Abstract
Purpose
In vitro antimicrobial activity and in vivo therapeutic efficacy of L. usitatissimum (linseed/flaxseed) fixed oil in bovine mastitis were investigated.
Method
In vitro antimicrobial activity of L. usitatissimum fixed oil was evaluated against a number of microorganisms by disc diffusion method and MIC determination. The in vivo efficacy of the oil was evaluated in nine mastitis-affected cows divided into three groups (three in each group), following once-a-day intramammary infusion of oil, cefoperazone or an oil-cefoperazone combination for 7 days and by monitoring the California mastitis test score, somatic cell count and microbial count in milk samples.
Results
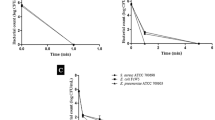
The in vitro antimicrobial activity of the oil against Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus agalactiae and Escherichia coli was comparable to that of cefoperazone while the antimicrobial activity against Enterococcus faecalis, Micrococcus luteus and Candida albicans, was greater than that of cefoperazone. In the in vivo study, the oil exhibited significant reduction in the California mastitis test score and somatic cell count in milk samples from infected udders following 7 days of intramammary administration suggesting its anti-inflammatory effect. The microbial count in milk samples was also reduced significantly following oil treatment. The effects were comparable to the treatment by cefoperazone (Mastiwock) alone or in combination with the oil. Apparently, the anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties of the oil contribute to its therapeutic efficacy in mastitis; the oil could be used as an alternative treatment for bovine mastitis
Conclusion
The results suggest possible therapeutic potential of L. usitatissimum fixed oil in bovine mastitis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Delignette-Muller ML, Flandrois JP (1994) An accurate diffusion method for determining bacterial sensitivity to antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother 34:73–81
Dilika F, Bremner PD, Meyer JJ (2000) Antibacterial activity of linoleic and oleic acids isolated from Helichrysum pedunculatum: a plant used during circumcision rites. Fitoterapia 71:450–452
Freese E, Shew CW, Galliers E (1973) Function of lipophilic acids as antimicrobial food additives. Nature 241:321–325
Greenway DL, Dyke KG (1979) Mechanism of the inhibitory action of linoleic acid on the growth of Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol 115:233–245
Hardman JG, Limbird LE (2001) Goodman and Gillman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. McGraw-Hill, New York
IDF (1995) Enumeration of somatic cells. FIL-IDF Standard No. 148 A. International Dairy Federation, Brussels
Kabara JJ, Swieczkowski DM, Conley AJ, Truant JP (1972) Fatty acids and derivatives as antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2(1):23–28
Kaithwas G, Majumdar DK (2010a) Therapeutic effect of Linum usitatissimum (flaxseed/linseed) fixed oil on acute and chronic arthritic models in albino rats. Inflammopharmacology 18(3):127–136
Kaithwas G, Majumdar DK (2010b) Evaluation of antiulcer and antisecretory potential of Linum usitatissimum fixed oil and possible mechanism of action. Inflammopharmacology 18(3):137–145
Kivaria FM, Noordhuizen JP (2007) A retrospective study of the aetiology and temporal distribution of bovine clinical mastitis in smallholder dairy herds in the Dar es Salaam region of Tanzania. Vet J 173(3):617–622
Knapp HR, Melly MA (1986) Bactericidal effects of polyunsaturated fatty acids. J Infect Dis 154:84–94
Kumar A, Kumar P, Singh RP (2007) Antibacterial profile of milk isolates collected from Allahabad, Project report submitted to Department of Veterinary Science, (Allahabad Agricultural Institute-Deemed University (AAI-DU), Allahabad, India
Lafi SQ (2006) Use of Somatic cell count and California mastitis test results from udder halves milk sample to detect subclinical intramammary infections in Awassi sheep. Small Rumin Res 62:83–86
Makovec JA, Ruegg PL (2003) Results of milk samples submitted for microbiological examination in Wisconsin from 1994 to 2001. J Dairy Sci 86:3466–3472
McDonald MI, Graham I, Harvey KJ, Sinclair A (1981) Antibacterial activity of hydrolysed linseed oil and linolenic acid against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet 2:1056
McGaw LJ, Jager AK, Van Staden J (2002) Isolation of antibacterial fatty acids from Schotia brachypetala. Fitoterapia 73:431–433
Seidel V, Taylor PW (2004) In vitro activity of extracts and constituents of Pelagonium against rapidly growing mycobacteria. Int J Antimicrob Agents 23:613–619
Singh S, Majumdar DK (1997) Evaluation of antiinflammatory activity of fatty acids of Ocimum sanctum fixed oil. Indian J Exp Biol 35:380–383
Singh S, Majumdar DK (1999) Effect of Ocimum sanctum fixed oil on vascular permeability and leukocytes migration. Indian J Exp Biol 37:1136–1138
Singh S, Malhotra M, Majumdar DK (2005) Antibacterial activity of Ocimum sanctum L fixed oil. Indian J Exp Biol 43:835–837
Sumathi BR, Veeregowda BM, Amitha RG (2008) Prevalence and antibiogram profile of bacterial isolates from clinical bovine mastitis. Vet World 1(8):237–238
Sun CQ, O’Connor CJ, Roberton AM (2003) Antibacterial actions of fatty acids and monoglycerides against Helicobacter pylori. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 36:9–17
The Wealth of India (1976) Industrial products. Part IX. Publication and Information Directorate, CSIR, p 110
The Wealth of India (2006) A dictionary of Indian raw materials and industrial products, vol 4(J-Q), 1st supplement series. National Institute of Science Communication and Information Resources, CSIR, New Delhi, pp 41–44
Wilson DJ, Gonzalez RN, Das HH (1997) Bovine mastitis pathogens in New York and Pennsylvania: prevalence and effects on somatic cell count and milk production. J Dairy Sci 80:2592–2598
Yagi Y, Shiono H, Shibahara T, Chikayama Y, Nakamura I, Ohnuma A (2002) Increase in apoptotic polymorphonuclear neutrophils in peripheral blood after intramammary infusion of Escherichia coli lipopolysaccaride. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 89:115–125
Zheng CJ, Yoo JS, Lee TG, Cho HY, Kim YH, Kim WG (2005) Fatty acid synthesis is a target for antibacterial activity of unsaturated fatty acid. FEBS Lett 579:5157–5162
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Ranbaxy Research Laboratories, Gurgaon, India, for GC analysis of L. usitatissimum fixed oil. The authors are also thankful to Prof. (Dr.) Neeraj Kumar and Dr. Ram Pal, Department of Veterinary Sciences, AAI-Deemed University, Allahabad, U.P., for providing valuable guidance and suggestions in the study and Dr. J. Bhattacharya, Wockhardt Laboratories, for supplying cefoperazone gift samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaithwas, G., Mukerjee, A., Kumar, P. et al. Linum usitatissimum (linseed/flaxseed) fixed oil: antimicrobial activity and efficacy in bovine mastitis. Inflammopharmacol 19, 45–52 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-010-0047-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-010-0047-3