling. J Nat Prod 78:1990–2000. doi:10.1021/acs.jnatprod.5b00288
Malekinejad H, Rahmani F, Valivande-Azar S, Taheri-Broujerdi M, Bazargani-Gilani B (2012) Long-term administration of Silymarin augments proinflammatory mediators in the hippocampus of rats: evidence for antioxidant and pro-oxidant effects. Hum Exp Toxicol 31:921–930. doi:10.1177/0960327112436405
Matthay MA, Zimmerman GA (2005) Acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome: four decades of inquiry into pathogenesis and rational management. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 33:319–327. doi:10.1165/rcmb.F305
Ramasamy K, Agarwal R (2008) Multitargeted therapy of cancer by silymarin. Cancer Lett 269:352–362. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2008.03.053
Ramos-Nino ME, Haegens A, Shukla A, Mossman BT (2002) Role of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) in cell injury and proliferation by environmental particulates. Mol Cell Biochem 234–235:111–118
Reuter S, Gupta SC, Chaturvedi MM, Aggarwal BB (2010) Oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer: how are they linked? Free Radic Biol Med 49:1603–1616. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2010.09.006
Rubenfeld GD, Caldwell E, Peabody E, Weaver J, Martin DP, Neff M, Stern EJ, Hudson LD (2005) Incidence and outcomes of acute lung injury. N Engl J Med 353:1685–1693. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa050333
Silversides JA, Ferguson ND (2013) Clinical review: acute respiratory distress syndrome—clinical ventilator management and adjunct therapy. Crit Care 17:225. doi:10.1186/cc11867
Surai PF (2015) Silymarin as a natural antioxidant: an overview of the current evidence and perspectives. Antioxidants (Basel) 4:204–247. doi:10.3390/antiox4010204
Toklu HZ, Tunali Akbay T, Velioglu-Ogunc A, Ercan F, Gedik N, Keyer-Uysal M, Sener G (2008) Silymarin, the antioxidant component of Silybum marianum, prevents sepsis-induced acute lung and brain injury. J Surg Res 145:214–222. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2007.03.072
Umbrello M, Formenti P, Bolgiaghi L, Chiumello D (2016) Current concepts of ARDS: a narrative review. Int J Mol Sci. doi:10.3390/ijms18010064
Williams AE, Chambers RC (2014) The mercurial nature of neutrophils: still an enigma in ARDS? Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 306:L217–230. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00311.2013
Yoshida N, Yoshikawa T, Manabe H, Terasawa Y, Kondo M, Noguchi N, Niki E (1999) Vitamin E protects against polymorphonuclear leukocyte-dependent adhesion to endothelial cells. J Leukoc Biol 65:757–763
Yoshikawa T, Yoshida N, Manabe H, Terasawa Y, Takemura T, Kondo M (1998) Alpha-tocopherol protects against expression of adhesion molecules on neutrophils and endothelial cells. BioFactors 7:15–19
Zhang Q, Bai X, Chen W, Ma T, Hu Q, Liang C, Xie S, Chen C, Hu L, Xu S, Liang T (2013) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling enhances hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma via crosstalk with hif-1alpha signaling. Carcinogenesis 34:962–973. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgt027
Zhao F, Shi D, Li T, Li L, Zhao M (2015) Silymarin attenuates paraquat-induced lung injury via Nrf2-mediated pathway in vivo and in vitro. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. doi:10.1111/1440-1681.12448
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving human and animal participants
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Z., Sun, G. Silymarin mitigates lung impairments in a rat model of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Inflammopharmacol 26, 747–754 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-017-0407-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-017-0407-3