Abstract
Aim
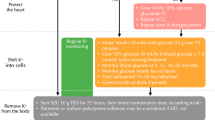
Stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157, administered before a high-dose magnesium injection in rats, might be a useful peptide therapy against magnesium toxicity and the magnesium-induced effect on cell depolarization. Moreover, this might be an NO-system-related effect. Previously, BPC 157 counteracts paralysis, arrhythmias and hyperkalaemia, extreme muscle weakness; parasympathetic and neuromuscular blockade; injured muscle healing and interacts with the NOS-blocker and NOS-substrate effects.
Main methods
Assessment included magnesium sulfate (560 mg/kg intraperitoneally)-induced muscle weakness, muscle and brain lesions, hypermagnesemia, hyperkalaemia, increased serum enzyme values assessed in rats during and at the end of a 30-min period and medication (given intraperitoneally/kg at 15 min before magnesium) [BPC 157 (10 µg, 10 ng), l-NAME (5 mg), l-arginine (100 mg), alone and/or together]. In HEK293 cells, the increasing magnesium concentration from 1 to 5 mM could depolarize the cells at 1.75 ± 0.44 mV.
Key findings
l-NAME + magnesium-rats and l-arginine + magnesium-rats exhibited worsened severe muscle weakness and lesions, brain lesions, hypermagnesemia and serum enzymes values, with emerging hyperkalaemia. However, l-NAME + l-arginine + magnesium-rats exhibited all control values and normokalaemia. BPC 157 abrogated hypermagnesemia and counteracted all of the magnesium-induced disturbances (including those aggravated by l-NAME or l-arginine). Thus, cell depolarization due to increasing magnesium concentration was inhibited in the presence of BPC 157 (1 µM) in vitro.
Significance
BPC 157 likely counteracts the initial event leading to hypermagnesemia and the life-threatening actions after a magnesium overdose. In contrast, a worsened clinical course, higher hypermagnesemia, and emerging hyperkalaemia might cause both l-NAME and l-arginine to affect the same events adversely. These events were also opposed by BPC 157.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balenovic D, Bencic ML, Udovicic M et al (2009) Inhibition of methyldigoxin-induced arrhythmias by pentadecapeptide BPC 157: a relation with NO-system. Regul Pept 156(1–3):83–89
Barisic I, Balenovic D, Klicek R et al (2013) Mortal hyperkalemia disturbances in rats are NO-system related. The life saving effect of pentadecapeptide BPC 157. Regul Pept 181:50–66
Boban Blagaic A, Blagaic V, Mirt M et al (2005) Gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157 effective against serotonin syndrome in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 512(2–3):173–179
Bowman WC (1983) Peripherally acting muscle relaxants. In: Parnham MJ, Bruinvels J (eds) Discoveries in pharmacology, volume I: psycho- and neuro-pharmacology. Elsevier Science Publishers BV, Amsterdam, pp 106–159
Cengiz M, Ülker P, Üyüklü M et al (2016) Effect of magnesium supplementation on blood rheology in NOS inhibition-induced hypertension model. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 63(1):57–67
Cesarec V, Becejac T, Misic M et al (2013) Pentadecapeptide BPC 157 and the esophagocutaneous fistula healing therapy. Eur J Pharmacol 701(1–3):203–212
Chang CH, Tsai WC, Lin MS, Hsu YH, Pang JH (2011) The promoting effect of pentadecapeptide BPC 157 on tendon healing involves tendon outgrowth, cell survival, and cell migration. J Appl Physiol (1985) 110(3):774–780
Chang CH, Tsai WC, Hsu YH, Pang JH (2014) Pentadecapeptide BPC 157 enhances the growth hormone receptor expression in tendon fibroblasts. Molecules 19(11):19066–19077
Collier HOJ, Dinnen LC, Johnson CA, Schneide C (1968) The abdominal constriction response and its suppression by analgesic drugs in the mouse. Br J Pharmacol Chemother 32:295–310
Euser AG, Cipolla MJ (2009) Magnesium sulfate treatment for the prevention of eclampsia: a brief review. Stroke 40(4):1169–1175
Gerard SK, Hernandez C, Khayam-Bashi H (1988) Extreme hypermagnesemia caused by an overdose of magnesium-containing cathartics. Ann Emerg Med 17(7):728–731
Guay J, Grenier Y, Varin F (1998) Clinical pharmacokinetics of neuromuscular relaxants in pregnancy. Clin Pharmacokinet 34(6):483
Gyires K, Torma Z (1984) The use of the writhing in mice for screening different types of analgesics. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 267:131–140
Huang T, Zhang K, Sun L et al (2015) Body protective compound-157 enhances alkali-burn wound healing in vivo and promotes proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis in vitro. Drug Des Dev Ther 9:2485–2499
Ilic S, Brcic I, Mester M et al (2009) Over-dose insulin and stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157. Attenuated gastric ulcers, seizures, brain lesions, hepatomegaly, fatty liver, breakdown of liver glycogen, profound hypoglycemia and calcification in rats. J Physiol Pharmacol 60(Suppl 7):107–114
Ilic S, Drmic D, Zarkovic K et al (2010) High hepatotoxic dose of paracetamol produces generalized convulsions and brain damage in rats. A counteraction with the stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157 (PL 14736). J Physiol Pharmacol 61(2):241–250
