Abstract
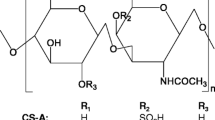
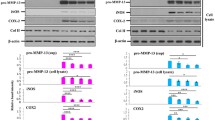
Chondroitin sulphate (CS) is recommended by the European League Against Rheumatism as a symptomatic slow-acting drug for the treatment of osteoarthritis on the basis of numerous clinical trials and meta-analyses. Furthermore, recent clinical trials have also demonstrated the possible structure-modifying effects of CS. This review focuses on recent experimental results and data available in the scientific literature regarding the anti-inflammatory properties of CS with a view to understanding the molecular basis responsible for its activity. Several animal studies have demonstrated that orally administered CS significantly inhibited hind paw oedema, synovitis and destruction of the articular cartilage in a dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, CS proved to have a beneficial effect in slowing down the development of adjuvant arthritis and in reducing disease markers, findings which support its beneficial activity in humans as a chondroprotective drug. Finally, several in vitro studies have focused on the hypothesis that CS may reduce inflammatory processes by acting on the nuclear translocation of NF-κB, which is closely associated with the blood biomarkers of inflammation, primarily IL-1, IL-6 and C-reactive protein.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BDNF:
-
Brain-derived growth factor
- CIA:
-
Collagen-induced arthritis
- CRP:
-
C-reactive protein
- CS:
-
Chondroitin sulphate
- EULAR:
-
European League Against Rheumatism
- FGF:
-
Fibroblast growth factor
- GAGs:
-
Glycosaminoglycans
- GalNAc:
-
N-acetyl-d-galactosamine
- GDNF:
-
Glial-derived growth factor
- GlcA:
-
d-Glucuronic acid
- HGF–FS:
-
Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor
- KGF:
-
Keratinocyte growth factor
- IFN-γ:
-
Interferon-γ
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- IP-10:
-
γ-Interferon inducible protein-10
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharides
- MAPK(s):
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinases
- MCP-1:
-
Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1
- MK:
-
Midkine
- MIP-1α:
-
Macrophage inflammatory peptides-1α
- OA:
-
Osteoarthritis
- PDGF:
-
Platelet-derived growth factor
- PF4:
-
Platelet factor 4
- PRR(s):
-
Pattern recognition receptor(s)
- PTN/HB-GAM:
-
Pleiotrophin
- RA:
-
Rheumatoid arthritis
- SDS-1β:
-
Stromal cell-derived factor-1β
- SLC:
-
Secondary lymphoid tissue chemokine
- SYSADOA:
-
Symptomatic slow-acting drugs for the treatment of osteoarthritis
- TNF-α:
-
Tumour necrosis factor-α
- TLR(s):
-
Toll-like receptor(s)
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
References
Bauerova K, Ponist S, Kuncirova V, Mihalova D, Paulovicova E, Volpi N (2011) Protective effect of chondroitin sulfate on induced arthritis in rats. Osteoarthr Cartil 19:1373–1379
Bendele A, McComb J, Gould T, McAbee T, Sennello G, Chlipala E, Guy M (1999) Animal models of arthritis: relevance to human disease. Toxicol Pathol 27:134–142
Burmester GR, Stuhlmuller B, Keyszer G, Kinne RW (1997) Mononuclear phagocytes and rheumatoid synovitis. Mastermind or workhorse in arthritis? Arthritis Rheum 40:5–18
Campo GM, Avenoso A, Campo S, D’Ascola A, Traina P, Samà D, Calatroni A (2008) Purified human plasma glycosaminoglycans reduced NF-kappaB activation, pro-inflammatory cytokine production and apoptosis in LPS-treated chondrocytes. Innate Immun 14:233–246
Campo GM, Avenoso A, Campo S, Traina P, D’Ascola A, Calatroni A (2009) Glycosaminoglycans reduced inflammatory response by modulating toll-like receptor-4 in LPS-stimulated chondrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys 491:7–15
Cañas N, Gorina R, Planas AM, Vergés J, Montell E, García AG, López MG (2010) Chondroitin sulfate inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in rat astrocytes by preventing nuclear factor kappa B activation. Neuroscience 167:872–879
Cho SY, Sim JS, Jeong CS, Chang SY, Choi DW, Toida T, Kim YS (2004) Effects of low molecular weight chondroitin sulfate on type II collagen-induced arthritis in DBA/1J mice. Biol Pharm Bull 27:47–51
Chu ZL, McKinsey TA, Liu L, Gentry JJ, Malim MH, Ballard DW (1997) Suppression of tumor necrosis factor-induced cell death by inhibitor of apoptosis c-IAP2 is under NF-kappaB control. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:10057–10062
Cinel I, Opal SM (2009) Molecular biology of inflammation and sepsis: a primer. Crit Care Med 37:291–304
Egea J, García AG, Verges J, Montell E, López MG (2010) Antioxidant, antiinflammatory and neuroprotective actions of chondroitin sulfate and proteoglycans. Osteoarthr Cartil 18(Suppl 1):S24–S27
Ghosh S, Hayden MS (2008) New regulators of NF-kappaB in inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 8:837–848