Ilic S, Drmic D, Franjic S et al (2011a) Pentadecapeptide BPC 157 and its effects on a NSAID toxicity model: diclofenac-induced gastrointestinal, liver, and encephalopathy lesions. Life Sci 88(11-12):535–542 A
Ilic S, Drmic D, Zarkovic K et al (2011b) Ibuprofen hepatic encephalopathy, hepatomegaly, gastric lesion and gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157 in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 667(1-3):322–329 B
Klicek R, Kolenc D, Suran J et al (2013) Stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157 heals cysteamine-colitis and colon-colon-anastomosis and counteracts cuprizone brain injuries and motor disability. J Physiol Pharmacol 64(5):597–612
Kokot A, Zlatar M, Stupnisek M et al (2016) NO system dependence of atropine-induced mydriasis and l-NAME- and l-arginine-induced miosis: reversal by the pentadecapeptide BPC 157 in rats and guinea pigs. Eur J Pharmacol 771:211–219
Krendel DA (1990) Hypermagnesemia and neuromuscular transmission. Semin Neurol 10:42–45
Lojo N, Rasic Z, Zenko Sever A et al (2016) Effects of diclofenac, l-NAME, l-Arginine, and pentadecapeptide BPC 157 on gastrointestinal, liver, and brain lesions, failed anastomosis, and intestinal adaptation deterioration in 24 hour-short-bowel rats. PLoS One 11(9):e0162590
Manzo-Avalos S, Pérez-Vázquez V, Ramírez J et al (2002) Regulation of the rate of synthesis of nitric oxide by Mg(2 +) and hypoxia. Studies in rat heart mitochondria. Amino Acids 22(4):381–389
Meinen S, Lin S, Rüegg MA, Punga AR (2012) Fatigue and muscle atrophy in a mouse model of myasthenia gravis is paralleled by loss of sarcolemmal nNOS. PLoS One 7:441–448
Moncada S, Palmer RM, Higgs EA (1991) Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev 43:109–142
Nordt SP, Williams SR, Turchen S, Manoguerra A, Smith D, Clark RF (1996) Hypermagnesemia following an acute ingestion of Epsom salt in a patient with normal renal function. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol 34(6):735–739
Novinscak T, Brcic L, Staresinic M et al (2008) Gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157 as an effective therapy for muscle crush injury in the rat. Surg Today 38(8):716–725
Pevec D, Novinscak T, Brcic L et al (2010) Impact of pentadecapeptide BPC 157 on muscle healing impaired by systemic corticosteroid application. Med Sci Monit 16(3):BR81–88
Quamme GA (2010) Molecular identification of ancient and modern mammalian magnesium transporters. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 298:C407–429
Rizzo MA, Fisher M, Lock JP (1993) Hypermagnesemic pseudocoma. Arch Intern Med 153:1130–1132
Sato K, Nishiwaki K, Kuno N et al (2000) Unexpected hyperkalemia following succinylcholine administration in prolonged immobilized parturients treated with magnesium and ritodrine. Anesthesiology 93(6):1539–1541
Sikiric P, Gyires K, Seiwerth S et al (1993) The effect of pentadecapeptide BPC 157 on inflmammatory, non-inflammatory, direct and indirect pain and capsaicin neortoxicity. Inflammopharmacology 2:121–127
Sikiric P, Seiwerth S, Rucman R et al (2014) Stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157-NO-system relation. Curr Pharm Des 20(7):1126–1135
Sikiric P, Seiwerth S, Rucman R et al (2016) Brain-gut axis and pentadecapeptide BPC 157. Theoretical and practical implications. Curr Neuropharmacol [Epub ahead of print]
Stambolija V, Stambolija TP, Holjevac JK et al (2016) BPC 157: the counteraction of succinylcholine, hyperkalemia, and arrhythmias. Eur J Pharmacol 781:83–91
Staresinic M, Petrovic I, Novinscak T et al (2006) Effective therapy of transected quadriceps muscle in rat: gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157. J Orthop Res 24(5):1109–1117
Tkalcević VI, Cuzić S, Brajsa K et al (2007) Enhancement by PL 14736 of granulation and collagen organization in healing wounds and the potential role of egr-1 expression. Eur J Pharmacol 570(1–3):212–221
Whang R, Papper S, Llach F (1988) Arginine-induced hypermagnesemia and hyperkalemia in nephrectomized rats. Magnesium 7(1):23–26
Whittle BJ, Lopez-Belmonte J, Moncada S (1992) Nitric oxide mediates rat mucosal vasodilatation induced by intragastric capsaicin. Eur J Pharmacol 218:339–341
Xie J, Sun B, Du J et al (2011) Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate [PIP(2)] controls magnesium gatekeeper TRPM6 activity. Sci Rep 1:146
Zivanovic Posilovic G, Balenovic D, Barisic I et al (2016) Stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157 and bupivacaine. Eur J Pharmacol 793:56–65
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science, Education and Sports, Republic of Croatia (Grant Number 108-1083570-3635).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors indicate no potential conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Medvidovic-Grubisic, M., Stambolija, V., Kolenc, D. et al. Hypermagnesemia disturbances in rats, NO-related: pentadecapeptide BPC 157 abrogates, l-NAME and l-arginine worsen. Inflammopharmacol 25, 439–449 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-017-0323-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-017-0323-6