Herrero-Beaumont G, Marcos ME, Sánchez-Pernaute O, Granados R, Ortega L, Montell E, Vergés J, Egido J, Largo R (2008) Effect of chondroitin sulphate in a rabbit model of atherosclerosis aggravated by chronic arthritis. Br J Pharmacol 154:843–851
Iwalewa EO, McGaw LJ, Naidoo V, Eloff JN (2007) Inflammation: the foundation of disease and disorders. A review of phytomedicines of South African origin used to treat pain and inflammatory conditions. Afr J Biotech 6:2868–2885
Jin C-H, Yang U, Kim S-H, Ryu J-W, Lee J-C, Lee D-S, Lee T-H (2007) The protective effect of chondroitin from Raja kenojei cartilage on collagen-induced arthritis in DBA/1. J Mice Food Sci Biotechnol 16:594–599
Jomphe C, Gabriac M, Hale TM, Héroux L, Trudeau LE, Deblois D, Montell E, Vergés J, du Souich P (2008) Chondroitin sulfate inhibits the nuclear translocation of nuclear factor-kappaB in interleukin-1beta-stimulated chondrocytes. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 102:59–65
Jordan KM, Arden NK, Doherty M, Bannwarth B, Bijlsma JW, Dieppe P et al (2003) EULAR Recommendations 2003: an evidence based approach to the management of knee osteoarthritis: report of a task force of the Standing Committee for International Clinical Studies Including Therapeutic Trials (ESCISIT). Ann Rheum Dis 62:1145–1155
Kahan A, Uebelhart D, De Vathaire F, Delmas PD, Reginster JY (2009) Long-term effects of chondroitins 4 and 6 sulfate on knee osteoarthritis: the study on osteoarthritis progression prevention, a two-year, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum 60:524–533
Kannan K, Ortmann RA, Kimpel D (2005) Animal models of rheumatoid arthritis and their relevance to human disease. Pathophysiology 12:167–181
Karin M, Lin A (2002) NF-kappaB at the crossroads of life and death. Nat Immunol 3:221–227
Kingston AE, Carney SL, Hicks CA, Billingham MEJ (1993) Arthritis and Osteoarthritis. Birkhauser, Basel, pp 75–79
Omata T, Itokazu Y, Inoue N, Segawa Y (2000) Effects of chondroitin sulfate-C on articular cartilage destruction in murine collagen-induced arthritis. Arzneimittelforschung 50:148–153
Reginster JY, Heraud F, Zegels B, Bruyere O (2007) Symptom and structure modifying properties of chondroitin sulfate in osteoarthritis. Mini Rev Med Chem 7:1051–1061
Ronca F, Palmieri L, Panicucci P, Ronca G (1998) Anti-inflammatory activity of chondroitin sulfate. Osteoarthr Cartil 6(Suppl A):14–21
Shriver Z, Raguram S, Sasisekharan R (2004) Glycomics: a pathway to a class of new and improved therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov 3:863–873
Stables MJ, Gilroy DW (2011) Old and new generation lipid mediators in acute inflammation and resolution. Progr Lipid Res 50:35–51
Sugahara K, Mikami T, Uyama T, Mizuguchi S, Nomura K, Kitagawa H (2003) Recent advances in the structural biology of chondroitin sulfate and dermatan sulfate. Curr Opin Struct Biol 13:612–620
Uebelhart D (2008) Clinical review of chondroitin sulfate in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr Cartil 16:S19–S21
Uebelhart D, Thonar EJ, Zhang J, Williams JM (1998) Protective effect of exogenous chondroitin 4,6-sulfate in the acute degradation of articular cartilage in the rabbit. Osteoarthr Cartil 6(Suppl A):6–13
Vallières M, du Souich P (2010) Modulation of inflammation by chondroitin sulfate. Osteoarthr Cartil 18(Suppl 1):S1–S6
Vanderlei ESO, Patoilo KKNR, Lima NA, Lima APS, Rodrigues JAG, Silva LMCM, Lima MEP, Lima V, Benevides NMB (2010) Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of lectin from the marine green alga Caulerpa cupressoides. Int Immunopharmacol 10:1113–1118
Volpi N (2007) Analytical aspects of pharmaceutical grade chondroitin sulfates. J Pharm Sci 96:3168–3180
Volpi N (2009) Quality of different chondroitin sulfate preparations in relation to their therapeutic activity. Pharm Pharmacol 61:1271–1280
Volpi N (2010) Dermatan sulfate: recent structural and activity data. Carb Polymers 82:233–239
Yamada S, Sugahara K (2008) Potential therapeutic application of chondroitin sulfate/dermatan sulfate. Curr Drug Discov Technol 5:289–301
Zhang W, Doherty M, Leeb BF, Alekseeva L, Arden NK, Bijlsma JW et al (2007) EULAR evidence based recommendations for the management of hand osteoarthritis: report of a task force of the EULAR Standing Committee for International Clinical Studies Including Therapeutics (ESCISIT). Ann Rheum Dis 66:377–388
Zhong J, Kyriakis JM (2007) Dissection of a signaling pathway by which pathogen-associated molecular patterns recruit the JNK and p38 MAPKs and trigger cytokine release. J Biol Chem 282:24246–24254
Conflict of interest
The author declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Volpi, N. Anti-inflammatory activity of chondroitin sulphate: new functions from an old natural macromolecule. Inflammopharmacol 19, 299–306 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-011-0098-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-011-0098-0